ECG Case 066
Elderly patient presenting with chest pain and diaphoresis. Describe and interpret his ECG
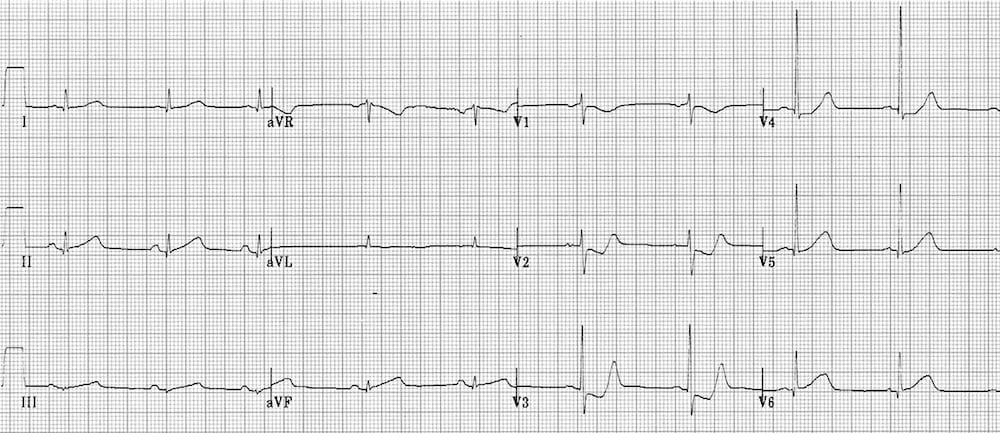
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
This ECG demonstrates an infero-posterior STEMI, as manifest by:
- Subtle inferior ST elevation and hyperacute T waves (T waves > QRS complexes)
- ST depression and terminal T-wave positivity in V2-3 = posterior wall involvement
See Quiz ECG 14 for another example of posterior infarction.
CLINICAL PEARLS
Tips for spotting posterior infarction
Look specifically at leads V2-3 for the combination of:
- Horizontal ST depression.
- Tall, broad R wave (>30ms wide, R/S ratio > 1) — this is a Q-wave equivalent.
- Upright T wave — particularly the terminal portion of the T wave.
One common trick is to turn the ECG over, hold it up to the light and look through it from behind. This inverts lead V2, which then takes on the appearance of a classic STEMI.
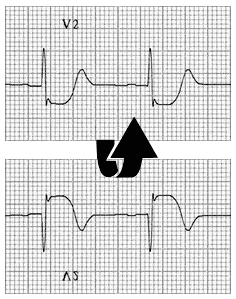
In this ECG example, V3 is the most characteristically abnormal lead.
Look for evidence of posterior involvement in any patient with an inferior or lateral STEMI.
Sometimes it can be difficult to determine whether ST depression in V2-3 is due to posterior STEMI or simply subendocardial ischaemia affecting the anteroseptal wall. The diagnosis can be confirmed by recording posterior leads V7-9 (Quiz 067).
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
