ECG Case 101
51 yr old female who presented with chronic vomiting. She has a history of rheumatoid arthritis and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Her medications include sotalol and rivaroxaban.
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
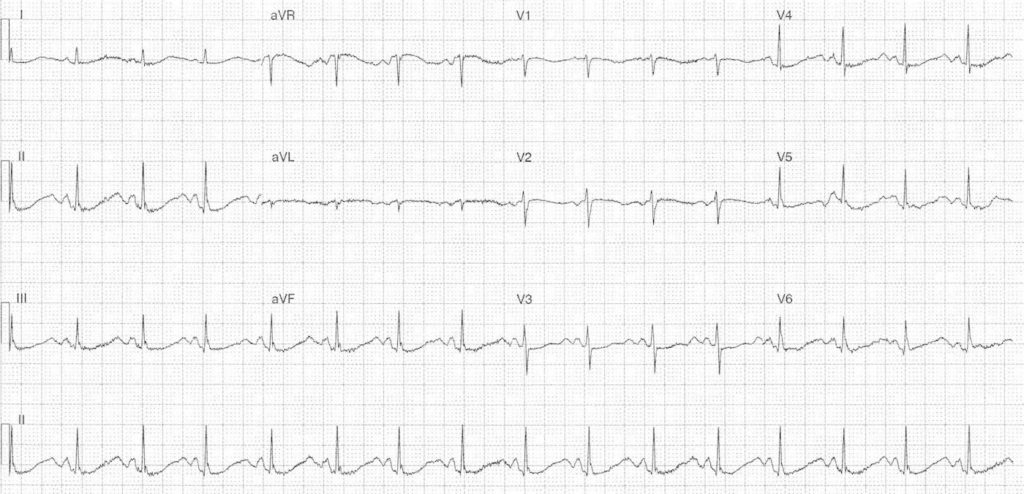
Rate:
- 96 bpm
Rhythm:
- Regular
- Sinus rhythm
Axis:
- Normal
Intervals:
- PR – Normal (~180ms)
- QRS – Normal (80ms)
- QT – 500-520ms (QTc Bazett 630-660 ms) Measured in lead II
Additional:
- ST depression in leads II, III, aVF, V4-6
- Prominent U waves in leads V3-5
- Occur just before the p wave
- T-U fusion in all other leads
Interpretation:
- Marked QT Prolongation
- Features supportive of hypokalaemia / hypomagnesaemia
- U waves T-U fusion
- Variable QT measurement lead II vs lead V3 (end of T wave more easily identifiable)
- Potential contribution from sotalol – known QTc prolonging agent
CLINICAL OUTCOME
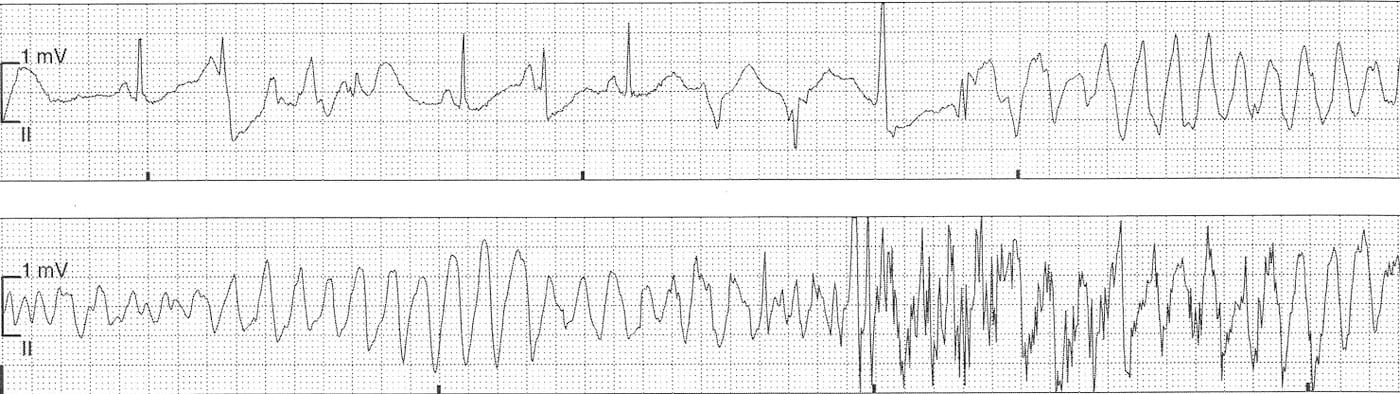
Shortly after this ECG was performed the patient became unresponsive with the following ECG rhythm strip.
The rhythm strip shows sinus rhythm with several PVC’s with resultant R-on-T phenomenon and degeneration into polymorphic VT. This episode of brief and self-terminated.
Bloods revealed several metabolic alkalosis, hypokalaemia and hypomagnesaemia.
The patient was admitted to a critical care area for monitoring and correction of electrolyte / acid-base disturbance. In addition her sotalol was ceased due to its associated risk of QTc prolongation and she was commenced on metoprolol.
FURTHER READING
- ECG Library – QT Interval
- ECG Library – Drugs Causing QT Prolongation
- ECG Library – Hypokalaemia
- ECG Library – Hypomagnesaemia
- ECG Library – Polymorphic VT / Torsades
TOP 150 ECG Series
Emergency Medicine Specialist MBChB FRCEM FACEM. Medical Education, Cardiology and Web Based Resources | @jjlarkin78 | LinkedIn |

I think the second ECG is torsades de pointes?