Hypomagnesaemia
Normal serum magnesium levels are generally considered to be 0.8 – 1.0 mmol/L. Hypomagnesaemia, defined as a level < 0.8 mmol/L, is associated with QT interval prolongation and an increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias.
ECG changes in isolated hypomagnesaemia
- Prolonged PR interval
- Prolonged QT interval
- Atrial and ventricular ectopy
- Predisposition to ventricular tachycardia and torsades de pointes
Patients with hypomagnesaemia often have concurrent hypokalaemia and/or hypocalcaemia and associated ECG features of these conditions.
Most literature on the ECG in hypomagnesaemia has not excluded patients with these other electrolyte disturbances, making exact changes difficult to ascertain. The only identifiable study examining patients with isolated hypomagnesaemia found no significant differences in QRS duration or ST segments compared to baseline ECGs.
Clinical relevance
- Correction of serum magnesium to > 1.0 mmol/L, with concurrent correction of serum potassium to > 4.0 mmol/L, is often effective in suppressing ectopy and supraventricular tachyarrhythmias
- A rapid IV bolus of magnesium 2g is a standard emergency treatment for torsades de pointes
- Further information regarding the causes and other clinical manifestations of hypomagnesaemia can be found here
ECG examples
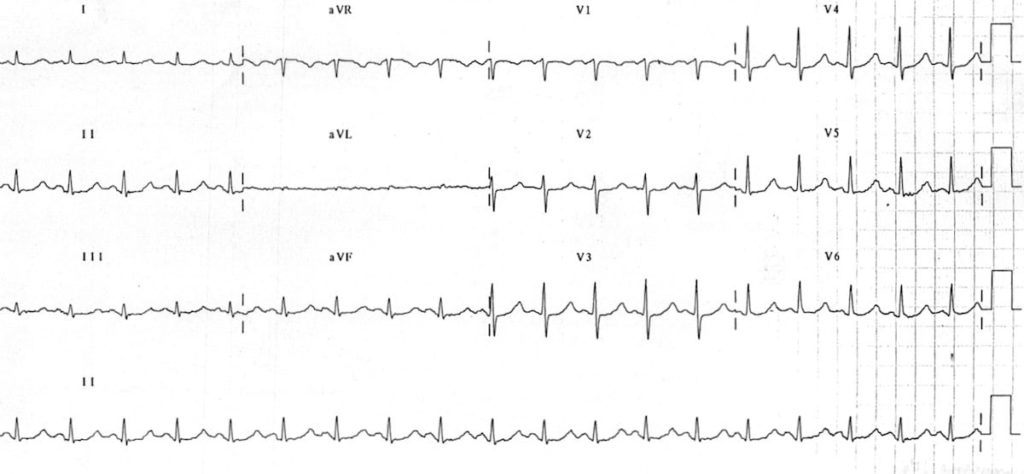
Example 1
The following ECGs were taken from a 76-year-old man presenting with palpitations. He was found to have a serum Magnesium level of 0.28 mmol/L.
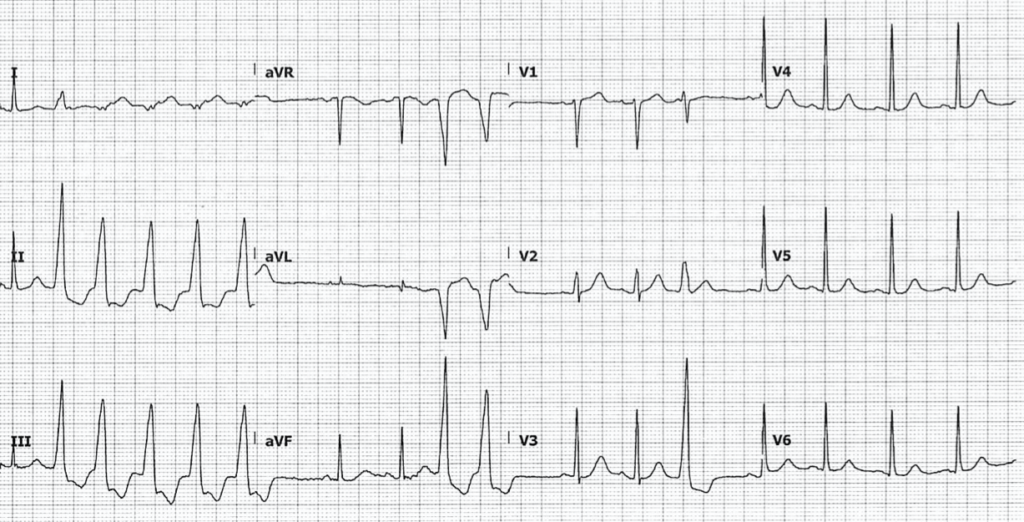
Example 2a
- There are runs of nonsustained ventricular tachycardia (NSVT), as well as ventricular ectopics
- QTC during normal rhythm is 465ms
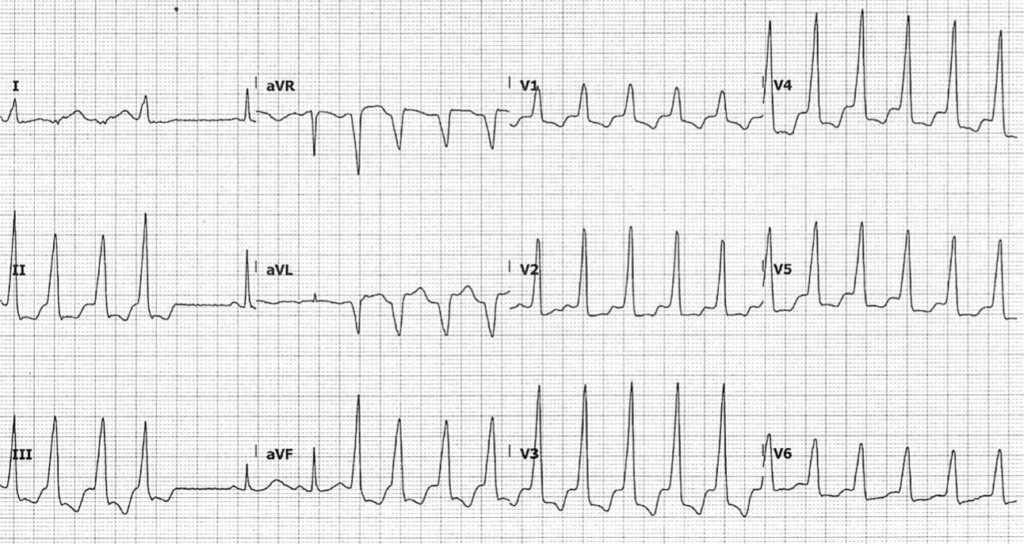
Example 2b
- Repeat ECG 30 minutes later, when the patient entered conscious sustained VT
Related Topics
References
- Dyckner T. Serum magnesium in acute myocardial infarction. Relation to arrhythmias. Acta Med Scand. 1980;207(1-2):59-66
- Haverkamp W et al. The potential for QT prolongation and proarrhythmia by non-antiarrhythmic drugs: clinical and regulatory implications. Report on a policy conference of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2000 Aug;21(15):1216-31.
- Brenda C et al. Serum Magnesium and the Risk of Death From Coronary Heart Disease and Sudden Cardiac Death. JAHA. 2016;5:1
- Yang et al. The ECG characteristics of patients with isolated hypomagnesemia. Frontiers in Physiology. 2021
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner
Emergency Medicine Specialist MBChB FRCEM FACEM. Medical Education, Cardiology and Web Based Resources | @jjlarkin78 | LinkedIn |