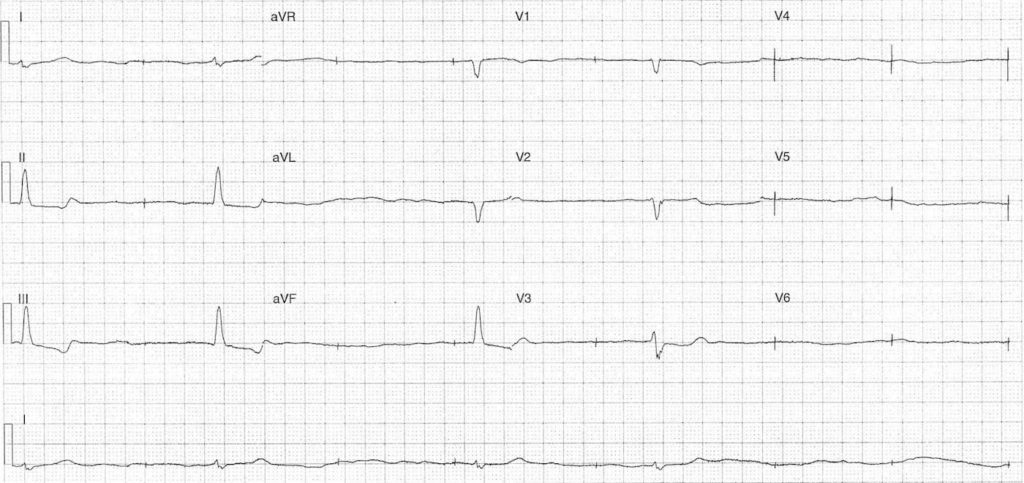
ECG Case 107
86 yr old male referred by his General Practitioner with worsening renal failure. He has a history of atrial fibrillation with bradycardia for which he had a PPM inserted. His medications include metoprolol.
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Rate:
- Mean ventricular rate ~24 bpm
Rhythm:
- Irregular ventricular rhythm
- No visible P waves
- Irregular pacing spikes mean rate of 43 bpm
- No evidence of capture
Axis:
- Normal
Intervals:
- QRS – Prolonged
Additional:
- ST depression with T wave inversion leads II, III, aVF
Interpretation:
- Pacemaker failure to capture
- Underlying marked slow atrial fibrillation
CLINICAL PEARLS
Causes of pacemaker failures
In broad terms there is either a problem with the pacemaker signal generator, the connection to the patient or the patient. These can be further expanded:
- Signal generator problems
- End-of-life
- Battery failure
- Programming issue
- Over or under sensing
- Connection between unit and patient
- Lead fracture
- Lead malposition
- Lead migration
- Lead fibrosis
- Patient factors
- Progression of underlying disease
- Ischaemia
- Electrolyte / acid-base disturbance
- Drug toxicity
Further reading:
CLINICAL OUTCOME
What happened next?
The patient had moderate renal failure with a normal potassium.
CXR showed no lead abnormality and lead placement appeared unaltered.
His metoprolol was ceased and the pacemaker threshold was reprogrammed with resultant 100% capture.
TOP 150 ECG Series
Emergency Medicine Specialist MBChB FRCEM FACEM. Medical Education, Cardiology and Web Based Resources | @jjlarkin78 | LinkedIn |