Louis Nelson Katz
Louis Nelson Katz (1897-1973) was an American cardiologist.
Widely respected for his contributions to cardiovascular physiology and clinical cardiology. Katz is eponymously associated with Katz-Wachtel phenomenon (1937)
Over 500 publications of original research across a wide range of cardiology, including electrophysiology, hypertension, haemodynamics, cardiovascular metabolism, experimental atherosclerosis, pharmacodynamics, respiration, cardiovascular anatomy and pathology, and psychosomatic and epidemiologic aspects of heart disease.
Katz played leading roles in the American Heart Association and in a large number of American and international organizations devoted to the heart and circulation. Major roles in numerous associations, including: International Society of Cardiology (1962), Inter-American Society of Cardiology (1948), American Physiological Society (1957), American Society for the Study of Arteriosclerosis (1954), Chicago Heart Association, and American Heart Association (1942)
Biography
- Born in 1897 in Pinsk, Poland
- 1900 – Emigrated to Cleveland, United States of America
- 1918 – Western Reserve University (WRU), Cleveland, A.B. degree; 1921 – M.D. degree; 1923 – M.A. degree
- 1924-25 Research Fellowship in the Department of Physiology, University of London, with Professor Archibald Hill (Nobel Laureate); elected to the American Physiological Society (APS)
- 1927 – Assistant Professor of Physiology, WRU
- 1928 – Consultant cardiologist St. Luke’s Hospital, Cleveland
- 1930 – Director of the Cardiovascular Research Department (Cardiovascular Institute) of Michael Reese Hospital, Chicago; and Assistant Professor of Physiology at the University of Chicago
- 1952-54 APS Membership Advisory Committee (chairman 1953-1954)
- 1954-57 Chairman of Program Advisory Committee
- 1957-58 Elected 30th President of the APS
- 1967 – Director emeritus of the Cardiovascular Institute
- Died 1973
Medical Eponyms
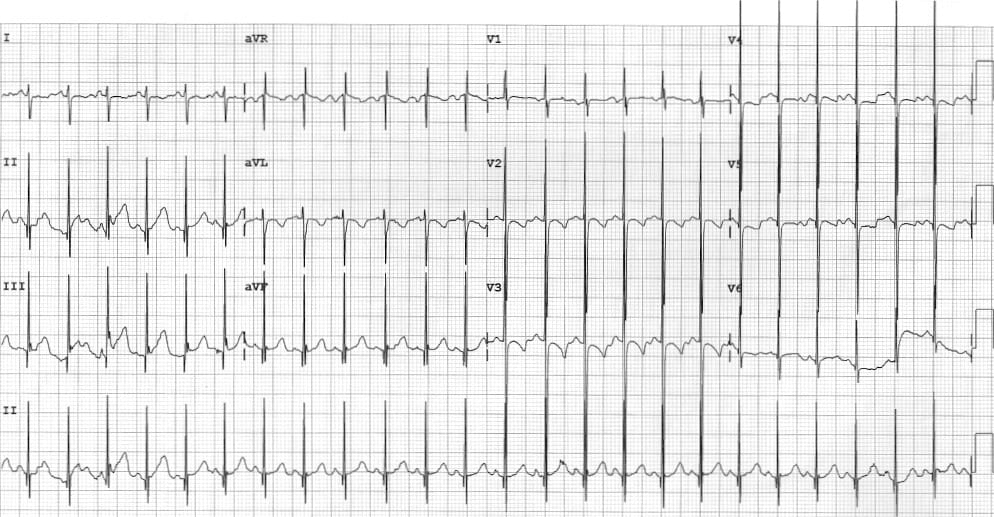
Katz-Wachtel phenomenon (1937)
Large biphasic RS complexes in V2-5. This is the classic ECG pattern of Biventricular Hypertrophy, most commonly seen in children with ventricular septal defect (VSD)
Katz and Wachtel suggested that large diphasic complexes in the standard limb leads were pathognomnic of congenital heart disease. They proposed that the QRS contour may represent combined right and left ventricular ‘strain‘
A biphasic QRS (with the size of the two phases being of the order of less than 1 to 4) was a frequent finding in congenital heart disease. The presence of such a diphasic QRS is confirmatory of this diagnosis, and, when the two phases are large and of equal extent, the finding is pathognomonic of congenital heart disease.
Katz and Wachtel, 1937
Major Publications
- Katz LN, Johnson VE. Elements of electrocardiographic interpretation. 1932
- Katz LN, Wachtel H. The diphasic QRS type of electrocardiogram in congenital heart disease. Am Heart J. 1937; 13: 202-206.
- Katz LN. Exercises in electrocardiographic interpretation. 1941
- Katz LN. Electrocardiography, including an atlas of electrocardiograms. 1947
- Katz LN, Langendorf R, Pick A. Introduction to the interpretation of the electrocardiogram. 1952
- Katz LN, Stamler J. Experimental Atherosclerosis. 1953
- Katz LN, Pick A. Clinical electrocardiography. 1956
- Katz LN, Cain AS. Instrumental methods in cardiac diagnosis. 1956
- Katz LN. Physiology and physiologists: a swan song. Physiologist. 1958;1(5): 18-25
- Katz LN. Nutrition and atherosclerosis. 1958
References
Biography
- Hellerstein HK. Louis Nelson Katz (1897-1973): an appreciative profile. Clin Cardiol. 1986 Sep;9(9):470-4
- Weisse AB. Remembering Louis N. Katz, MD (1897-1973) Circulation. 1998;97(14):1338-9
- Fenn WO. History of the American Physiological Society: The Third Quarter Century, 1937-1962. American Physiological Society. 1963: 42-43.
- Bibliography. Katz, Louis N. (Louis Nelson) 1897-1973. WorldCat Identities
Eponymous terms
- Cadogan M. History of the Electrocardiogram. LITFL
[cite]
Doctor in Australia. Keen interest in internal medicine, medical education, and medical history.