Austin Flint Murmur
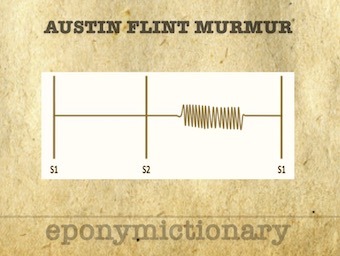
Austin Flint Murmur: Mid diastolic, low pitch rumble heard best at the apex. Absence of opening snap/loud S1 distinguishes from that of mitral stenosis

Austin Flint Murmur: Mid diastolic, low pitch rumble heard best at the apex. Absence of opening snap/loud S1 distinguishes from that of mitral stenosis

Franklin Adin 'Sam' Simmonds (1910–1983) British orthopaedic surgeon. Simmonds-Thompson Test for Achilles tendon rupture with TC Thompson (1902-1986)

T. Campbell Thompson (1902 – 1986) American Orthopedic Surgeon. Simmonds-Thompson Test for Achilles tendon rupture with Sam Simmonds (1910–1983)

Austin Flint (1812-1886) American Physician. Eponym - mid-diastolic aortic regurgitant murmur heard at the apex - Austin Flint Murmur 1862

Ernest Amory Codman (1869-1940) was an American surgeon. Founder of an 'end results system' to track the outcomes of patient treatments.

Roger’s murmur: holosystolic, loud murmur compared to the sound of a 'rushing waterfall'. Associated with ventricular septal defects (VSD)

Henri-Louis Roger (1809 – 1891) was a French paediatrician. Bruit de Roger and the misnomer... Maladie de Roger (Roger's disease)

Katharine Krom Merritt (1886 - 1986) was an American pediatrician. Kasabach–Merritt syndrome (1940)

Dame Ida Caroline Mann (1893 - 1983) was an English ophthalmologist. Ida Mann classification of Coloboma (1937)

The Cabot-Locke murmur is an early diastolic murmur found in patients with severe anaemia. The murmur resolves with treatment of the anaemia. There is no functional valvular abnormality present.

Richard Clarke Cabot (1868-1939) American physician - clinical haematology; pioneering approach to social work; Cabot-Locke murmur (1903)

Edwin Allen Locke (1874-1971) was an American Physician involved care and treatment of TB and pulmonary disease. Eponym: Cabot-Locke murmur (1903)