Bidirectional Ventricular Tachycardia (BVT)
Bidirectional ventricular tachycardia (BVT) is a rare ventricular dysrhythmia characterised by a beat-to-beat alternation of the frontal QRS axis. It is most commonly associated with severe digoxin toxicity
- In the example below, you can see the QRS axis shifts 180 degrees from left to right with each alternate beat
- Another possible pattern is alternating left and right bundle-branch block (see Figure 2 in the paper by Smith et al)

Causes
- This rhythm is most commonly associated with severe digoxin toxicity
- It may be the presenting rhythm in patients with familial catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT)
- BVT has also been reported with herbal aconite poisoning
ECG Examples
Example 1
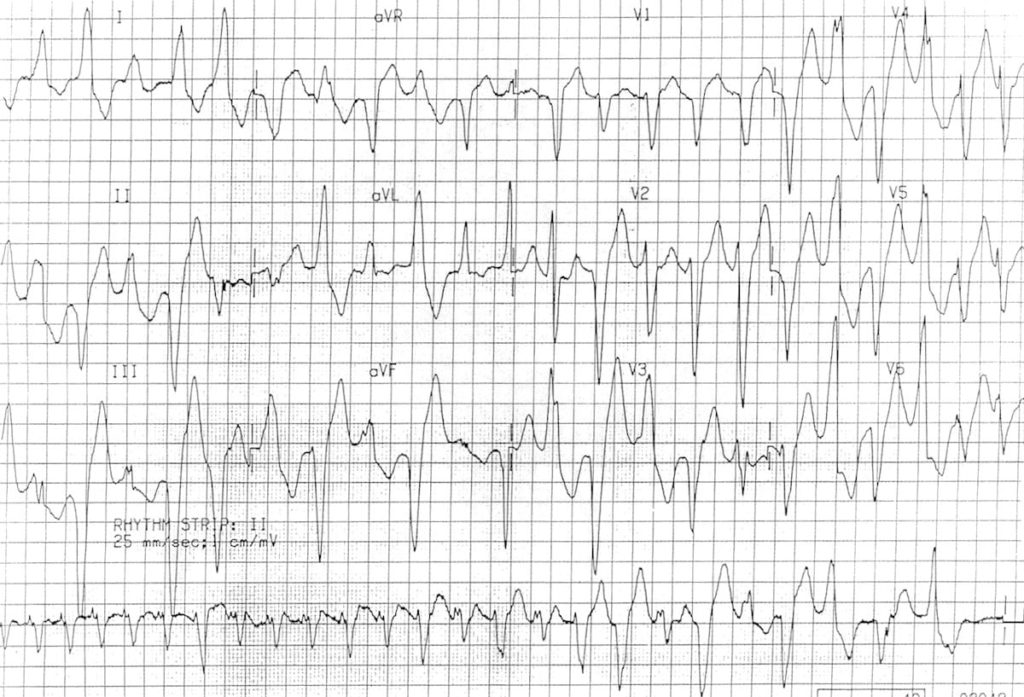
- Multifocal ectopy and bidirectional VT secondary to digoxin poisoning
Example 2
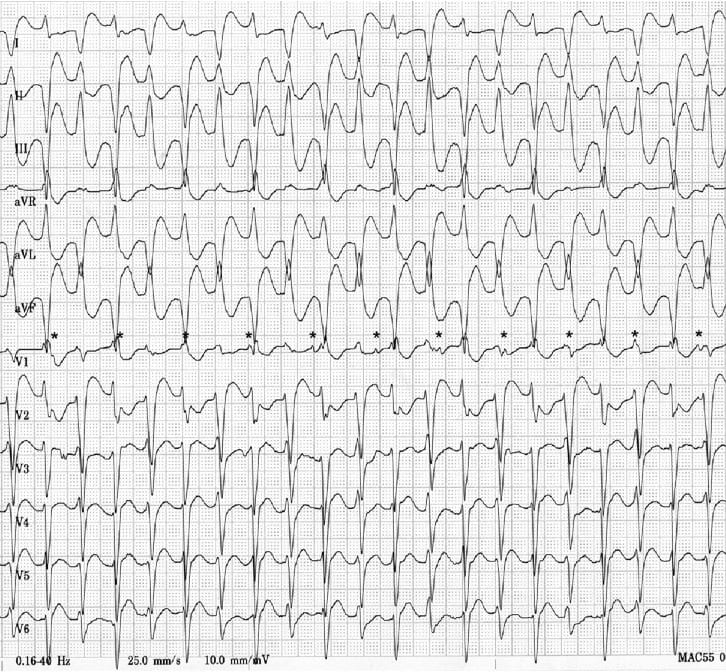
- Bidirectional VT due to digoxin toxicity
Example 3
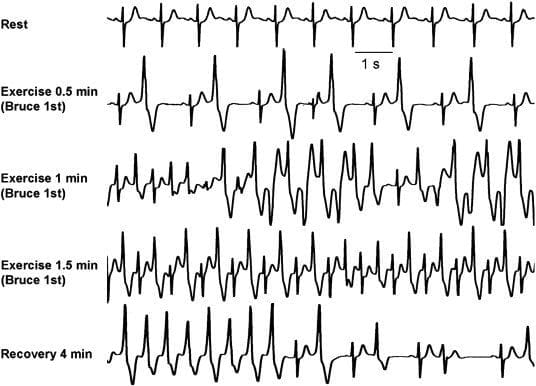
Exercise stress test in a patient with CPVT:
- Progressively worsening ventricular arrhythmias are observed during exercise
- Typical bidirectional VT develops after 1 minute of exercise with a sinus heart rate of approximately 120 beats per minute
- Arrhythmias rapidly recede during recovery
Related Topics
References
- Menduiña MJ, Candel JM, Alaminos P, Gómez FJ, Vílchez J. Bidirectional ventricular tachycardia due to digitalis poisoning. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2005 Aug;58(8):991-3.
- Smith SW, Shah RR, Hunt JL, Herzog CA. Bidirectional ventricular tachycardia resulting from herbal aconite poisoning. Ann Emerg Med. 2005 Jan;45(1):100-1
- Richter S, Brugada P. Bidirectional ventricular tachycardia. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009 Sep 22;54(13):1189.
- Napolitano C, Priori SG, Bloise R. Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia. 2004 Oct 14 [updated 2009 Jul 7]. In: Pagon RA, Bird TC, Dolan CR, Stephens K, editors. GeneReviews [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle (1993)
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner

