Brugada Syndrome
Brugada Syndrome History
Brugada Syndrome is a cardiac abnormality with a high incidence of sudden death in patients with structurally normal hearts.
First described in 1992 by the Brugada brothers, the disease has since had an exponential rise in the numbers of cases reported. The mean age of sudden death is 41, with the age at diagnosis ranging from 2 days to 84 years.
Incidence is high in Southeast Asia where it had been previously described as Sudden Unexplained Nocturnal Death Syndrome (SUNDS).
Previously known colloquially in the Philippines as bangungut (‘to rise and moan in sleep’); in Japan as pokkuri (‘sudden and unexpectedly ceased phenomena’) and in Thailand as Lai Tai (‘death during sleep’).
Brugada Syndrome Key Points
- There’s really only one type of Brugada syndrome.
- Diagnosis depends on a characteristic ECG finding AND clinical criteria.
- Further risk stratification is controversial.
- Definitive treatment = ICD.
- Brugada sign in isolation is of questionable significance.
Aetiology of Brugada Syndrome
In a nutshell, Brugada syndrome is due to a mutation in the cardiac sodium channel gene. This is often referred to as a sodium channelopathy. Over 60 different mutations have been described so far and at least 50% are spontaneous mutations, but familial clustering and autosomal dominant inheritance has been demonstrated.
ECG changes can be transient with Brugada syndrome and can also be unmasked or augmented by multiple factors:
- Fever
- Ischaemia
- Multiple Drugs
- Sodium channel blockers eg: Flecainide, Propafenone
- Calcium channel blockers
- Alpha agonists
- Beta Blockers
- Nitrates
- Cholinergic stimulation
- Cocaine
- Alcohol
- Hypokalaemia
- Hyperkalaemia
- Hypothermia
- Post DC cardioversion
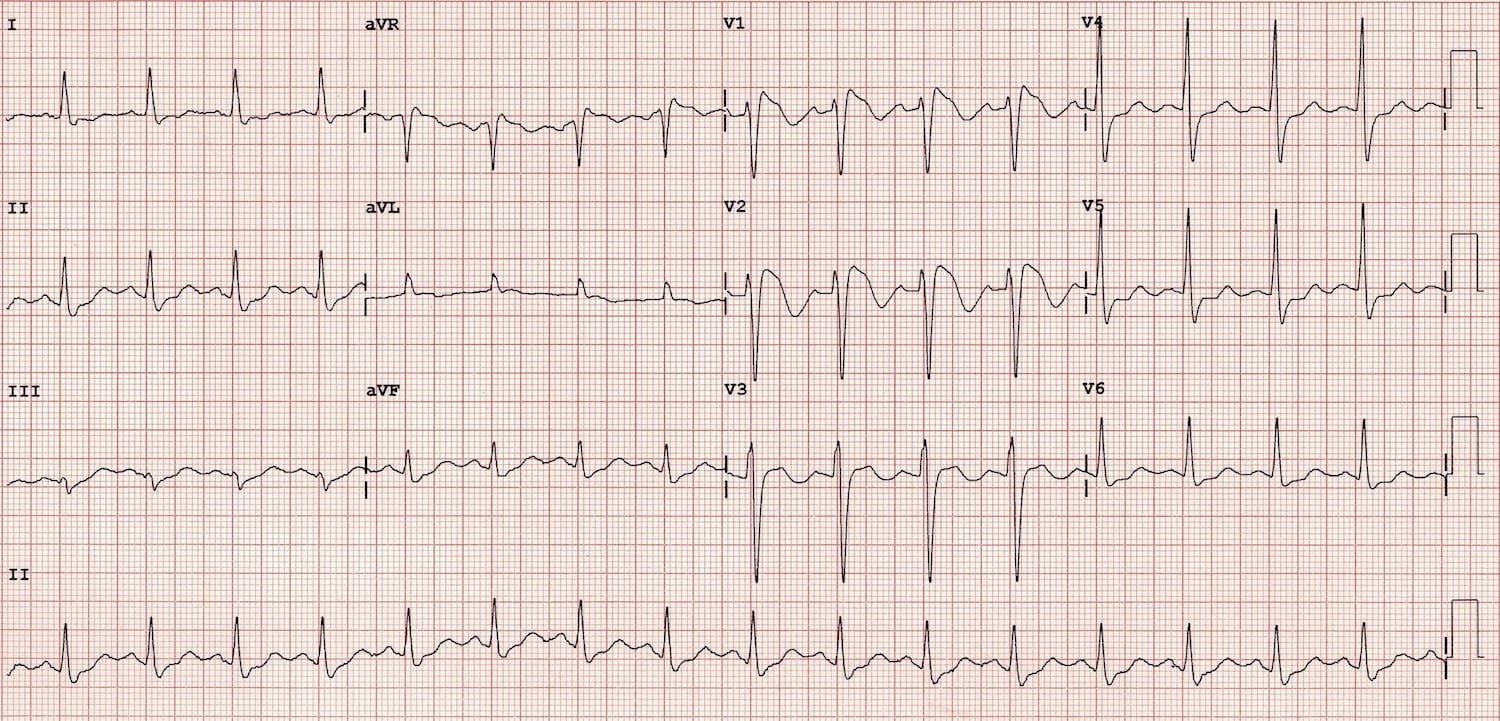
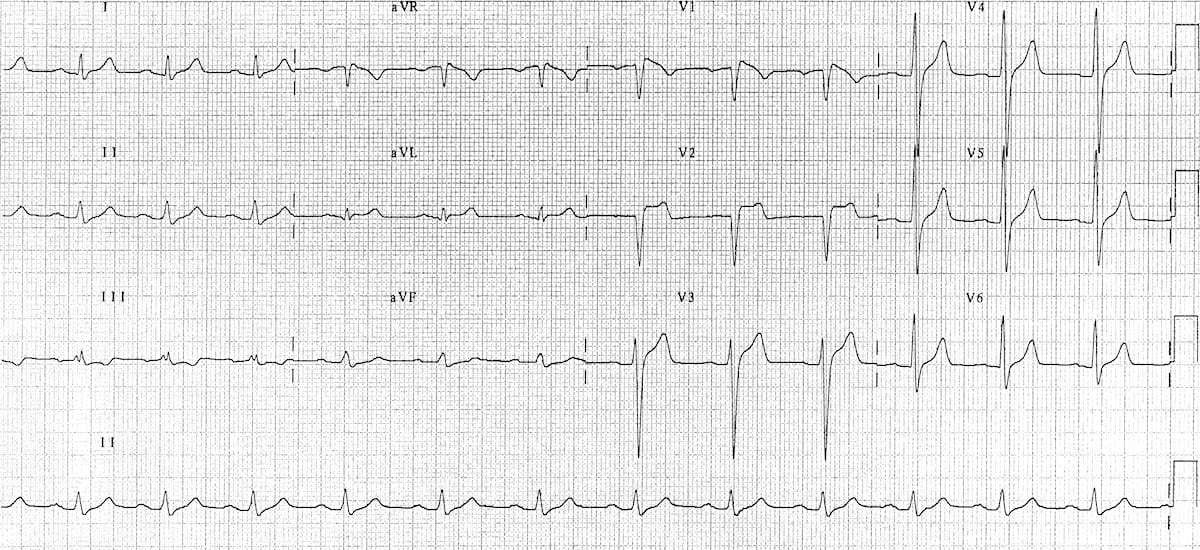
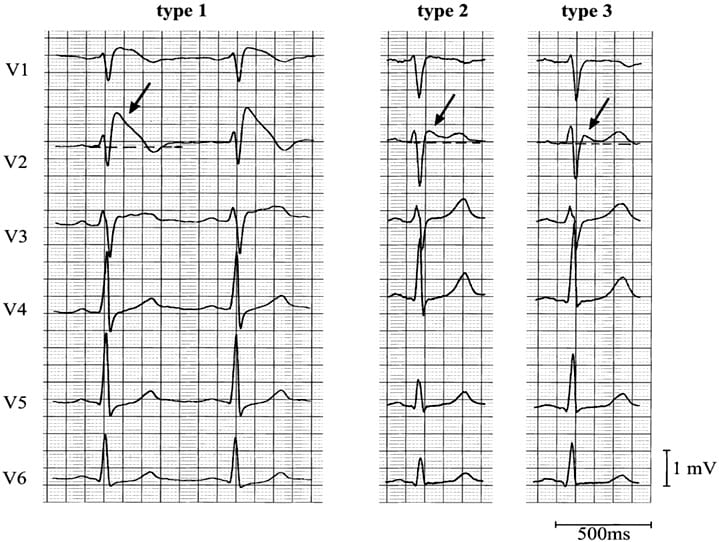
Diagnostic Criteria
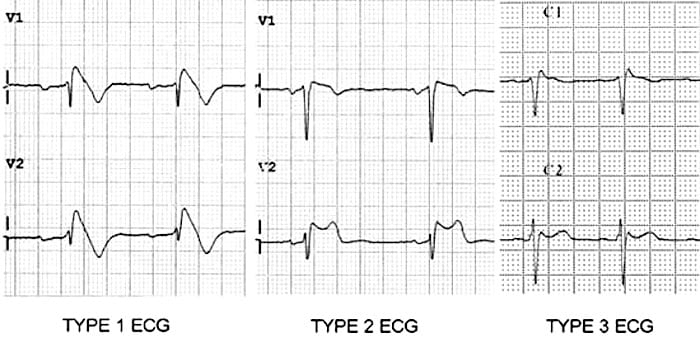
Type 1
- Coved ST segment elevation >2mm in >1 of V1-V3 followed by a negative T wave.
- This is the only ECG abnormality that is potentially diagnostic.
- It is often referred to as Brugada sign.
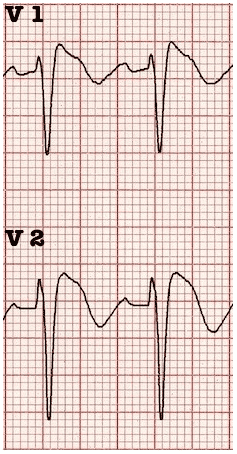
This ECG abnormality must be associated with one of the following clinical criteria to make the diagnosis:
- Documented ventricular fibrillation (VF) or polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT).
- Family history of sudden cardiac death at <45 years old .
- Coved-type ECGs in family members.
- Inducibility of VT with programmed electrical stimulation .
- Syncope.
- Nocturnal agonal respiration.
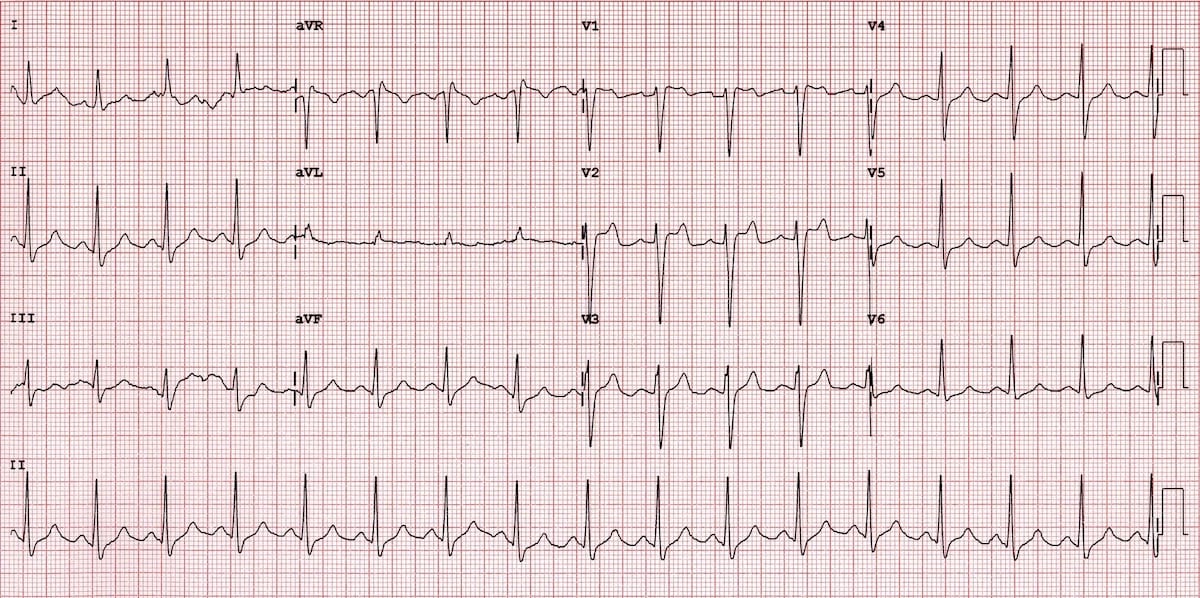
The other two types of Brugada are non-diagnostic but possibly warrant further investigation (see discussion below).
Type 2
- Brugada Type 2 has >2mm of saddleback shaped ST elevation.
Type 3
- Brugada type 3: can be the morphology of either type 1 or type 2, but with <2mm of ST segment elevation.
Management
The only proven therapy is an implantable cardioverter – defibrillator (ICD). Quinidine has been proposed as an alternative in settings where ICD’s are unavailable or where they would be inappropriate (eg: neonates).
Undiagnosed, Brugada syndrome has been estimated to have a mortality of 10% per year. Does this mean that a diagnosis in ED mandates admission? Probably yes for all type 1 patients if they present with suggestive clinical criteria.
It may be appropriate for risk stratification on an outpatient basis with an electrophysiology study (EPS) to see if the patient has inducible ventricular tachycardia (VT) or fibrillation (VF)in the following settings:
- Asymptomatic patients with a type 1 ECG pattern.
- All type 2 + 3 ECG patterns.
However this is controversial with much debate in the literature ranging from a very low threshold for EPS studies and ICD insertion (Brugada et al) to more conservative approaches. One of the problems is that EPS are far from a gold standard, with a negative predictive value of less than 50% and some studies suggest that we might be getting a little over-excited about this relatively recently described ECG finding.
Admittedly study sizes are pretty small – but one study followed 98 asymptomatic Japanese patients with ‘Brugada sign’ on routine ECG for 7.8 years and found them to have no greater mortality than the rest of a 14000 strong cohort. This highlights the importance of the clinical criteria required for diagnosis listed above.
Pharmacological assessment has been suggested by some in Type 2 + 3 patterns, if Brugada syndrome is suspected clinically – the administration of sodium channel blocking drugs may convert these non-diagnostic forms into the diagnostic type 1, however the sensitivity of this test is unknown and it would appear that this subgroup is at extremely low / no increased mortality when compared to the general population.
References
- Dr Smith’s ECG Blog — Brugada syndrome (case discussions)
- ECG Top 100 — Case 080
- Salim Rezaie at ALiEM — Brugada syndrome (review of key features and treatment)
- J Brugada – How to manage a patient with a Brugada ECG pattern (review of diagnosis and management)
- Allely P. What is Brugada Syndrome?
- Martini B, Nava A, Thiene G, Buja GF, Canciani B, Scognamiglio R, Daliento L, Dalla Volta S. Ventricular fibrillation without apparent heart disease: description of six cases. Am Heart J. 1989 Dec;118(6):1203-9
- Brugada P, Brugada J. Right bundle branch block, persistent ST segment elevation and sudden cardiac death: a distinct clinical and electrocardiographic syndrome. A multicenter report. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992 Nov 15;20(6):1391-6.
- Antzelevitch C, Brugada P, Brugada J, Brugada R, Towbin JA, Nademanee K. Brugada syndrome: 1992-2002: a historical perspective. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003 May 21;41(10):1665-71
- Littmann L, Monroe MH, Kerns WP 2nd, Svenson RH, Gallagher JJ. Brugada syndrome and “Brugada sign”: clinical spectrum with a guide for the clinician. Am Heart J. 2003 May;145(5):768-78.
- Antzelevitch C, Brugada P, Borggrefe M, Brugada J, Brugada R, Corrado D, Gussak I, LeMarec H, Nademanee K, Perez Riera AR, Shimizu W, Schulze-Bahr E, Tan H, Wilde A. Brugada syndrome: report of the second consensus conference: endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society and the European Heart Rhythm Association. Circulation. 2005 Feb 8;111(5):659-70
- Hoogendijk MG, Opthof T, Postema PG, Wilde AA, de Bakker JM, Coronel R. The Brugada ECG pattern: a marker of channelopathy, structural heart disease, or neither? Toward a unifying mechanism of the Brugada syndrome. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2010 Jun;3(3):283-90
- Mizusawa Y, Wilde AA. Brugada syndrome. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012;3:606-16.
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Medicine Specialist MBChB FRCEM FACEM. Medical Education, Cardiology and Web Based Resources | @jjlarkin78 | LinkedIn |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner


I believe hyperkalemia should be included under the list of acquired Brugada pattern (Brugada phenocopy) etiologies. Hyperkalemia tends to disable sodium channels and is actually more relevant than hypokalemia in this regard.