
Lauge-Hansen classification of ankle injury
Lauge-Hansen classification of ankle injuries (1950) - predictable fracture patterns defined by injury mechanism and resultant radiological findings

Lauge-Hansen classification of ankle injuries (1950) - predictable fracture patterns defined by injury mechanism and resultant radiological findings
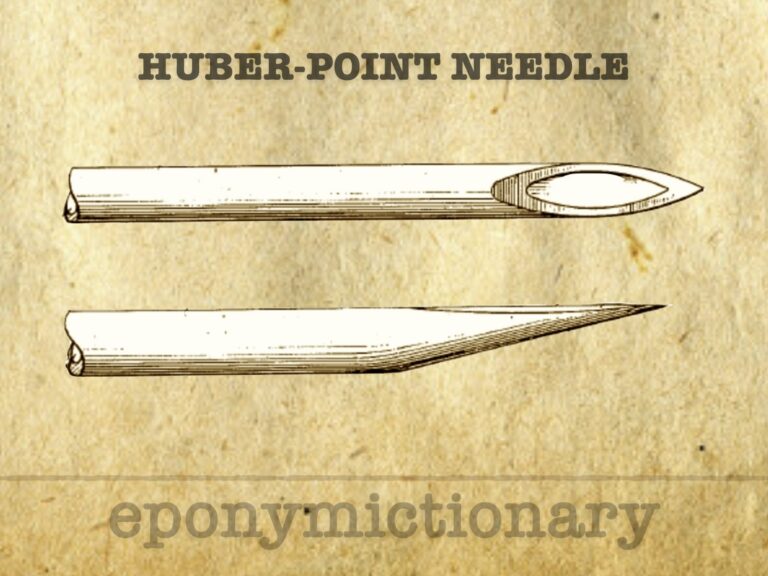
Hypodermic needle (needle which enters the skin) Originally described in 1946 by Ralph Huber. More commonly known as the Tuohy Needle

Jess Bernard Weiss (1917 – 2007) was an American anesthesiologist. Best known for designing the Weiss needle for the placement of epidural catheters

Carl (Karl) Koller (1857–1944), Austrian ophthalmologist who introduced cocaine as the first practical local anaesthetic in 1884, transforming surgery and enabling regional and neuraxial anaesthesia.

Jacques Forestier (1890-1978) was a French physician and rheumatologist, depiction of hyperostosis (1959) later called Forestier’s disease.
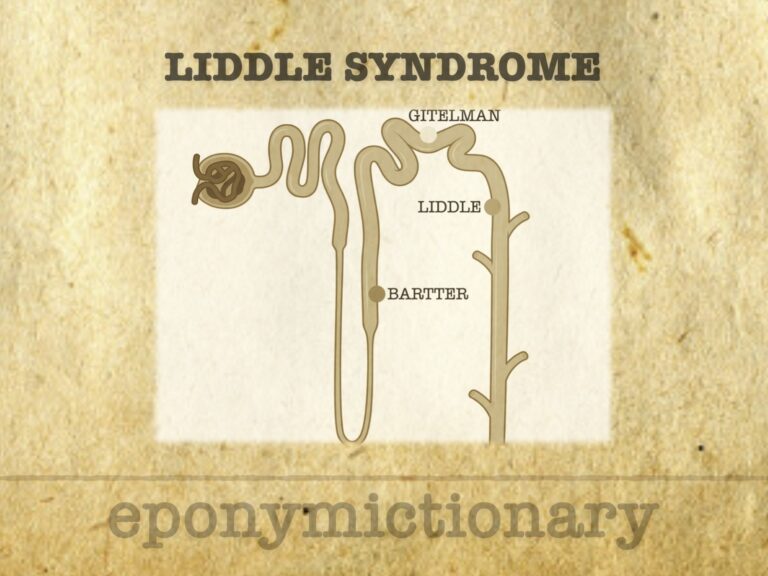
Liddle Syndrome: Monogenic hypertension due to ENaC overactivity in the collecting duct. Causes sodium retention, hypokalaemia, low renin and aldosterone—pseudo-aldosteronism.

Grant Winder Liddle (1921-1989) American endocrinologist. Pioneer of endocrine diagnostics; discovered Liddle syndrome, developed suppression tests, and defined ectopic ACTH

Gitelman Syndrome: Inherited defect in Na⁺-Cl⁻ cotransport in the distal tubule, causing hypokalaemia, alkalosis, hypomagnesaemia, and hypocalciuria—thiazide-like effect.

Hillel J. Gitelman (1932–2014) American nephrologist. Described Gitelman syndrome, a renal tubulopathy mimicking thiazide effect with hypokalaemia and hypomagnesaemia.
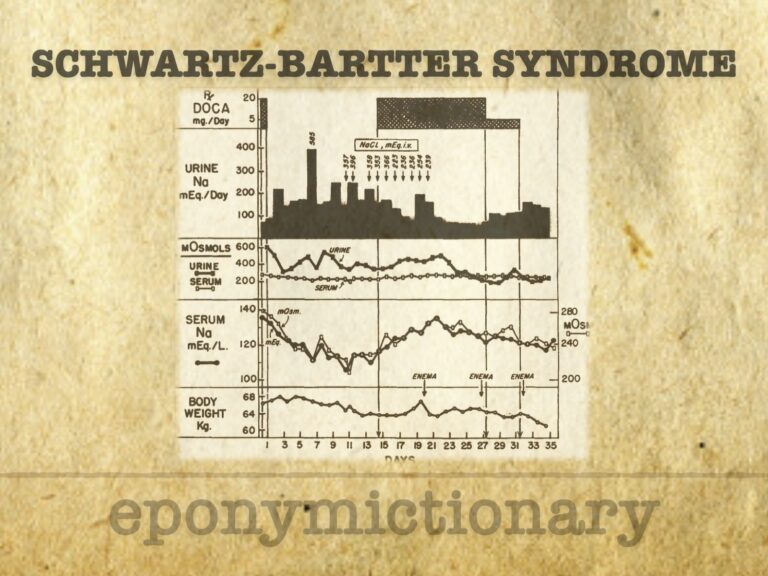
Schwartz-Bartter Syndrome (SIADH): Excess ADH leads to water retention and dilutional hyponatraemia, with low serum sodium and osmolality but inappropriately concentrated urine.
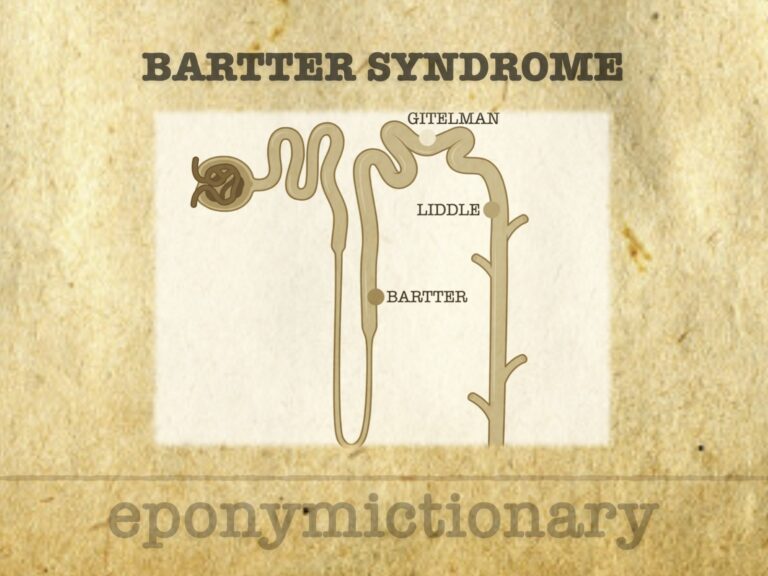
Bartter Syndrome: Renal tubulopathy with hypokalaemic alkalosis, high renin and aldosterone, normal BP, and polyuria—mimics loop diuretic effect at the thick ascending limb.

Frederic Crosby Bartter (1914–1983) American endocrinologist. Defined Bartter syndrome, co-described SIADH, and advanced adrenal and renal physiology.