
J. Leonard Corning
James Leonard Corning (1855 - 1923) was an American neurologist. Epidural block (1885); Regional anaesthesia (1885)

James Leonard Corning (1855 - 1923) was an American neurologist. Epidural block (1885); Regional anaesthesia (1885)

Frédéric Justin Collet (1870–1964), Lyon physician and ENT professor; described the 1915 skull-base palsy of CN IX–XII later known as Collet–Sicard syndrome

Brain Herniation Syndromes. Clinical and radiological assessment of 13 cases. Neuroimaging case study series with Teresa Crow, Troy Carnwath, Scott DiMeo, L. Erin Miller and Natalie Rall

Romberg’s sign: a classic neurological test detecting proprioceptive loss by demonstrating postural instability with eyes closed.

Marshall Hall (1790–1857): Pioneer of reflex physiology, anti-bloodletting reformer, creator of the Ready Method for resuscitation, and advocate for animal ethics.

Pierre Marie (1853–1940), French neurologist and endocrinologist; defined acromegaly, described progressive aphasia, and helped shape modern neurology.

Jean-Alexandre Barré (1880–1967). French neurologist ; co-described Guillain–Barré syndrome; pioneer in vestibular neurology and semiology; eponyms include Barré test and Barré–Liéou syndrome.
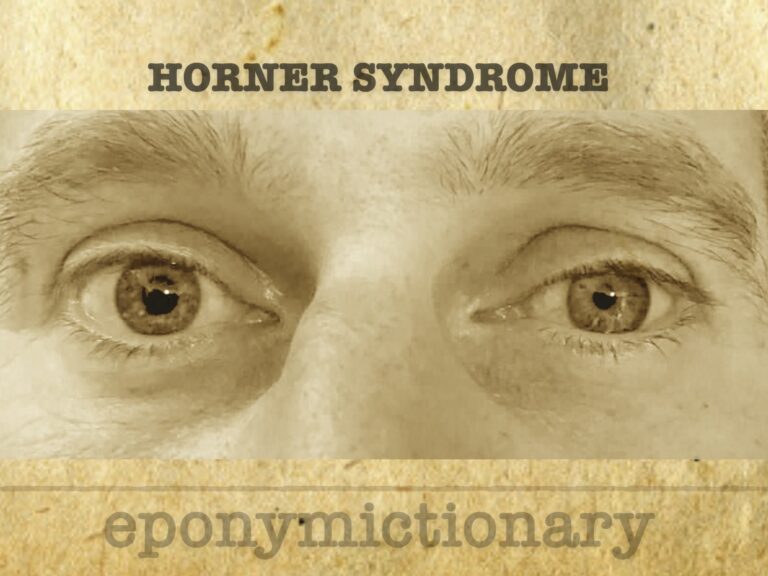
Horner syndrome is associated with an interruption to the sympathetic nerve supply of the eye. It is characterized by the classic triad of miosis, partial ptosis, and anhidrosis +/- enophthalmos
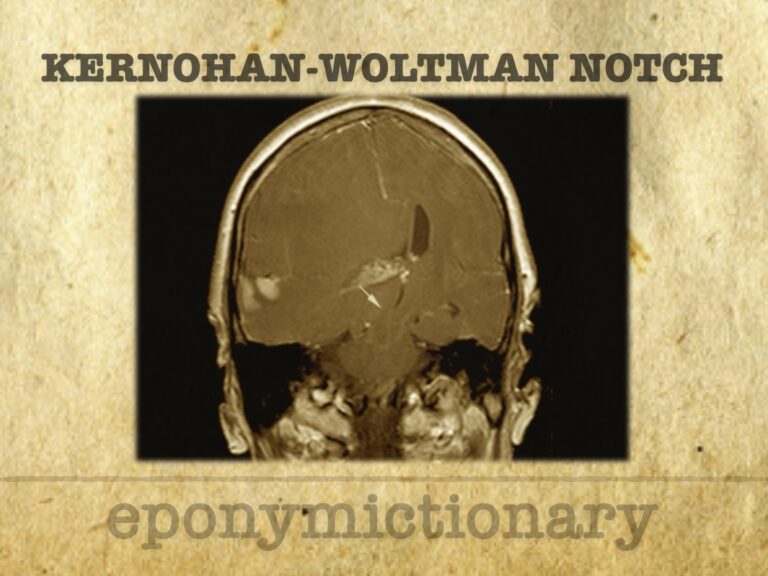
Kernohan-Woltman Notch Phenomenon (KWNP): false localising sign with mass effect and ipsilateral hemiparesis via contralateral peduncle compression.

James W. Kernohan (1896–1981), pioneer of glioma grading and the Kernohan notch, shaped modern neuropathology through diagnostic clarity and clinical insight.

Henry Woltman (1889–1964), Mayo Clinic neurologist, Kernohan-Woltman notch, stiff-man syndrome, and myxoedema reflex; leader in U.S. neurology

Woltman’s Sign is delayed reflex relaxation in hypothyroidism, often seen as a hung-up ankle jerk; a classic but non-specific clinical finding.