ECG Case 012
Young male found collapsed at home, apparently intoxicated. What does the ECG show?
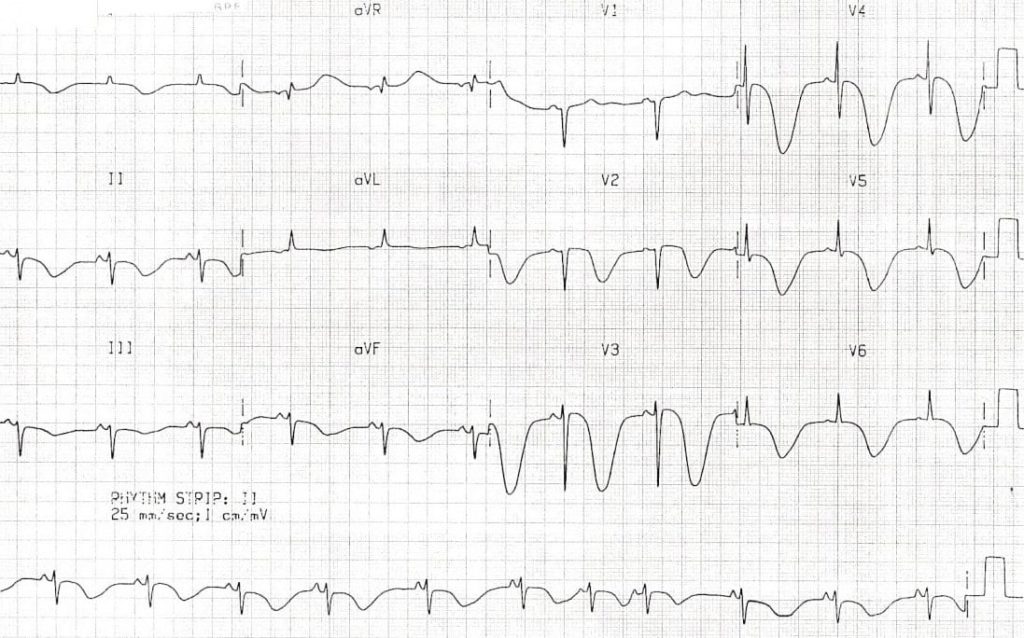
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Main Abnormalities
- Giant T-wave inversions in multiple leads, most prominent in V2-6
- Marked QT prolongation > 600 ms
Diagnosis
This ECG pattern is characteristic of raised intracranial pressure and is classically seen in the context of massive intracranial haemorrhage, particularly:
- Aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage
- Haemorrhagic stroke
Similar ECG patterns have also been reported in patients with raised ICP due to:
- Large-territory ischaemic stroke causing cerebral oedema (e.g. MCA occlusion)
- Traumatic brain injury
The differential diagnosis for widespread T-wave inversions and QT prolongation includes myocardial ischaemia (e.g. Wellens syndrome) and electrolyte abnormalities (e.g. hypokalemia). However, neither condition would cause the gigantic “cerebral T waves” seen here.
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
