ECG Case 013
Middle-aged patient presenting with palpitations and dizziness.
What does the ECG show?
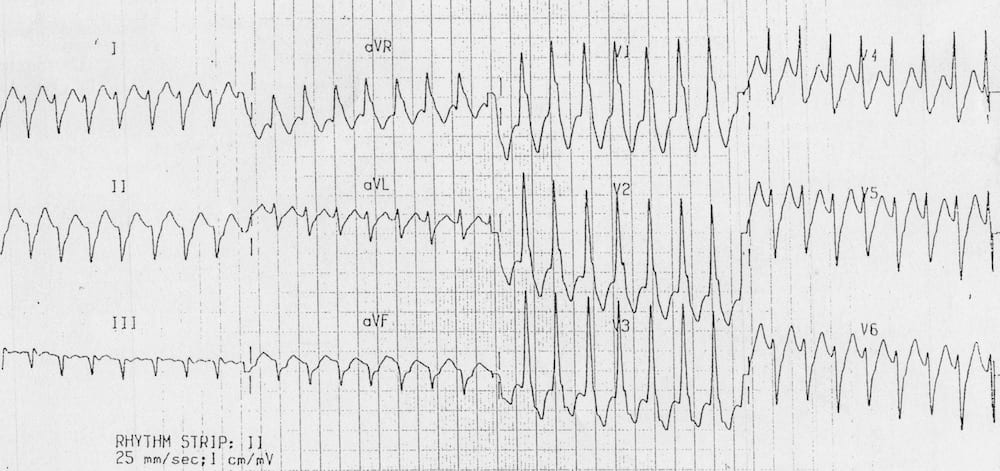
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Diagnosis
This ECG shows a regular broad complex tachycardia with an RSR’ pattern in V1.
The differential diagnosis could include:
- Ventricular tachycardia.
- SVT with aberrant conduction — either due to RBBB or WPW.
On closer inspection, the ECG demonstrates some classic features of ventricular tachycardia:
- Northwest axis — QRS is positive in aVR, negative in I and aVF
- The taller left rabbit ear sign — There is an atypical RBBB pattern in V1, where the left “rabbit ear” is taller than the right
- Negative QRS complex (R/S ratio < 1) in V6
These findings indicate VT rather than SVT with aberrancy.
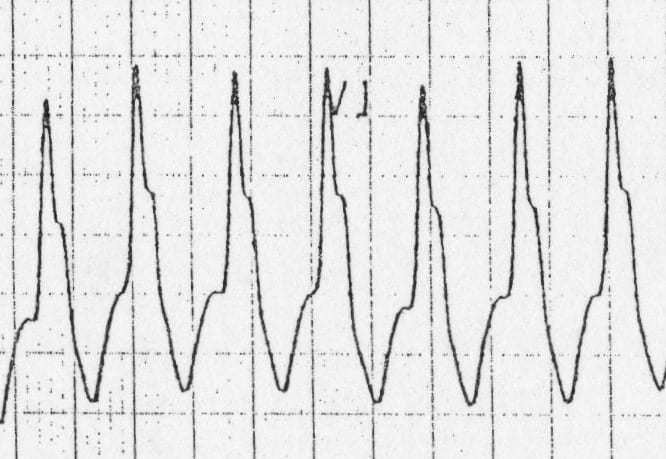
- Taller left rabbit ear = VT
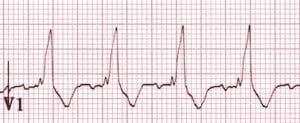
- Taller right rabbit ear = RBBB
CLINICAL PEARLS
Other factors that increase the likelihood of VT in patients presenting with regular broad complex tachycardia include:
- Age > 35 (positive predictive value of 85%)
- Structural heart disease — e.g. IHD, CCF, cardiomyopathy
- Family history of sudden cardiac death or arrhythmogenic conditions such as HOCM, Brugada syndrome or ARVD that are associated with episodes of VT
In any patient with a broad complex rhythm, also consider the possibility of toxic / metabolic conditions such as hyperkalaemia or sodium-channel blockade.
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
