ECG Case 023
Elderly patient with accidental overdose of sotalol. Describe the ECG.
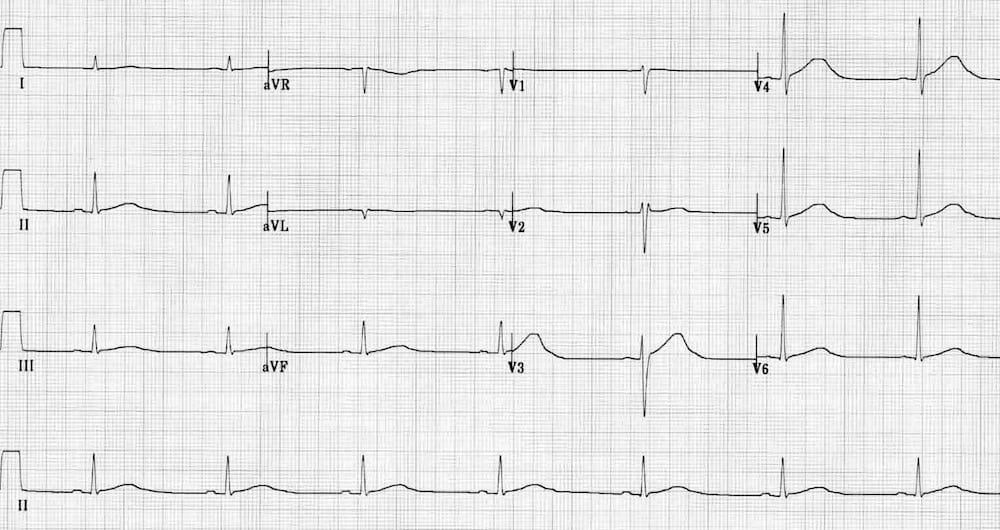
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Main Abnormalities
This ECG demonstrates the key features of sotalol toxicity:
- Sinus bradycardia (42 bpm)
- Very long QT interval (~600 ms)
Sotalol is a beta blocker with additional class III effects (potassium channel blockade), so it causes both bradycardia and QT prolongation in overdose.
Risk of Torsades
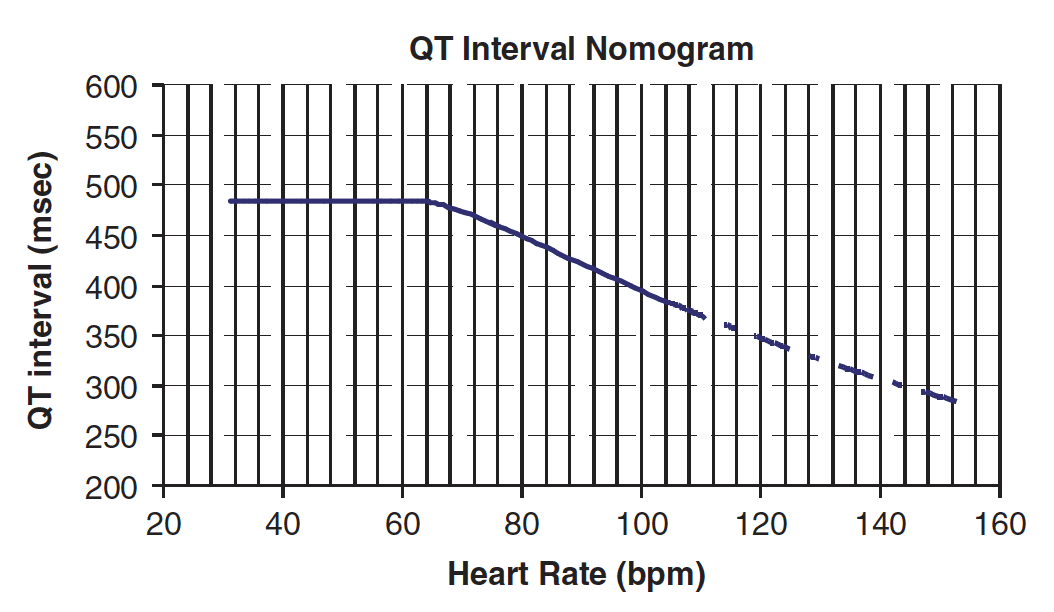
- In comparison to ECG Quiz 022, this patient is at significant risk of TdP
- The combination of bradycardia and significant QT prolongation means that this patient plots well above the “at risk” line on the QT nomogram
- Prophylaxis of TdP in this case would include correction of QT-dependent electrolytes (K, Mg, Ca) to the high-normal range and positive chronotropy (e.g. with isoprenaline) to move the patient below the at-risk line
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner

