ECG Case 022
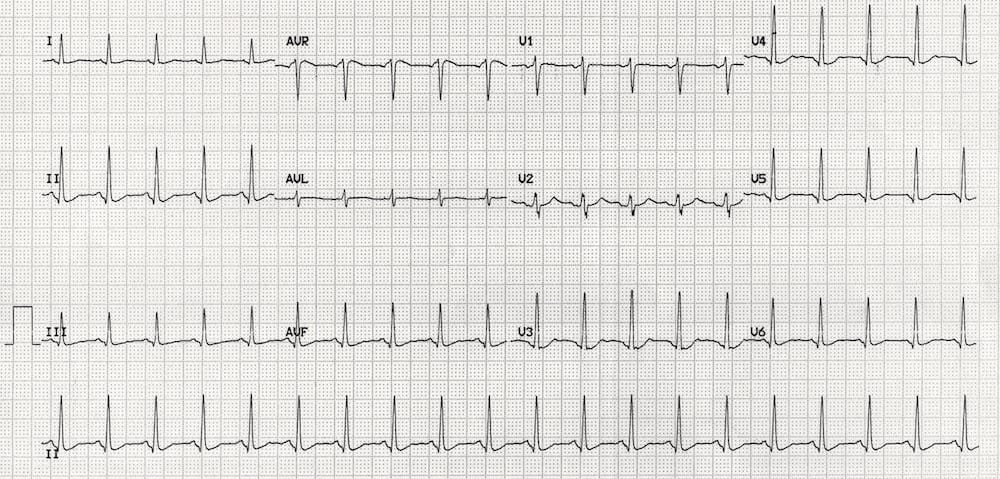
Post-intubation ECG of a young adult presenting with coma following a 6g quetiapine overdose. Describe the ECG.
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Main Abnormalities
This ECG displays the characteristic electrocardiographic features of quetiapine toxicity:
- Sinus tachycardia due to anticholinergic effects
- Prolonged QT interval (QT interval > half the RR interval; QTc = 560ms)
A similar pattern would be seen with other atypical antipsychotic agents such as olanzapine or clozapine.
Significance of QT prolongation
- QT prolongation is a common source of concern in patients with antipsychotic toxicity, because of the theoretical risk of Torsades de Pointes
- A QTc interval > 500 ms is commonly cited as a marker of increased risk of TdP
- However, tachycardia (which is almost ubiquitous in significant poisoning with quetiapine, olanzapine or clozapine) is actually protective against TdP
- For this reason, TdP rarely occurs with quetiapine toxicity
CLINICAL PEARLS
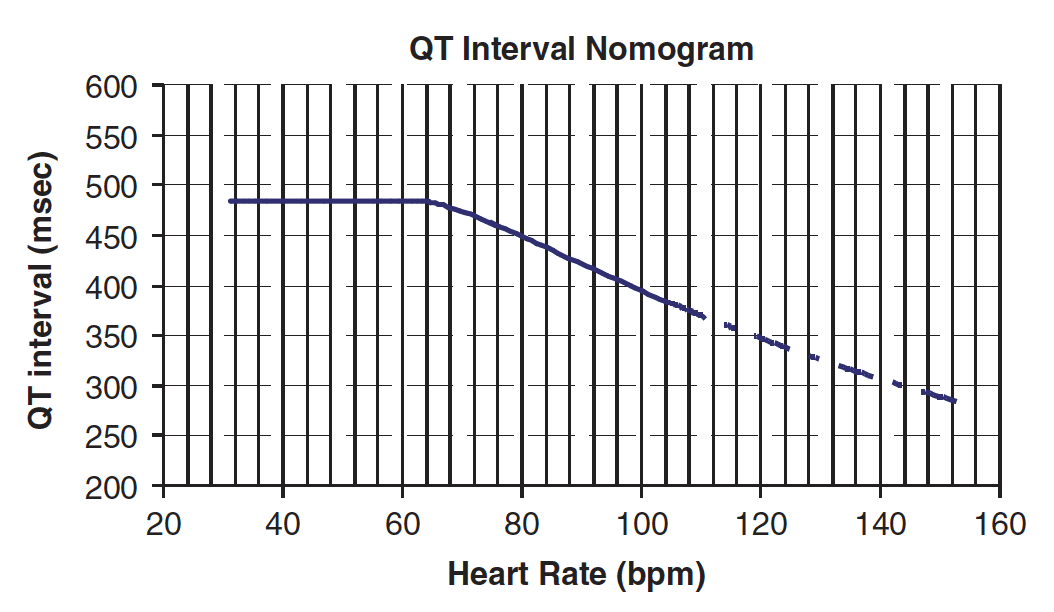
QT interval nomogram
- Many Australian toxicologists use the QT interval nomogram to assess risk of TdP
- The absolute QT interval is measured manually in multiple leads and the median QT interval plotted on the nomogram (read how to do this here)
- Plots above the line indicate significant QT prolongation and consequent risk of TdP
By my measurements, our patient has an absolute QT of ~320 ms with HR 120 so plots below the line — i.e. not at significant risk of TdP.
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS (UWA) CCPU (RCE, Biliary, DVT, E-FAST, AAA) Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Editor-in-chief of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner


Hi. It would be very helpful if you to marked the point where it is easier to determine the qt interval of in this example
Thanks