ECG Case 038
15-year old patient presenting with rapid palpitations and dizziness. Symptoms recur in ED. Describe the ECG.
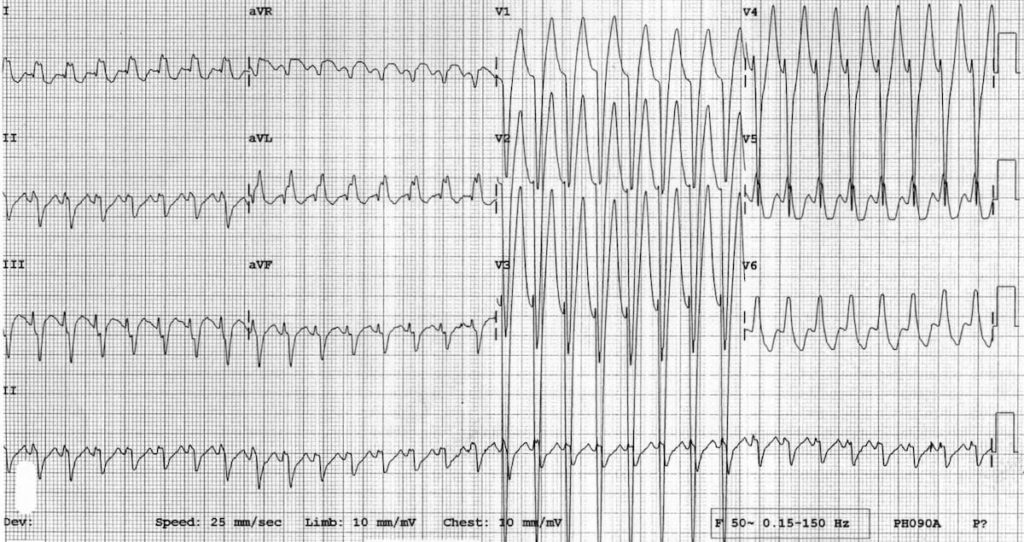
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Main Abnormalities
- Very rapid, regular broad-complex tachycardia (~ 200 bpm).
- LBBB morphology (dominant S wave in V1).
- No clear atrial activity — no flutter waves or fibrillatory waves.
- No obvious diagnostic features for VT
Differential Diagnosis
In a patient presenting with a regular broad-complex tachycardia and no evidence of atrial activity, the main diagnostic considerations are:
- Ventricular tachycardia.
- SVT with aberrant conduction due to bundle branch block.
- SVT with aberrant conduction due to WPW.
Although diagnostic criteria exist to aid in differentiation of these rhythms, none of them have 100% sensitivity or specificity — leading many authors to recommend treating as VT if uncertain.
However, clinical context is everything…
This patient has two strong indicators of SVT with aberrancy:
- Young age — the vast majority of BCTs in children are SVT with aberrancy.
- Evidence of WPW on previous ECGs.
CLINICAL PEARLS
This is an example of antidromic AV reentry tachycardia — a reentrant SVT seen in WPW where the impulse travels from atria to ventricles via the accessory pathway, recycling backwards through the AV node (hence “antidromic”).
Activation of the ventricles via the accessory pathway produces a broad complex that may be indistinguishable from VT. This is in comparison to orthodromic SVT, where the impulse travels forwards through the AV node producing a normal-looking, narrow QRS.
This patient reverted back to sinus rhythm with vagal maneouvres. The WPW pattern was once again visible on his sinus rhythm ECG.
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |

Hi
To be more precise, it’s better to describe the differences in differentials:
– SVT with aberrancy due to BBB.
– SVT with accessory pathway to do e.g. WPW.
ECG features:
1. During sinus rhythm, QRS is normal or displays different degrees of manifest pre-excitation with LBBB morphology.
2. During tachycardia, antidromic AVRT over a Mahaim fiber has a LBBB morphology, various QRS patterns and axis.
Mahaim syndrome is also possible.
In my opinion vagal maneouver in antidromic AV reentry tachycardia is not the best thing to do because blocking the reentry by AV node is changed by ventricular overstimulus with high risk of fibrilation. Am I right?