ECG Case 046
Middle-aged patient presenting with palpitations. Describe the ECG
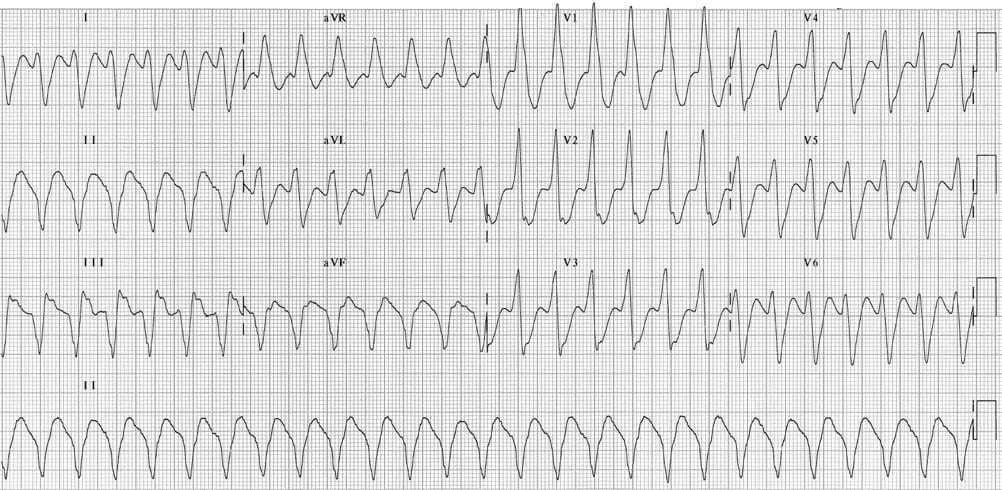
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
This ECG contains multiple diagnostic features for ventricular tachycardia:; dominant R wave in V1/V2 and therefore a RBBB morphology (compare this with ECG 047)
- Regular broad complex tachycardia at ~150 bpm.
- Very broad QRS complexes (~200 ms).
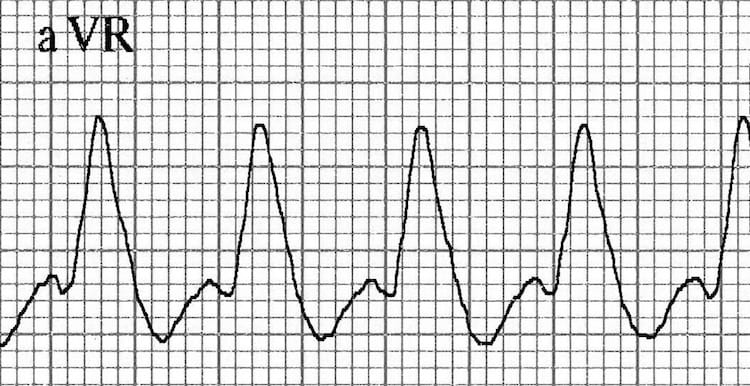
- Northwest axis (-120 degrees) with positive QRS in aVR.
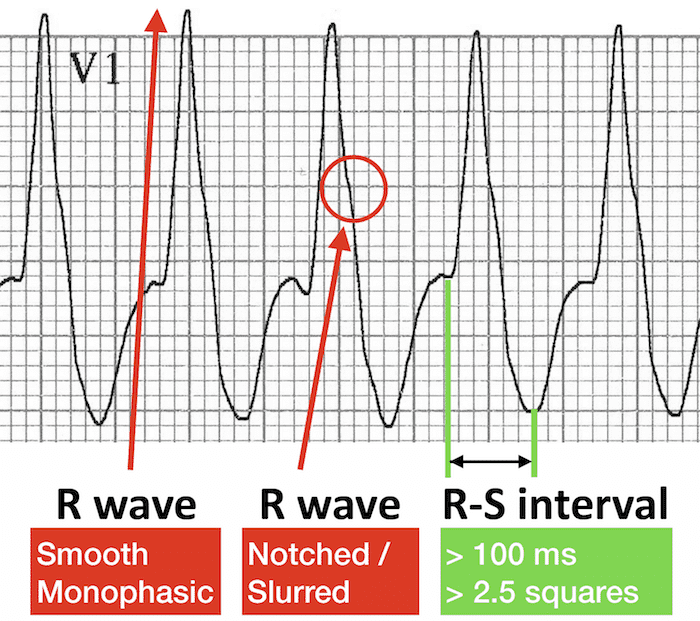
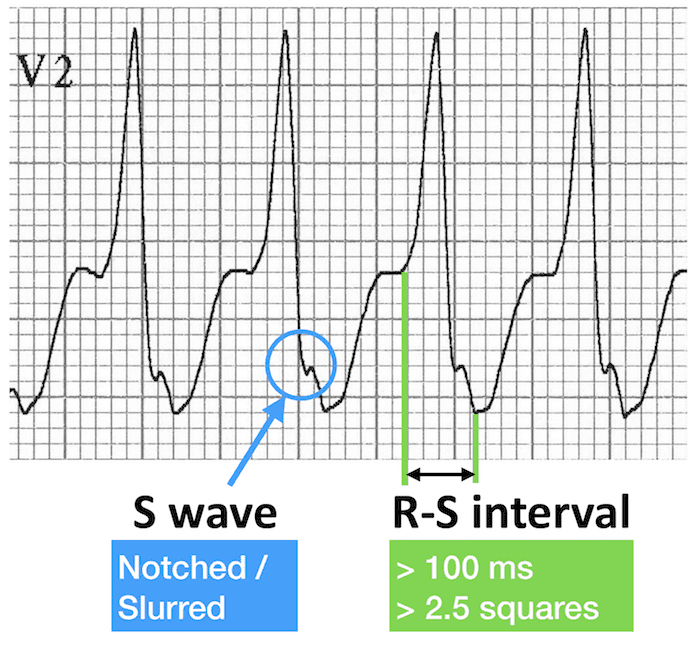
- Time from onset of the QRS complex to nadir of the S-wave > 100ms in any of the precordial leads (Brugada 1991)
- Notching/slurring of the downslope of the S wave in V1/V2 (Josephson’s sign 1988)
Northwest Axis
Dominant R Wave in V1 or V2 – RBBB Morphology
Note the presence of morphology criteria favouring VT over RBBB such as Tall monophasic R wave in V1; Dominant S wave in V6
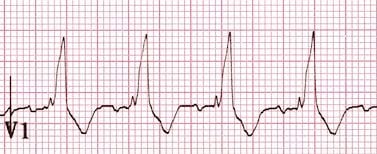
Lead V1 and V2 morphology
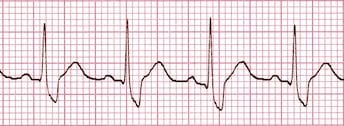
Lead V6 morphology
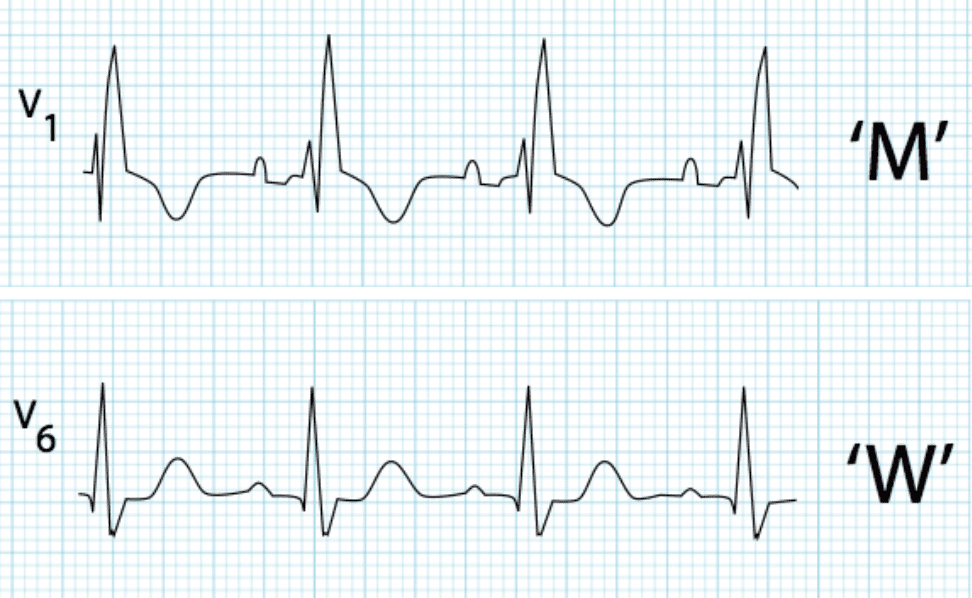
This pattern in V1 and V6 is very different from the expected morphology in RBBB. RSR’ pattern in V1 and Dominant R wave with wide slurred S wave in V6
CLINICAL PEARLS
Tips for Spotting VT when RBBB morphology present
[NB. RBBB morphology = QRS > 120ms with dominant R wave in V1]
Suspect VT in any patient with a regular broad complex tachycardia (especially if > 160 ms wide).
Look at aVR
- Positive QRS complex?
- Leads I and aVF negative?
- If yes to both -> northwest axis is present -> probable VT.
Look at V1
- Monophasic R wave; qR wave; or taller left rabbit ear? -> probable VT.
- RSR’ pattern with taller right rabbit ear? -> possible SVT with RBBB.
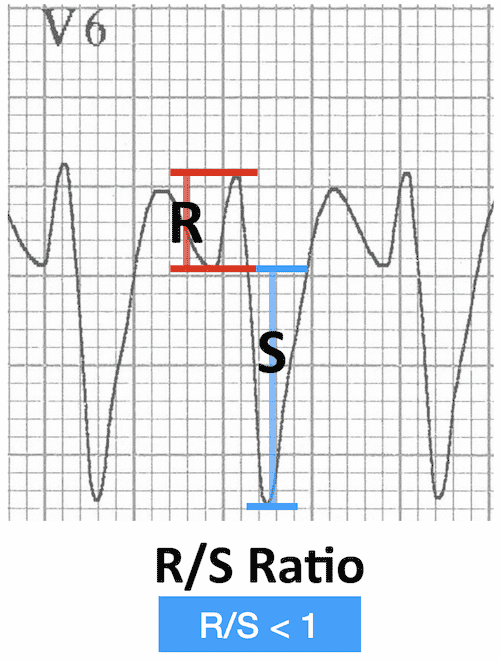
Look at V6
- Dominant S wave (R/S ratio < 1)? -> probable VT.
- Dominant R wave with wide slurred S wave -> possible SVT with RBBB.
If still uncertain…review the ECG for:
- AV dissociation — P waves randomly deforming the QRS complexes and T waves.
- Fusion and capture beats.
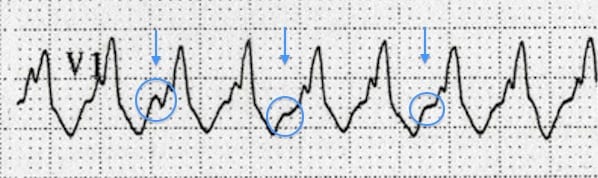
AV dissociation: superimposed P waves at a different rate to the QRS complexes
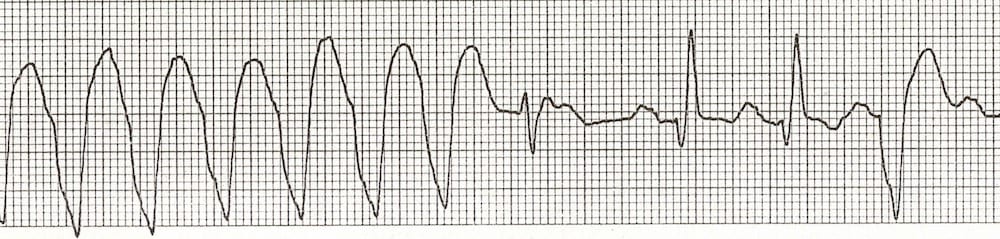
The first of the narrower complexes is a fusion beat, the next two are capture beats.
For more tips on spotting VT, read this article.
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
