ECG Case 045
64-year old female presenting with severe chest pain and diaphoresis. Describe the ECG
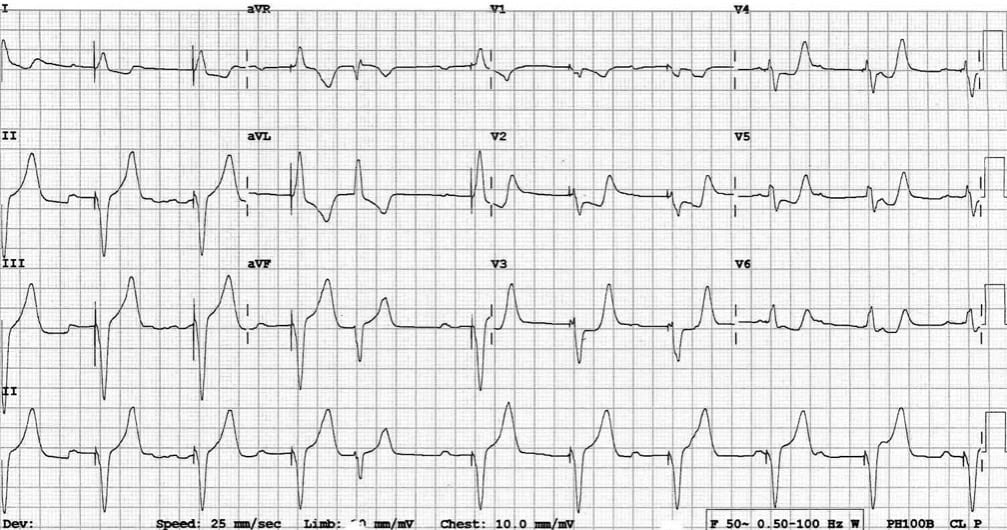
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
This ECG shows a ventricular paced rhythm with positive Sgarbossa criteria:
- There is concordant ST depression in V2-5. This violates the expected pattern of discordance for a V-paced rhythm and is a marker of superimposed myocardial infarction.
- The morphology in V2-5 is reminiscent of posterior STEMI, with horizontal ST depression and prominent upright T waves.
- Multiple non-conducted P waves are seen, indicating the presence of underlying high-grade AV block (probably the indication for pacemaker insertion). However, the fusion complex (beat #5 on rhythm strip) suggests that P waves are occasionally transmitted, arguing against complete heart block.
This patient did indeed have an isolated posterior infarction, due to complete occlusion of a posterolateral branch of the RCA. She was successfully treated with PCI.
CLINICAL PEARLS
Sgarbossa Criteria
These criteria allow for detection of myocardial infarction in patients with LBBB and V-paced rhythms (previously thought to be “impossible”).
Normal Pattern in LBBB / VPR
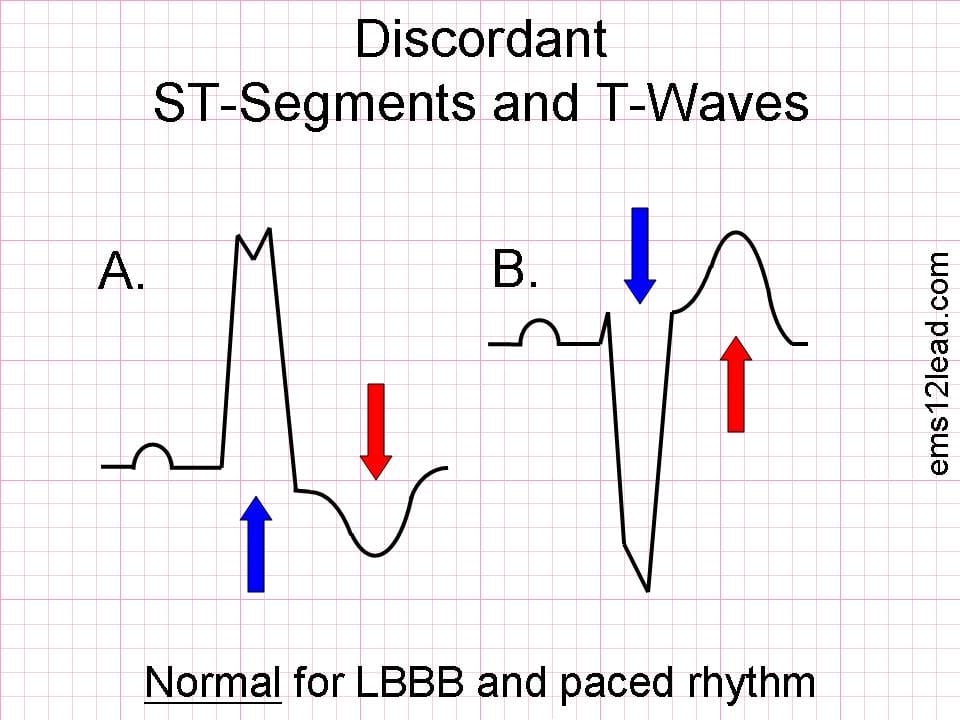
The expected finding in patients with uncomplicated LBBB / V-paced rhythm is discordance — i.e. the ST segments and T waves point in the opposite direction to the QRS complex.
How To Spot Superimposed MI
Superimposed myocardial infarction is suspected if there is either:
- Loss of the usual pattern of discordance — i.e. concordant ST changes.
- Excessive discordant ST elevation — i.e. out of proportion to what would be expected for LBBB / paced rhythm.

Diagnosis of MI in LBBB / VPR requires at least one of the following criteria to be present:
- Concordant ST depression > 1 mm in V1-3.
- Concordant ST elevation > 1 mm in any lead.
- Excessively discordant ST elevation in any lead >5 mm (original Sgarbossa criteria) or >25% of the corresponding S-wave depth (modified Sgarbossa criteria = more specific).
Changes only have to be present in a single lead to be diagnostic of MI.
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |

thanks a lot for this nice ECG with great explanation but i will argue with that, the ectopic beat wasn’t a fusion beat, instead it’s premature ventricular contraction. The evidence of that are QRS occurred prematurely and the PPM is programmed to pace every 5 seconds. there is also no spike preceding the QRS. so its PVC and the heart block is complete