ECG Case 116
These ECGs were taken from a 40 yr old male who presented with a 60 minute history of central chest pain.
On arrival to the Emergency Department he was pain free (ECG 1). Four minutes later he developed further intense chest pain and a repeat ECG was performed (ECG 2).
Describe and interpret ECG 1
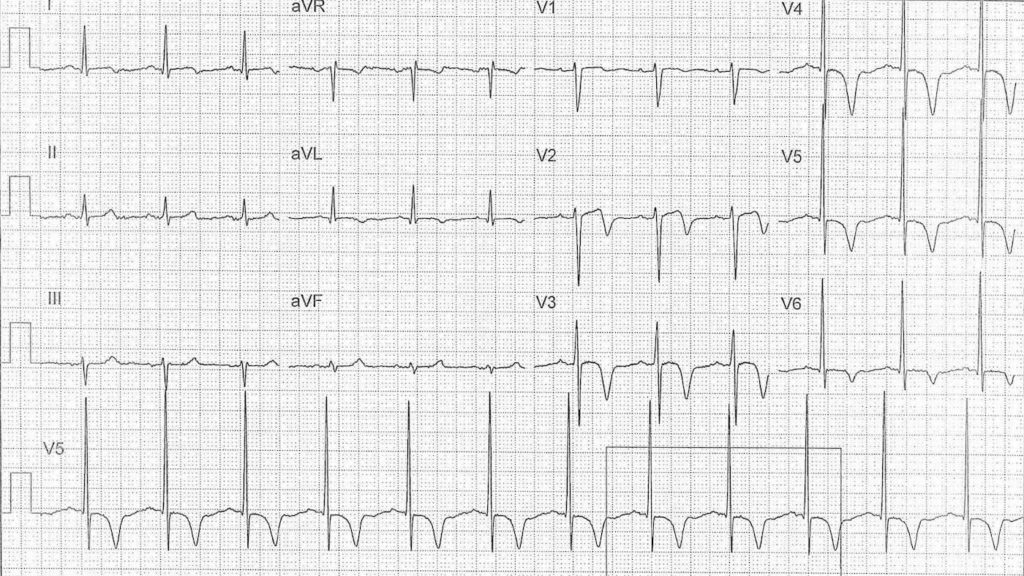
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Rate:
- 72 bpm
Rhythm:
- Regular
- Sinus rhythm
Axis:
- Normal
Intervals:
- PR – Normal (160ms)
- QRS – Normal (100ms)
- QT – 400ms (QTc Bazett 440 ms)
Segments:
- ST elevation lead V1 (<1mm)
Additional:
- Biphasic T wave lead V2
- T wave inversion leads I, aVL, aVR, V1, V3-6
- Deep inversion leads V3-5
- Voltage criteria for LVH
Interpretation:
The differentials of deep T wave inversion are relatively broad but in a patient with a history of chest pain, a pain free ECG and these ECG features the major concern is Wellens syndrome – signifying a critical LAD lesion.
The subsequent ECG, taken whilst having chest pain, highlights the need to recognize the Wellens pattern.
Describe and interpret ECG 2
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Rate:
- 84 bpm
Rhythm:
- Regular
- Sinus rhythm
Axis:
- Normal
Intervals:
- PR – Normal (160ms)
- QRS – Normal (100ms)
- QT – 360ms (QTc Bazett 430 ms)
Segments:
- ST Elevation leads I (<1mm); aVL (1 mm); V1 (1mm); V2 (6mm); V3 (7mm); V4 (7mm); V5 (4mm); V6 (1-2mm)
- ST Depression leads III, aVF
Additional:
- Note resolution of deep T wave inversion with hyperacute T waves on ST segments in leads V2-3
- Voltage changes as above
Interpretation:
- Antero-lateral STEMI
- Occlusion of critical lesion suspected from first ECG
FURTHER READING
- ECG Library – Anterior STEMI
- ECG Library – Lateral STEMI
- ECG Library – Wellens syndrome
TOP 150 ECG Series
Emergency Medicine Specialist MBChB FRCEM FACEM. Medical Education, Cardiology and Web Based Resources | @jjlarkin78 | LinkedIn |


Very well explained
So clearly explained. Hats off to the team. This is a blessing for professionals like us – THANK YOU SO MUCH