
John Barlow
John Brereton Barlow (1924-2008) was a South African cardiologist. Barlow described mitral valve prolapse (eponymously known as Barlow’s syndrome) in 1963

John Brereton Barlow (1924-2008) was a South African cardiologist. Barlow described mitral valve prolapse (eponymously known as Barlow’s syndrome) in 1963

Biography Medical Eponyms Hudson Mask Patented in 1958 by Charles H. Hudson (US Patent No. 2,843,121), the “Hudson mask” became the archetype of the disposable oxygen face mask Designed for low-flow oxygen therapy (5–10 L/min), delivering approximately 35–60% FiO₂. Constructed from…

A. F. Stanley Kent (1863–1958), cardiac physiologist; 'bundle of Kent', shaped early electrophysiology; pioneered industrial fatigue science

Charles Foix (1882–1927), French neurologist; defined brainstem vascular syndromes, Foix–Alajouanine syndrome, and helped shape modern cerebrovascular neurology.

Bamberger–Marie syndrome (hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy): clubbing, bone periostosis, and joint effusions—historically recognised as a paraneoplastic syndrome linked to lung disease.

Théophile Alajouanine (1890–1980), French neurologist and humanist; described Foix–Alajouanine syndrome, studied aphasia, epilepsy, and neurological creativity.

Georges Charles Guillain (1876-1961) was a French neurologist. Multiple neurology-related eponyms including Guillain-Barré syndrome

Woldemar Mobitz (1889-1951) was a Russian-German physician. Applied mathematical approach to arrhythmias 1924 Mobitz Type I and II AV Block

Ernst Adolf Gustav Gottfried von Strümpell (1853-1925) was a German neurologist. Strümpell signs, Strümpell-Lorrain disease, Marie-Strümpell disease and Westphal-Strümpell pseudosclerosis.
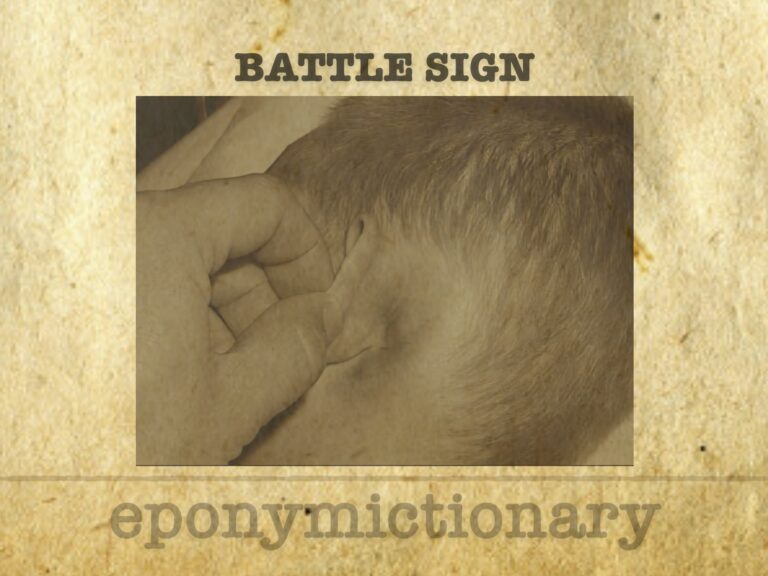
Battle sign: mastoid ecchymosis indicating basilar skull fracture, described by W.H. Battle in 1890; it holds >75% PPV for posterior fossa injury.

William Henry Battle (1855–1936) English surgeon. Battle incision, Battle operation and Battle sign postauricular (mastoid) ecchymosis

Carl Gerhardt (1833–1902), German internist and paediatric pioneer, described Gerhardt’s sign and advanced diagnostics, paediatrics, and laryngology