
Procedure: Postpartum haemorrhage
Emergency procedure, instructions and discussion: Postpartum haemorrhage (PPH). Take a few deep breaths and your own pulse, then dive into the video

Emergency procedure, instructions and discussion: Postpartum haemorrhage (PPH). Take a few deep breaths and your own pulse, then dive into the video

Harold Leeming Sheehan (1900-1988) was an English physician and pathologist. Eponymously remembered for his description of Sheehan Syndrome in 1937
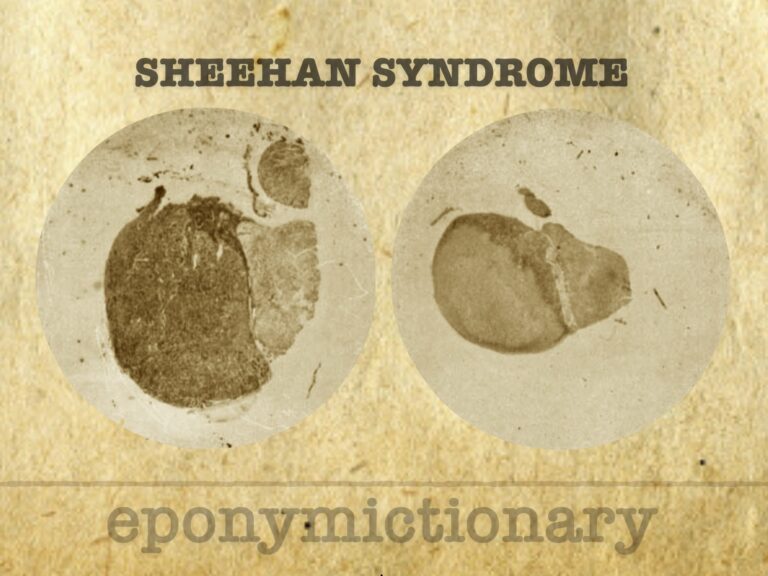
Postpartum hypopituitarism following ischaemic necrosis of the anterior pituitary gland. Pituitary necrosis occurs secondary to hypophyseal portal vessel thrombosis following significant postpartum haemorrhage, hypovolemia, and shock.

Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) is a permanent localised or diffuse dilatation of the abdominal aorta to 1.5 times its normal diameter that involving all three layers of the vessel wall

Critical Care Compendium pharmacology entry for prazosin.

Lemierre syndrome is infective thrombophlebitis of the internal jugular vein caused primarily by anaerobic organisms from a focus of oropharyngeal infection

Emergency Procedure: Today we tackle postpartum haemorrhage (PPH). Take a few deep breaths and your own pulse, then dive into the video

Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) Surveillance Chart. All incidentally found aortic aneurysms should be referred to a vascular surgeon if the patient is a potential candidate for surgery.

Acute Aortic Dissection (AAD) is uncommon but highly lethal, requiring prompt recognition and management. Due to its non-specific clinical presentation, a high index of suspicion is necessary, particularly in high-risk patients.

Adolphe Pinard (1844–1934) was a French obstetrician. Inventor of the Pinard horn (fetoscope) and Pinard Obstetric Palpation

The Aortic Dissection Detection Risk Score (ADD-RS) is a validated scoring system that helps stratify low to moderate risk patients who may have an aortic dissection.

Superficial venous thrombosis is rarely life-threatening. It carries a low risk of pulmonary embolism(1%), with concurrent DVT(~25%).