
Tuning Fork Tests (Weber and Rinne)
The Weber and Rinne tuning fork tests differentiate conductive from sensorineural hearing loss using the principles of bone and air conduction.

The Weber and Rinne tuning fork tests differentiate conductive from sensorineural hearing loss using the principles of bone and air conduction.

Holmes–Adie syndrome: a benign neurological condition marked by tonic pupils and areflexia, historically mistaken for neurosyphilis.

Cornelia Catharina de Lange (1871-1950) was a Dutch pediatrician. Described Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS) in 1933

Charles Gilbert Chaddock (1861-1936) was an American neurologist, psychiatrist, poet and medical translator. Chaddock sign and Chaddock wrist sign

Neurocysticercosis. Third edition in our Neuroimaging case study series with guest editors Drs. Michael Leonard and David Weinrib

Charles Foix (1882–1927), French neurologist; defined brainstem vascular syndromes, Foix–Alajouanine syndrome, and helped shape modern cerebrovascular neurology.

Georges Charles Guillain (1876-1961) was a French neurologist. Multiple neurology-related eponyms including Guillain-Barré syndrome

Ernst Adolf Gustav Gottfried von Strümpell (1853-1925) was a German neurologist. Strümpell signs, Strümpell-Lorrain disease, Marie-Strümpell disease and Westphal-Strümpell pseudosclerosis.

Adolphe-Marie Gubler (1821-1879) was a French physician and therapeutic pharmacologist. Millard-Gubler syndrome (1856)
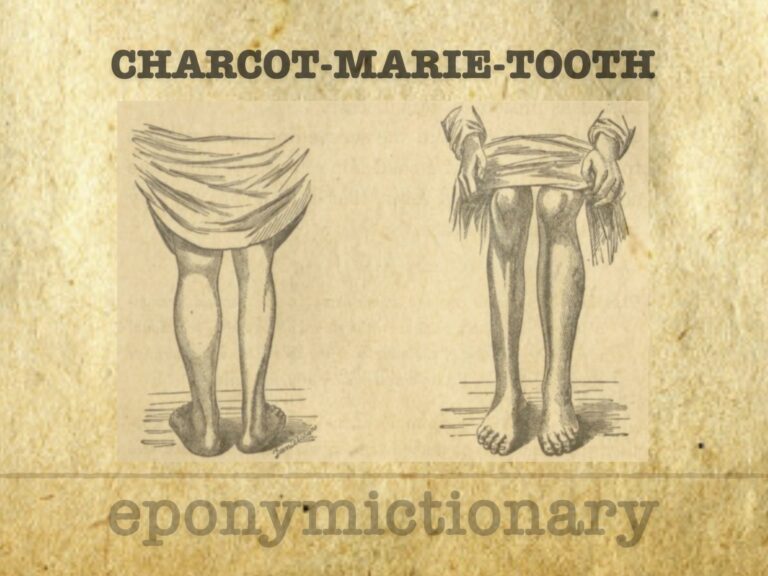
Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT) is the most common inherited neuropathy, encompassing genetically diverse subtypes of peripheral nerve dysfunction.

James Ramsay Hunt (1874-1937) American neurologist. Renowned for his contributions to the field of neurology. Several conditions bear his name including Ramsay Hunt syndrome (1907)
Robert Bentley Todd (1809-1860) was an Irish physician. Provided early depictions of migraine, peripheral neuritis, and postepileptic paralysis (Todd's palsy). He also gave an important discourse on locomotor ataxy (tabes dorsalis).