Sinus tachycardia
Definition
Sinus rhythm with resting heart rate (HR) > 100 bpm in adults, or above the normal range for age in children
Normal heart rates in children
- Newborn: 110 – 150 bpm
- 2 years: 85 – 125 bpm
- 4 years: 75 – 115 bpm
- 6 years+: 60 – 100 bpm
Causes
Sinus tachycardia is usually a secondary condition. Inappropriate sinus tachycardia is a primary condition diagnosed in patients with symptomatic persisting sinus tachycardia in which the below causes have been excluded.
Non-pharmacological
- Exercise
- Pain
- Anxiety
- Hypovolaemia
- Hypoxia, hypercarbia
- Acidaemia
- Sepsis, pyrexia
- Anaemia
- Pulmonary embolism
- Cardiac tamponade
- Hyperthyroidism
- Alcohol withdrawal
Pharmacological
- Beta-agonists: adrenaline, isoprenaline, salbutamol, dobutamine
- Sympathomimetics: amphetamines, cocaine, methylphenidate
- Antimuscarinics: antihistamines, TCAs, carbamazepine, atropine
- Others: caffeine, theophylline, marijuana
Example ECG
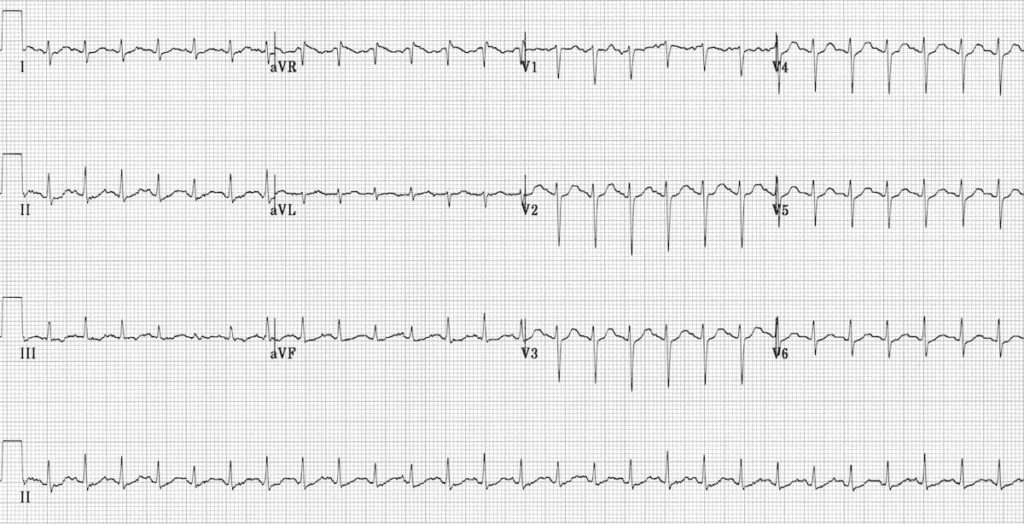
Sinus tachycardia:
- Heart rate 150 bpm.
- P waves are hidden within each preceding T wave.
Handy Tip
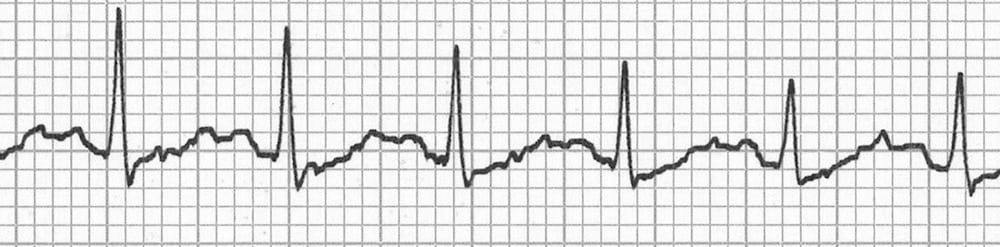
With very fast heart rates the P waves may be hidden in the preceding T wave, producing a ‘camel hump’ appearance.
Related Topics
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner

