Quetiapine Toxicity
Quetiapine Toxicity Overview
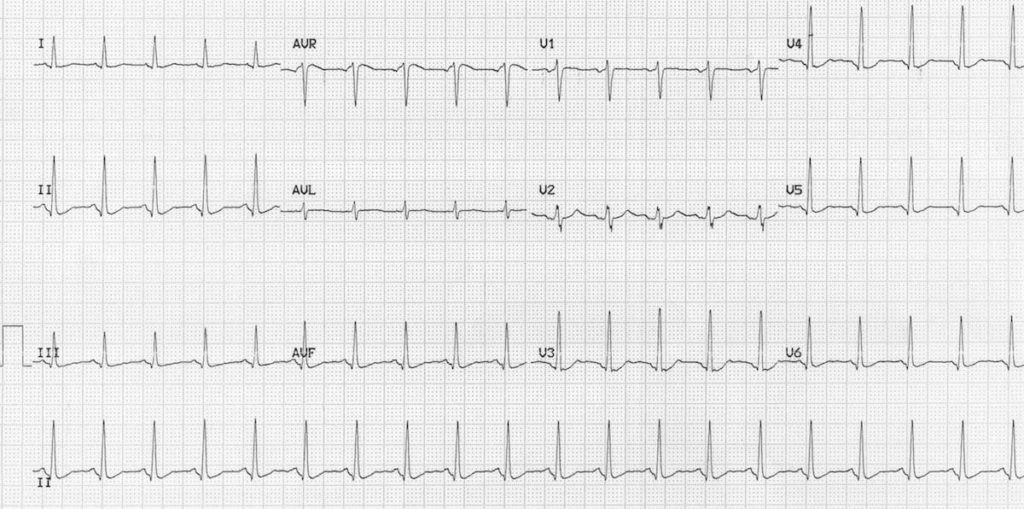
- Brisk sinus tachycardia (HR = 120 bpm)
- Prolonged QTc interval (QTc = 560ms; the absolute QT interval is more than half the R-R interval)
Clinical Features
- Quetiapine (a second-generation atypical antipsychotic) is a leading cause of toxic coma in Australia.
- Main toxic effects in overdose include coma, anticholinergic delirium, prolonged QTc and a brisk sinus tachycardia.
- Doses > 3g are associated with coma.
- Despite the prolonged QTc, Torsades de Pointes does not occur (see below).
- A similar pattern of clinical and ECG features is seen with other atypical antipsychotics, such as olanzapine or clozapine.
Drug-Induced QT-Prolongation And Torsades
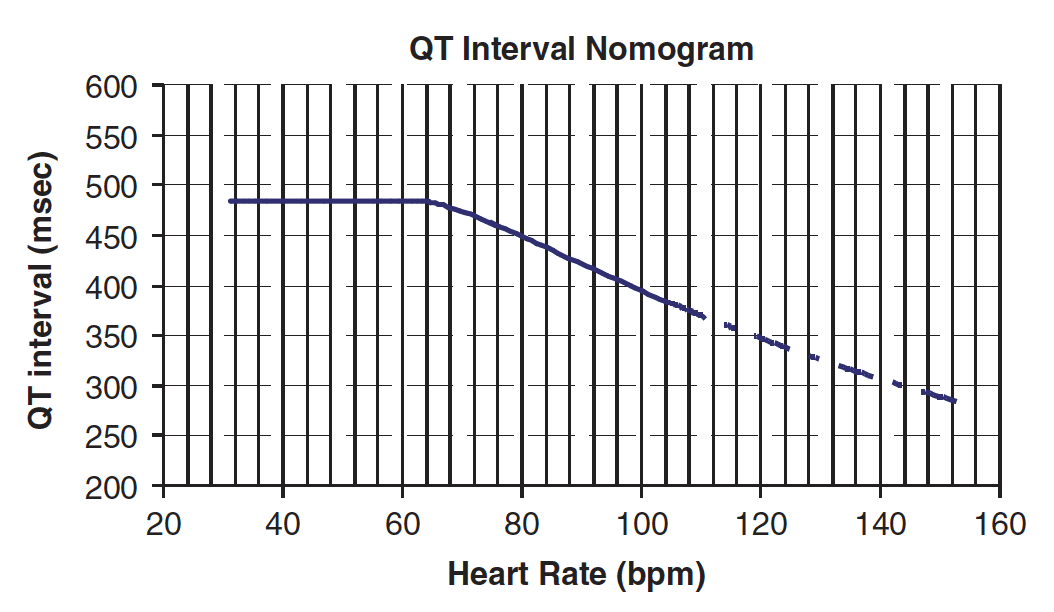
- In the context of acute poisoning with QT-prolonging agents, the risk of TdP is better described by the absolute rather than corrected QT.
- More precisely, the risk of TdP is determined by considering both the absolute QT interval and the simultaneous heart rate (i.e. on the same ECG tracing).
- These values are then plotted on the QT nomogram (below) to determine whether the patient is at risk of TdP.
- A QT interval-heart rate pair that plots above the line indicates that the patient is at risk of TdP.
- From the nomogram, you can see that QTc-prolonging drugs that are associated with a relative tachycardia (e.g. quetiapine) are much less likely to cause TdP than those that are associated with a relative bradycardia (e.g. amisulpride).
ECG Example
This ECG (taken following a 6g quetiapine overdose) with characteristic features of quetiapine toxicity
Related Topics
- Beta-blocker toxicity
- Calcium-channel blocker toxicity
- Carbamazepine cardiotoxicity
- Tricyclic overdose (sodium-channel blocker toxicity)
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |

Hi There. I don’t know if I understand this incorrectly but your statements about QT prolongation and HR, in drug induced qt prolongation, above doesn’t make sense. You said that if the HR is rapid and QT prolonged this plots below the nomogram curve and makes one less likely to have TdP. However if my HR is 40 and my Qt is 400 I’m still below the curve, but if my HR is 140 and my qt is 400 I’m above the curve and at then should be at higher risk of TdP. Thus, drugs that cause tachycardia should be associated with a higher risk of TdP? Please let me know if I’m missing something somewhere. Thanks.