ECG Case 044
Middle-aged patient presenting with syncope. Becomes hypotensive in ED (BP 80/50). Describe the ECG
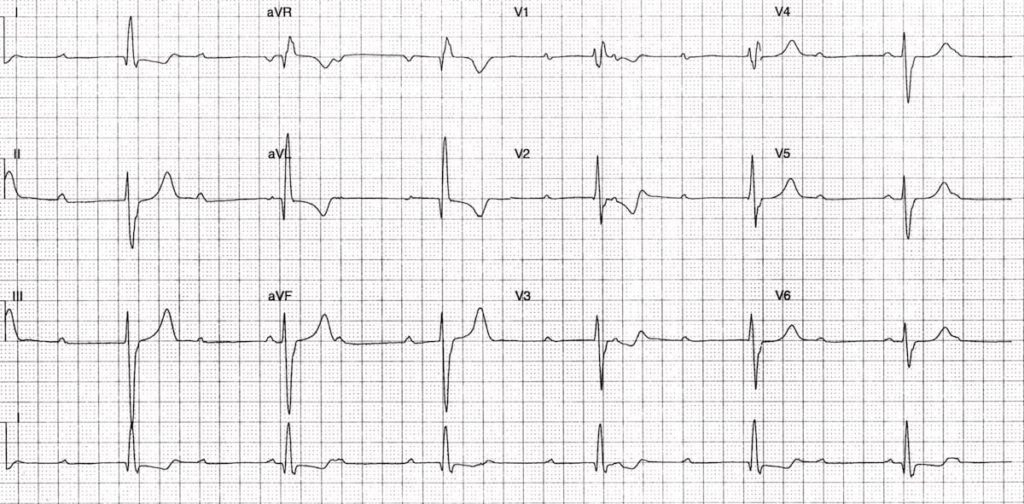
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
There is sinus rhythm with complete heart block:
- Normal P waves (upright in II, inverted in aVR) are present at a rate of ~ 85 bpm.
- There is no relationship between the P waves and QRS complexes — the PR intervals vary randomly.
- A ventricular escape rhythm is present at ~ 36 bpm.
The broad QRS complexes, RBBB morphology and left axis deviation (resembling trifascicular block) indicate a ventricular escape rhythm arising in the left posterior fascicle. Note how the QRS axis and morphology have changed significantly from ECG Quiz 043.
This patient had complete heart block due to cardiac sarcoidosis.
CLINICAL PEARLS
Sarcoidosis should always be considered as a differential diagnosis in younger patients presenting with complete heart block, particularly if other manifestations of sarcoidosis are present such as bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy or cutaneous lesions (erythema nodosum, lupus pernio).
One of the most common reversible causes of complete heart block is severe hyperkalaemia — always get an urgent K+ (e.g. run a VBG) on patients presenting with CHB. You look a bit silly inserting an unnecessary pacing wire when you could have corrected the problem with some calcium gluconate!
Causes of Complete Heart Block
- AV nodal blocking drugs (e.g.calcium-channel blockers, beta-blockers, digoxin)
- Severe hyperkalaemia.
- Inferior myocardial infarction — due to increased vagal tone.
- Anterior myocardial infarction — due to septal necrosis.
- Idiopathic fibrosis of the conducting system (Lenègre-Lev disease)
- Cardiac surgery (especially surgery occurring close to the septum, e.g. mitral valve repair)
- Infiltrative myocardial disease (amyloidosis, haemochromatosis, sarcoidosis).
- Inflammatory conditions (rheumatic fever, myocarditis, Lyme disease).
- Autoimmune (SLE, systemic sclerosis).
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |

Hi Dr Burns,
Thank you for your wonderful work.
Can this be a Mobitz 1 second degree block?
also we have features of HOCM
Voltage criteria in lead AVL>11mm
Met non voltage criteria RWPT>45ms
and St depression and t inversion in lead 1 and AVL with dagger q wave in lead 1 and AVL.
so the diagnosis HOCM complicated trifasicular and complete HB with ventricular escape rythm