ECG Rate Interpretation
Understanding paper speeds
- Paper output speed is the rate at which the ECG machine produces a trace
- Standard output is 25mm per second
- If a different paper speed is used, standard rate calculations will have to be modified appropriately (see other examples below)
The standard paper speed is 25mm/sec:
- 1 SMALL square (1mm) = 0.04 sec (40ms)
- 5 SMALL squares (5mm) = 1 LARGE square = 0.2 sec (200ms)
- 5 LARGE squares = 1 second
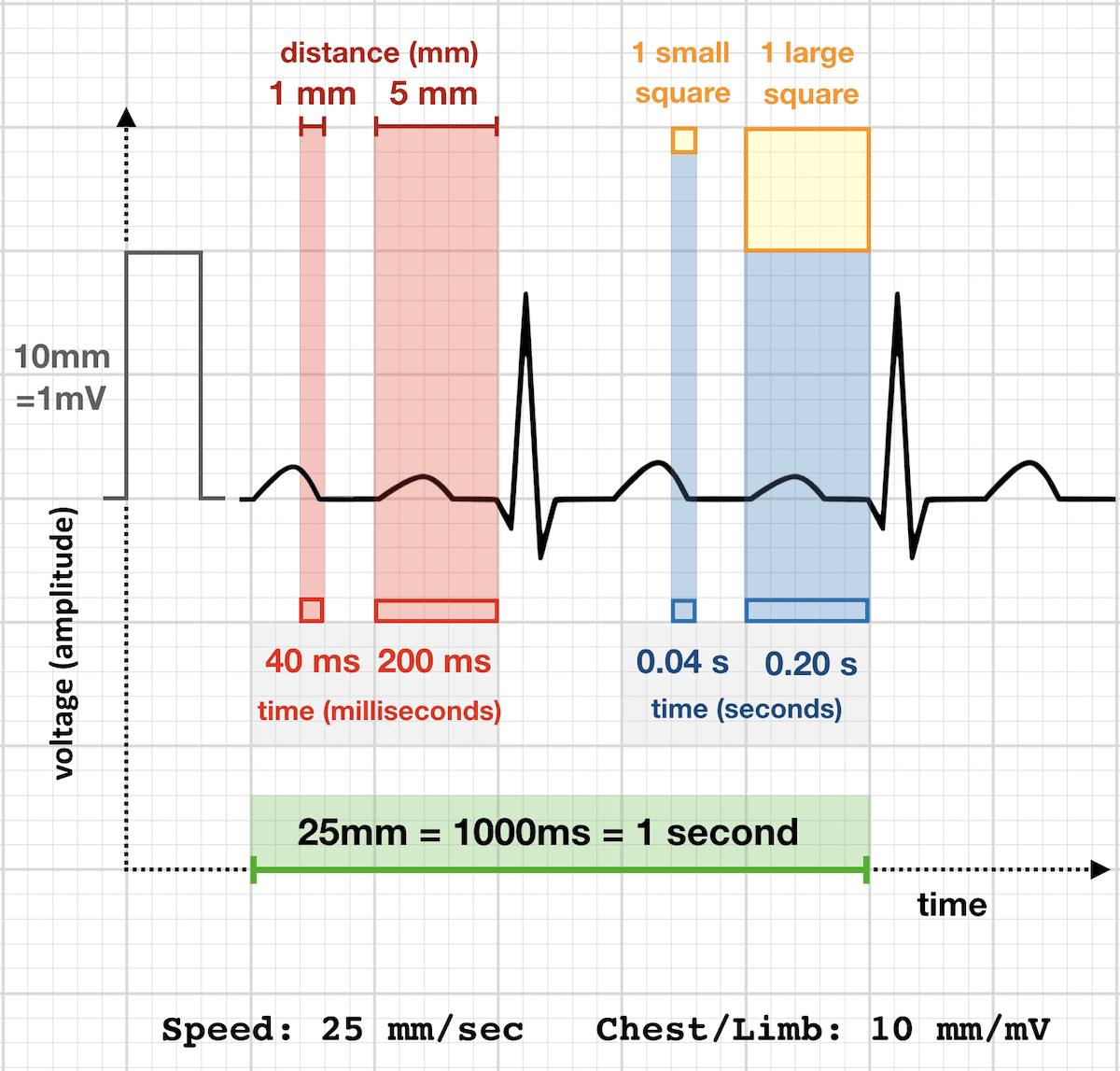
At standard paper speed of 25mm/sec, the rhythm strip comprises of:
- 250 SMALL squares = 50 LARGE squares = 10 seconds
Before calculating rate in beats per minute (bpm), we should understand that a rhythm strip recorded for 1 minute will therefore compromise:
- 1500 SMALL squares = 300 LARGE squares = 1 minute
Calculating rate
There are three main methods of calculating ECG rate. There is no specific best method, and preference varies between clinicians. However, certain methods may be better suited for rhythms such bradyarrhythmias or tachyarrhythmias.
1) Large square method
- Recall above that 300 large squares is equal to 1 minute at a paper speed of 25mm/sec
- We can thus calculate bpm by dividing 300 by the number of LARGE squares between each R-R interval (space between two consecutive R waves = one beat)
- For example, two large squares between each R-R interval implies a rate of 150 bpm, three implies a rate of 100 bpm and so forth:
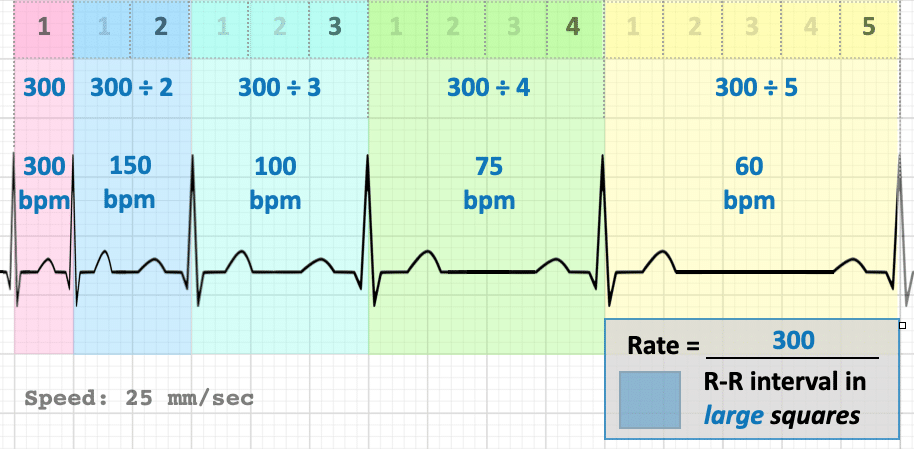
- Useful as quick calculation for regular rhythms at regular rate
2) Small square method
- Similar to above, except 1500 is divided by the number of SMALL squares between consecutive R waves
- For example, 10 small squares between R-R interval implies a rate of 150 bpm, 15 implies a rate of 100 bpm, and so forth:

- Useful for very fast regular rhythms, as likely to provide more accurate rate than large square method
3) R wave method
- Rate = Number of R waves (rhythm strip) X 6
- The number of complexes (count R waves) on the rhythm strip gives the average rate over a ten-second period. This is multiplied by 6 (10 seconds x 6 = 1 minute) to give the average beats per minute (bpm)
- Useful for slow and/or irregular rhythms

Note:
- Calculate atrial and ventricular rates separately if they are different (e.g. complete heart block)
- The machine reading can also be used and is usually correct — however, it may occasionally be inaccurate in the presence of abnormal QRS/T-wave morphology, e.g. may count peaked T waves as QRS complexes or miss QRS complexes with reduced amplitude.
Interpretation (adults)
- Normal: 50 – 100 bpm
- Tachycardia: > 100 bpm
- Bradycardia: < 50 bpm
Normal Heart Rates in Children
- Newborn: 110 – 150 bpm
- 2 years: 85 – 125 bpm
- 4 years: 75 – 115 bpm
- 6 years+: 60 – 100 bpm
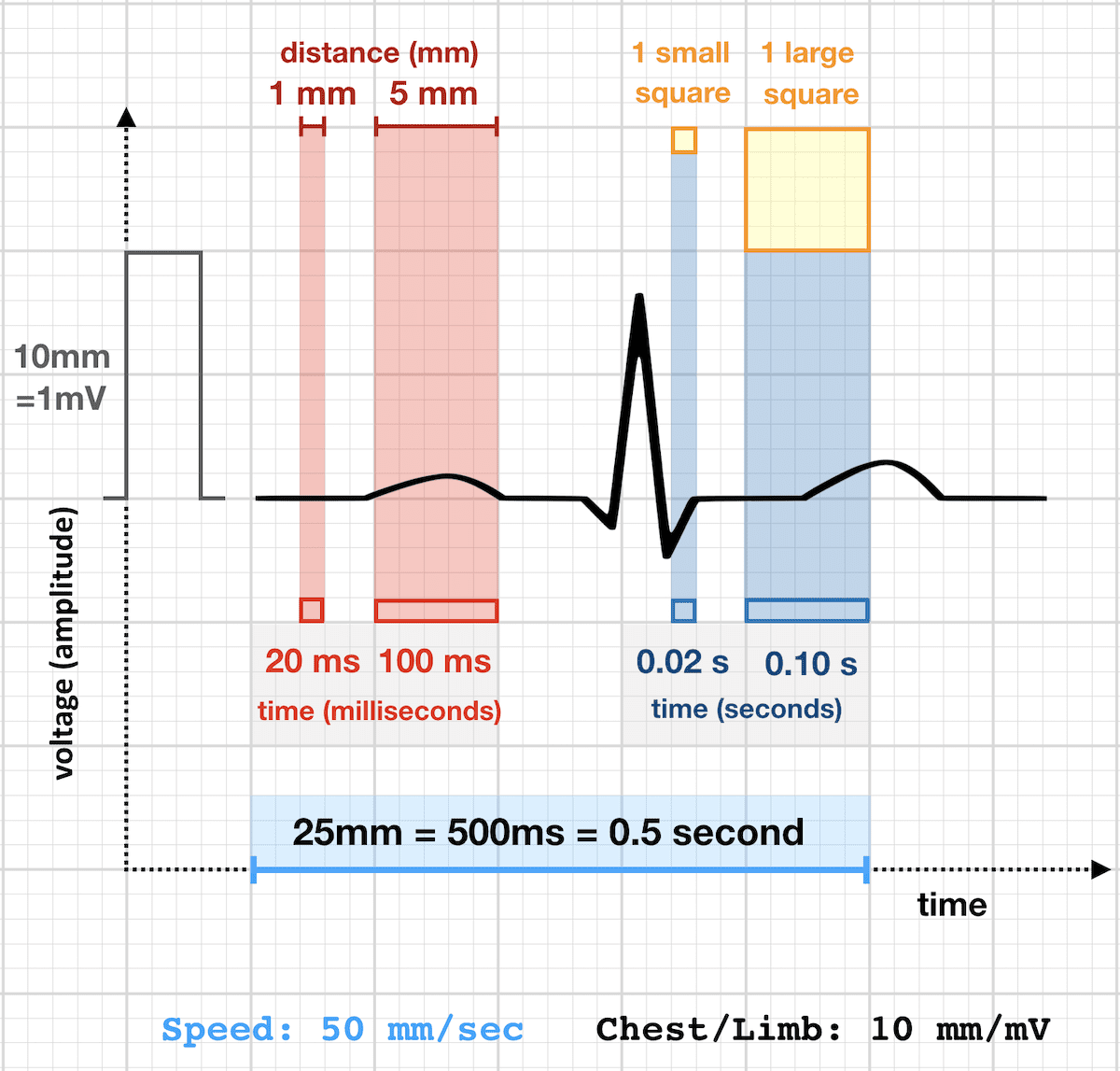
Other paper speeds: 50mm/sec
Doubling the standard rate will cause the ECG to appear drawn out or wider complex than 25mm/sec paper speeds
- 1mm (small square) = 0.02 sec (20ms)
- 5mm (large square) = 0.1 sec (100ms)
The rhythm strip will thus comprise 5 seconds total capture compared to the standard 10 seconds.
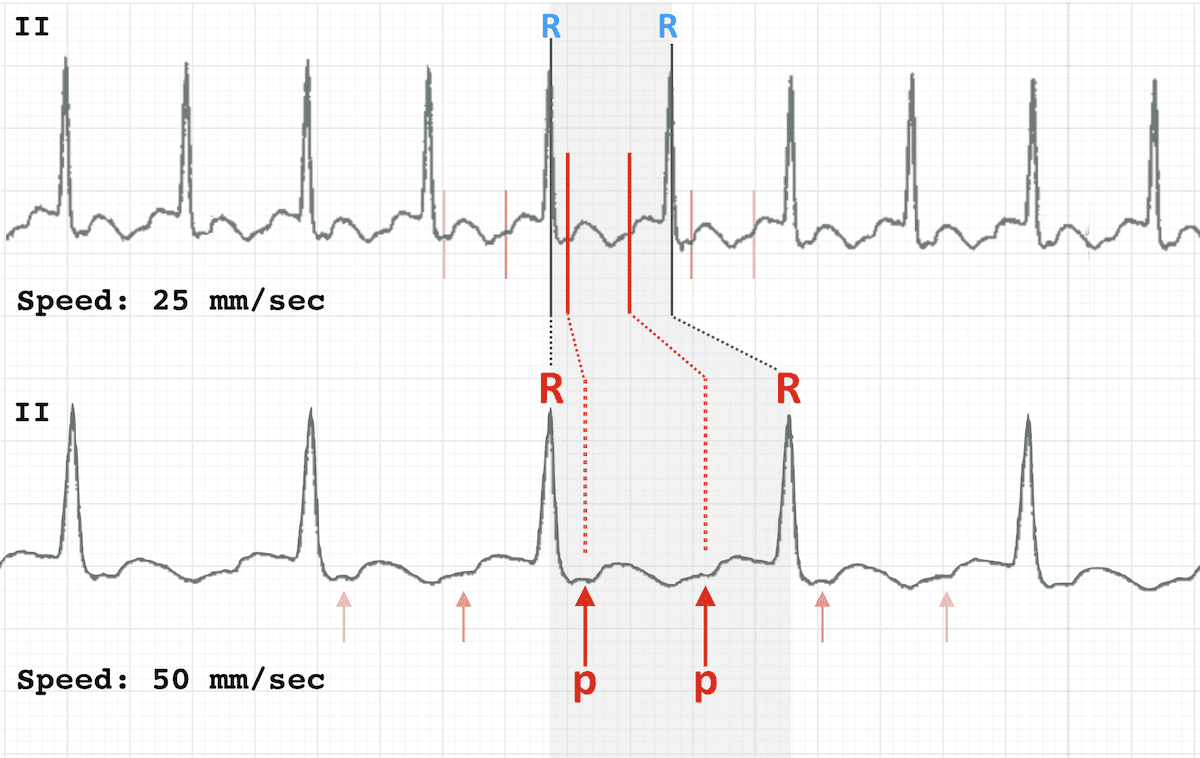
Why use 50 mm/second?
Doubling the standard rate can reveal subtle ECG findings hidden at the slower rates, in particular atrial flutter waves in a 2:1 block:
C. Paper speed: 10mm/sec
- 1mm (small square) = 0.1 sec (100ms)
- 5mm (large square) = 0.5 sec (500ms)
References
- Accardi A, Miller R, Holmes J. Enhanced diagnosis of narrow complex tachycardias with increased electrocardiograph speed. J Emerg Med. 2002;22(2):123-126
- Gaspar J, Body R. Best evidence topic report. Differential diagnosis of narrow complex tachycardias by increasing electrocardiograph speed. Emerg Med J. 2005;22(10):730-732.
- Lin M. Trick of the Trade: Speed up ECG paper rate to differentiate tachycardias
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner


It was very effective. Thank you Doctor. Best regards.
it is very informative and easily understandable.
thank you for the great service.
Amezing thankyou
Thank you for sharing your knowledge perfectly. This ECG Library is brilliant. That’s what I was looking for! I really enjoy the podcasts too, they are definitely useful. Yes, it is about Life. Congratulations for You and your Colleagues. I share this page with my colleagues and medical students. Greetings from Hungary 😉 Katalin
Ma il genere cosa si usa il 25mm o il 50mm?
This is great!!! I had a abnormal EKG on shift last night and I just was unsure what to make of it so naturally after we dropped the Pt off I spoke with the ER attending and he broke it down for me and then gave me this site to learn more and I LOVE THIS!! Seriously thank you for sharing and not making this cost!!
This is very informative and simple. I love it. Thank you so much 🙌