Guy Fontaine

Guy Hugues Fontaine (1936-2018) was a French cardiologist and electrophysiolgist.
Fontaine was a pioneer in cardiology who made seminal contributions to modern clinical electrophysiology. Internationally recognised for his work on arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD), he combined technical ingenuity with clinical insight, leaving an indelible mark on cardiac pacing, mapping, and ablation techniques.
Trained in both electrical engineering and medicine, Fontaine’s interdisciplinary background positioned him at the forefront of cardiac device innovation during the rapid technological expansion of the 1960s. He was the first physician in Paris to implant permanent pacemakers using intracardiac leads (1967), and his early research introduced concepts such as pacing threshold assessment and dynamic antitachycardia pacing.
Fontaine developed and refined the method of epicardial mapping in collaboration with surgeon Dr. Gérard Guiraudon, enabling precise localisation of arrhythmogenic foci during surgery. Their pioneering work led to the first successful surgical ablations of accessory pathways in Europe and provided foundational evidence for reentrant mechanisms underlying ventricular tachycardia.
In 1977, Fontaine first described a new clinical entity in patients with unexplained ventricular tachycardia and fatty replacement of the right ventricular myocardium: arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD). His work with Frank Marcus (b. 1928) helped define the disease’s clinical profile; identify and name the epsilon wave as a key diagnostic marker; and describe bipolar lead placements to best visualise the characteristic waves (Fontaine leads; F-ECG). He remained a global authority on ARVD for the remainder of his career, contributing to international registries, symposiums, and diagnostic criteria.
Biography
- Born on December 24, 1936 in Corbeil-Essonne, France
- 1940s – Lived in Orléans during World War II while his father was a prisoner of war.
- Early education – Attended Loyola primary school and Lycée Montesquieu in Bordeaux; completed secondary schooling in Paris.
- 1950s – Completed electrical engineering training.
- 1960s – Began medical studies in Paris; combined engineering and medical expertise in early pacemaker development.
- 1966 – Doctoral degree (MD) for thesis: Contribution à l’étude de la stimulation électrique du cœur de l’homme.
- 1967 – First physician in Paris to implant permanent pacemakers using intracardiac leads.
- 1968 – Joined cardiology department at Hôpital de la Salpêtrière under Professor Jean Facquet.
- 1971 – Developed epicardial mapping technique with Dr. Guiraudon; began surgical treatment for WPW syndrome.
- 1973 – Published first European case of surgical accessory pathway ablation.
- 1975 – Developed antitachycardia pacing technique using properly timed stimulation; began working on reentrant VT mechanisms.
- 1976 – Co-authored The Essentials in Cardiac Pacing with Professors Grosgogeat and Welti.
- 1977 – First described arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD).
- 1979 – Relocated to Hôpital Jean Rostand, continued electrophysiological work; collaborated with Frank Marcus (b. 1928) on ARVD.
- 1985 – Organized first international symposium in Paris on fulguration and lasers; conducted entirely in English.
- 1990 – Performed first bundle of Kent ablation in Shanghai; treated four patients in three days.
- 1991 – Awarded doctoral degree in sciences (PhD) from University of Orsay; thesis on biophysics of fulguration.
- 1993 – Elected corresponding member of the French Académie Nationale de Médecine.
- 1995 – Received Pierre Rijlandt Prize of Electrophysiology (with Dario di Francesco and Allan Scher).
- 1996 – President of the First International Symposium on Right Ventricular Dysplasia, Paris.
- 1999 – Initiated the French Registry of ARVD; collaborated on the European Registry.
- 2001 – Reported cardiomyoplasty as potential treatment for ARVD at ACC.
- 2005 – Honored with “Pioneer in Pacing and Electrophysiology” award by the Heart Rhythm Society.
- 2015 – Presented CO₂ brain cooling data at Great Wall Congress; recounted wife’s survival via home defibrillation and cooling.
- 2017 – Diagnosed with advanced amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
- Died on March 7, 2018 in Saint Mandé, France age 82
Medical Eponyms
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia and the epsilon wave
Fontaine coined the term arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD) as well as the epsilon wave – a small deflection (‘blip’ or ‘wiggle’) buried in the end of the QRS complex – the characteristic finding in ARVD.
The term “epsilon” was nice, because it occurs in the Greek alphabet after delta; thus, delta represents the pre-excitation and epsilon the post-excitation phenomenon. In addition, epsilon is also used in mathematics to express a very small phenomenon…
Fontaine 1997
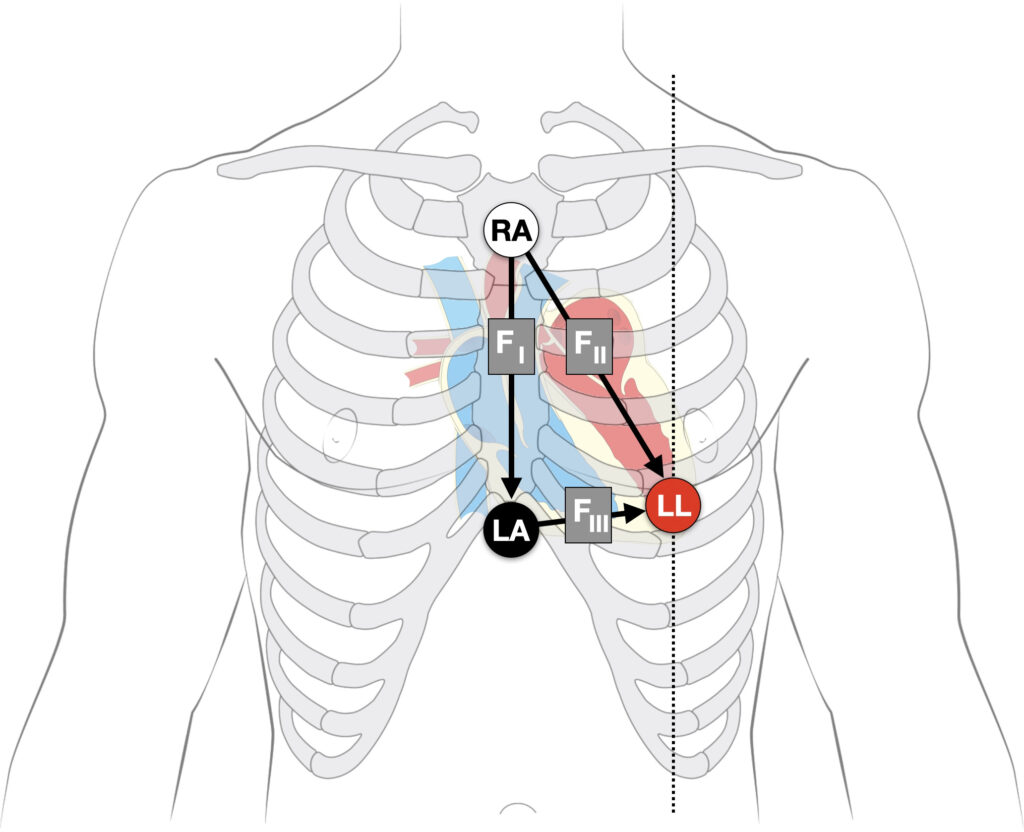
Fontaine leads
Fontaine bipolar precordial leads (F-ECG) are used to increase the sensitivity of epsilon wave detection. Fontaine leads are placed as shown:
- Right Arm (RA) electrode on the manubrium;
- Left Arm (LA) electrode over the xiphoid process;
- Left Leg (LL) electrode in the standard V4 position (5th ICS MCL).
- Creating F-ECG with FI, FII, FIII leads
Instead of regular leads I, II, and III there are now three bipolar chest leads that are termed FI, FII, and FIII which record the potentials developed in the right ventricle, from the infundibulum to the diaphragm.
The vertical bipolar lead FI, (similar to aVF) magnifies the atrial potentials and can be used to record epsilon waves; search for AV dissociation in ventricular tachycardia; and to study abnormal atrial rhythms when the P waves are too small on regular leads.
Instead of regular leads I, II, and III there are now three bipolar chest leads that are termed FI, FII, and FIII which record the potentials developed in the right ventricle, from the infundibulum to the diaphragm.
- Right Arm (RA) electrode on the manubrium;
- Left Arm (LA) electrode over the xiphoid process;
- Left Leg (LL) electrode in the standard V4 position (5th ICS MCL).
- Creating F-ECG with FI, FII, FIII leads
Note: Increasing calibration from 10 to 20mm/mV; and paper speed from 25 to 50mm/second can further amplify the atrial activity.
[Epsilon] waves are better demonstrated by placement of a suction electrode connected to the right arm connection (negative) on the manubrium sternum and the left arm connection (positive) on the xyphoid. This produces a first (FI) bipolar chest lead. In addition, the placement of the foot lead (positive) in position V4 provides three bipolar chest leads (FI, FII, FIII) instead of regular leads (I, II, III). This arrangement is used to record more specifically the potentials developed by the delayed right ventricular fibers, covering the infundibulum, the apex, and the diaphragmatic aspect of the right ventricle.
Fontaine 1999
Major Publications
- Fontaine G. Contribution à l’étude de la stimulation électrique du cœur de l’homme.
Thèse Médecine, N° d’ordre : 806: Paris, 1966 - Fontaine G, Grosgogeat Y, Welti J-J. The Essentials in Cardiac Pacing. 1978
- Fontaine G, Frank R, Guiraudon G, Pavie A, Tereau Y, Chomette G, Grosgogeat Y. Signification des troubles de conduction intraventriculaires observés dans la dysplasie ventriculaire droite arythmogène [Significance of intraventricular conduction disorders observed in arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia]. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 1984 Aug;77(8):872-9
- Fontaine G. Technique, physique, biophysique et électrophysiologie de la fulguration. application au traitement des troubles du rythme cardiaque. Thèse de doctorat: Sciences médicales. Paris 11, 1991
- Fontaine G. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. Curr Opin Cardiol. 1995 Jan;10(1):16-20.
- Fontaine G, Fontaltaliran F. About the histology of arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. Circulation. 1997 Sep 16;96(6):2089-90.
- Fontaine G, Fontaliran F, Frank R. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathies: clinical forms and main differential diagnoses. Circulation. 1998 Apr 28;97(16):1532-5
- Fontaine G, Fontaliran F, Hébert JL, Chemla D, Zenati O, Lecarpentier Y, Frank R. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. Annu Rev Med. 1999;50:17-35
- Fontaine GH. The multiple facets of right ventricular cardiomyopathies. Eur Heart J. 2011 May;32(9):1049-51
- Fontaine G, Chen HS. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia back in force. Am J Cardiol. 2014 May 15;113(10):1735-9.
References
Biography
- Marcus FI. Guy Fontaine: a pioneer in electrophysiology. Clin Cardiol. 1998 Feb;21(2):145-6.
- Frank R. Guy Fontaine MD PhD HDR. European Heart Journal. 2018; 39(24): 2226–2227
- Li G. Guy Fontaine, a personal tribute. European Heart Journal. 2018; 39(24): 2228–2229
- Bibliography. Fontaine, Guy. WorldCat Identities
Eponymous terms
- Hurst JW. Naming of the waves in the ECG, with a brief account of their genesis. Circulation. 1998 Nov 3;98(18):1937-42.
- Berry D. Guy Fontaine and arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. Eur Heart J. 2011 May;32(9):1042-3
- Pérez-Riera AR, Barbosa-Barros R, Daminello-Raimundo R, de Abreu LC, García-Niebla J, de Deus Morais MJ, Nikus K, Marcus FI. Epsilon wave: A review of historical aspects. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2019 Mar-Apr;19(2):63-67.
- The Standard 12 Lead ECG. ECG learning center
- Cadogan M. History of the Electrocardiogram. LITFL
- Cadogan M. ECG Lead positioning. LITFL
Eponym
the person behind the name
