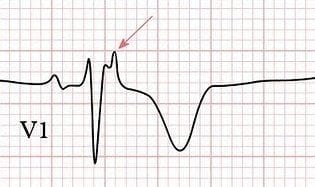
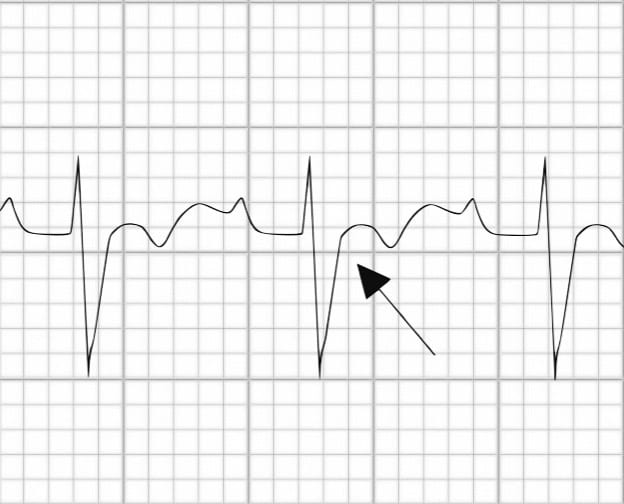
Epsilon Wave
Epsilon Wave Definition
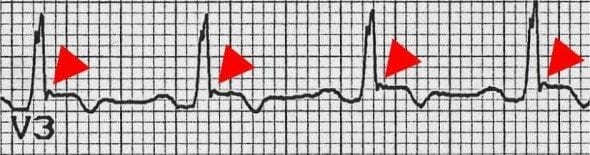
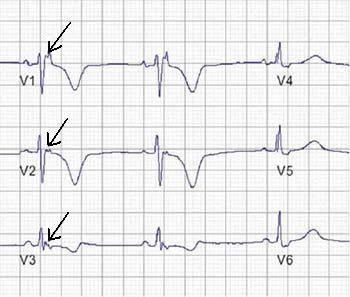
- Small deflection (“blip” or “wiggle”) buried in the end of the QRS complex
- On Standard 12-lead ECG (S-ECG), best seen in ST segment of V1 and V2, they are usually present in leads V1 through V4
- Caused by post-excitation of myocytes in the right ventricle
- Characteristic finding in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD)
Epsilon waves are the most specific and characteristic finding in arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD). In ARVD, myocytes are replaced by fat, producing islands of viable myocytes in a sea of fat. This causes a delay in excitation of some of the myocytes of the right ventricle, producing a small “blip” seen during the ST segment of the ECG.
Epsilon waves have also been described in patients with:
- Posterior myocardial infarction
- Right ventricular infarction
- Infiltrative disease
- Sarcoidosis
ECG Examples of Epsilon Waves
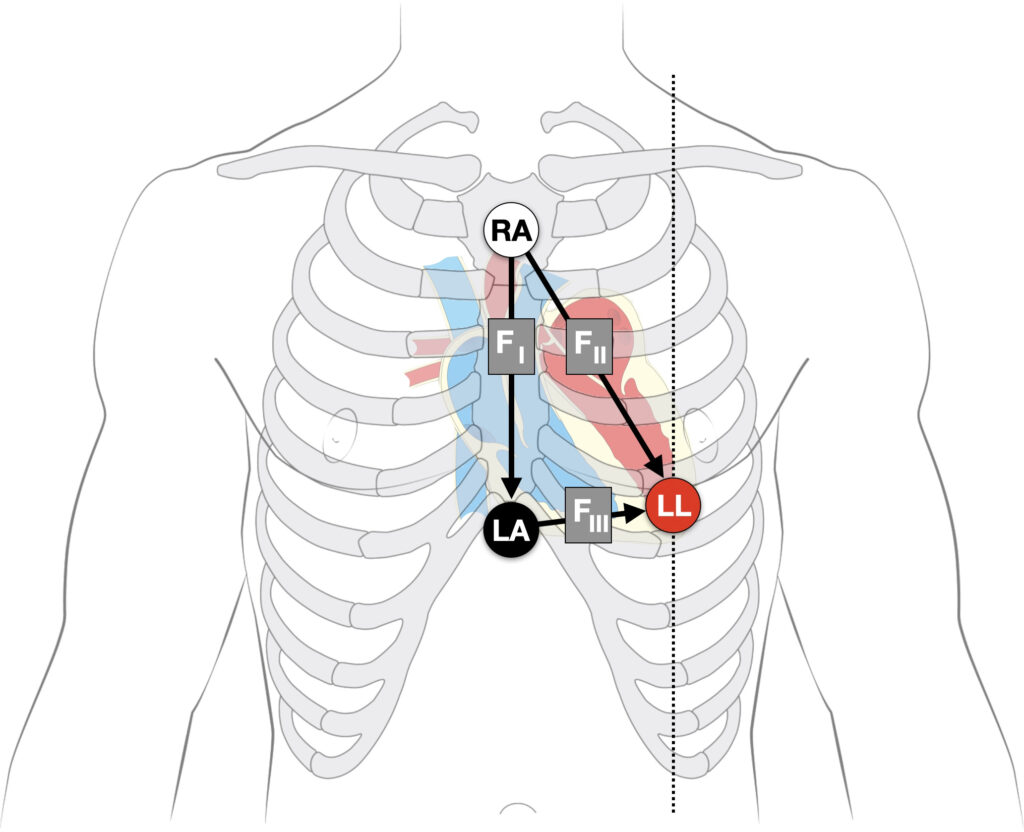
Fontaine lead
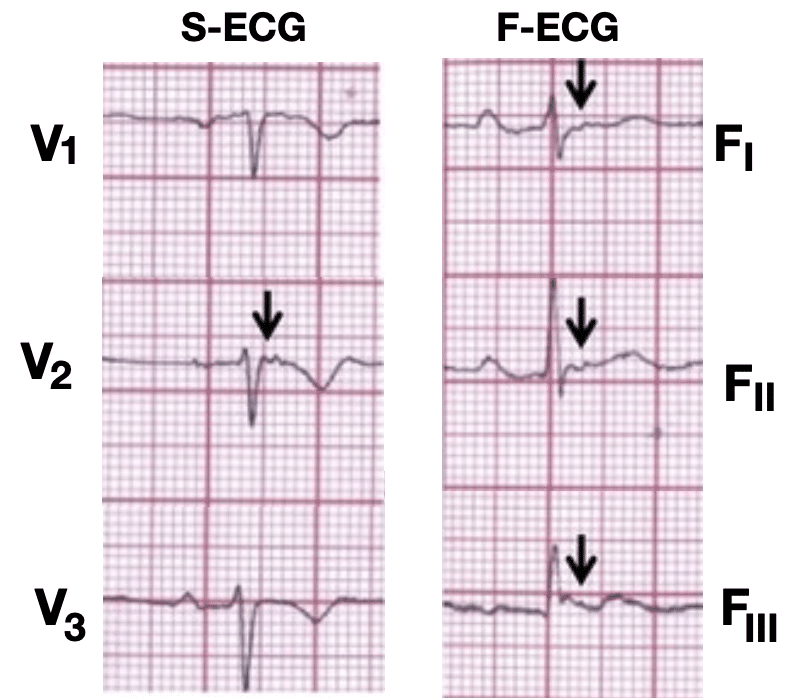
The Fontaine lead placement increases sensitivity of detecting epsilon waves so that they are detected in three leads (FI, FII, FIII) rather than one lead in the regular placement.
History of the Epsilon Wave
Guy Hugues Fontaine (1936-2018) was a French cardiologist and electrophysiologist. In 1977 he defined and named arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia ARVD; the epsilon wave; and the Fontaine lead placement to best amplify the waves on an ECG
The term “epsilon” was nice, because it occurs in the Greek alphabet after delta; thus, delta represents the pre-excitation and epsilon the post-excitation phenomenon. In addition, epsilon is also used in mathematics to express a very small phenomenon…
Fontaine 1997
Fontaine bipolar precordial leads (F-ECG) can be used to increase the sensitivity of epsilon wave detection. Leads are placed as shown:
- Right Arm (RA) over the manubrium;
- Left Arm (LA) over the xiphoid process;
- and Left Leg (LL) in the standard V4 position (5th ICS MCL).
Instead of regular leads I, II, and III there are now three bipolar chest leads that are termed FI, FII, and FIII which record the potentials developed in the right ventricle, from the infundibulum to the diaphragm.
The vertical bipolar lead FI, (similar to aVF) magnifies the atrial potentials and can be used to record:
- epsilon waves;
- search for AV dissociation in ventricular tachycardia;
- and to study abnormal atrial rhythms when the P waves are too small on regular leads.
Clinical studies
In 2010, Wang et al published their study on Epsilon waves detected by various electrocardiographic recording methods: in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. In particular they compared the three ECG methods of S-ECG, R-ECG and F-ECG in known ARVD/C patients.
They identified 3 patterns of epsilon waves:
- (A) wiggle waves
- (B) small spike waves [B1 – spike upward; B2 – spike downward]
- (C) smooth potential waves with the QRS duration in V1 exceeding the QRS duration in V3 by at least 25ms.

They found that
- The duration and amplitude of epsilon waves detected by F-ECG were longer and larger than those detected by the other 2 ECG recording methods.
- Epsilon waves are relatively low in sensitivity, manifesting themselves during S-ECG in only 20% to 25% of ARVC patients; and those waves are usually seen in leads V1 through V3.
- Epsilon waves were found in 38% of all patients using S-ECG and increased that to 50% by using F-ECG.
- The detection rate of epsilon waves using combined methods of ECG recording was significantly higher than that of S-ECG alone (S-ECG 38%; SF-ECG 56%; and SRF-ECG 66%, P=0.0039).
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia (ARVD)
The ECG changes in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia include:
- Epsilon wave (most specific finding, seen in 50% of patients)
- T wave inversions in V1-3 (85% of patients)
- Prolonged S-wave upstroke of 55ms in V1-3 (95% of patients)
- Localised QRS widening of 110ms in V1-3
- Paroxysmal episodes of ventricular tachycardia with a LBBB morphology (RVOT tachycardia)
ECG Examples
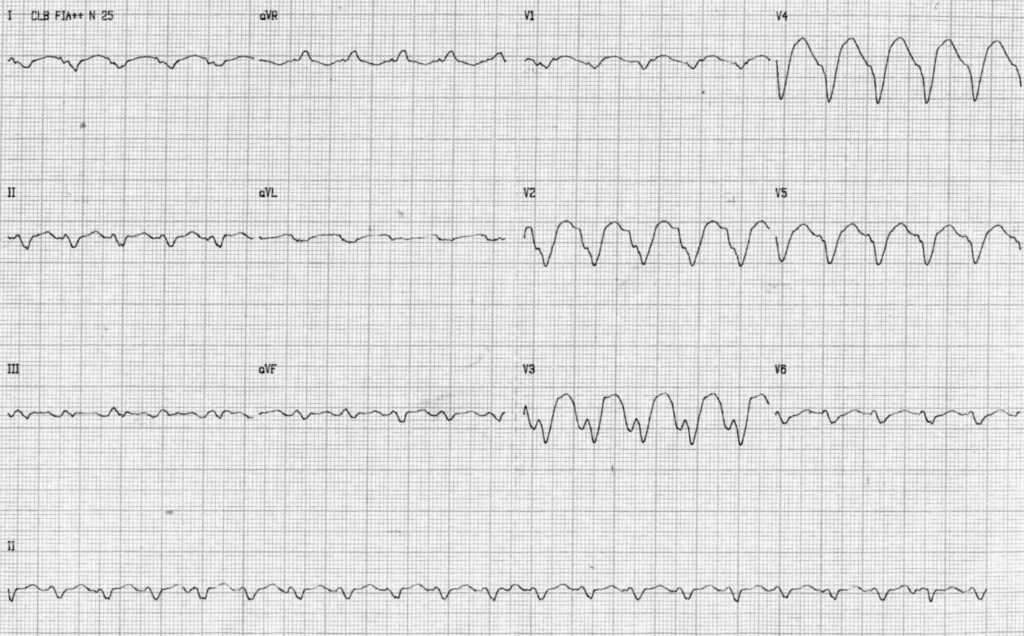
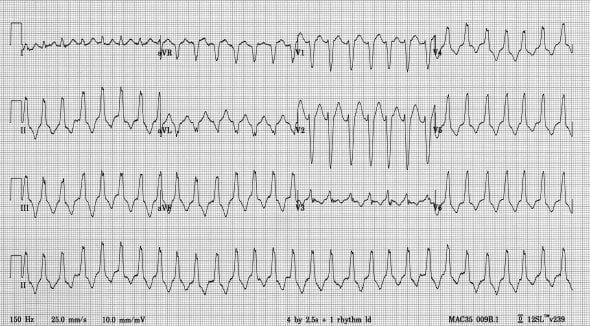
Example 1
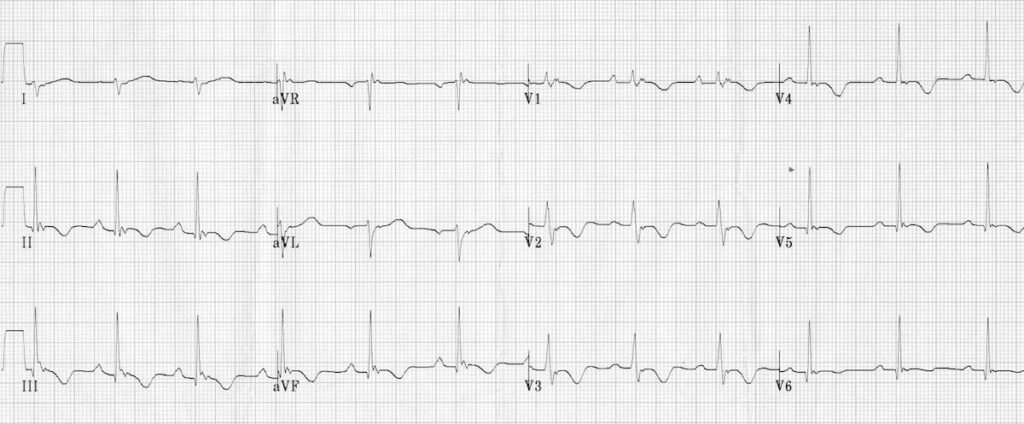
- 12-lead ECG is a typical example of ARVD.
Example 2
26 year old male presents to emergency with palpitations, dizziness and diaphoresis., No complaints of chest pain or shortness of breath.
ECG on arrival:
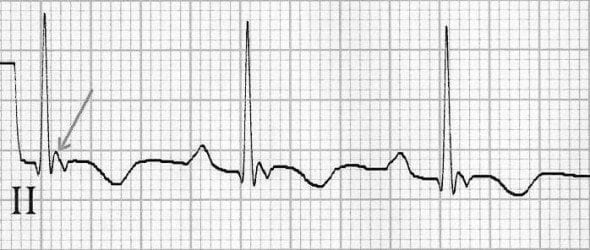
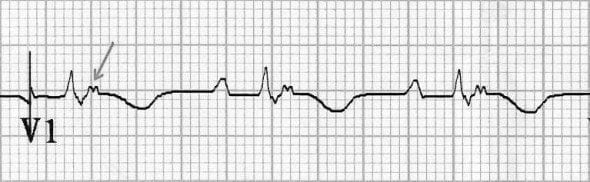
ECG diagnosis: sustained VT with LBBB pattern, heart rate = 125 bpm and right superior QRS axis (only aVR lead with positive QRS complexes). This atypical axis is a hallmark of VT with focus in apex of right ventricle.
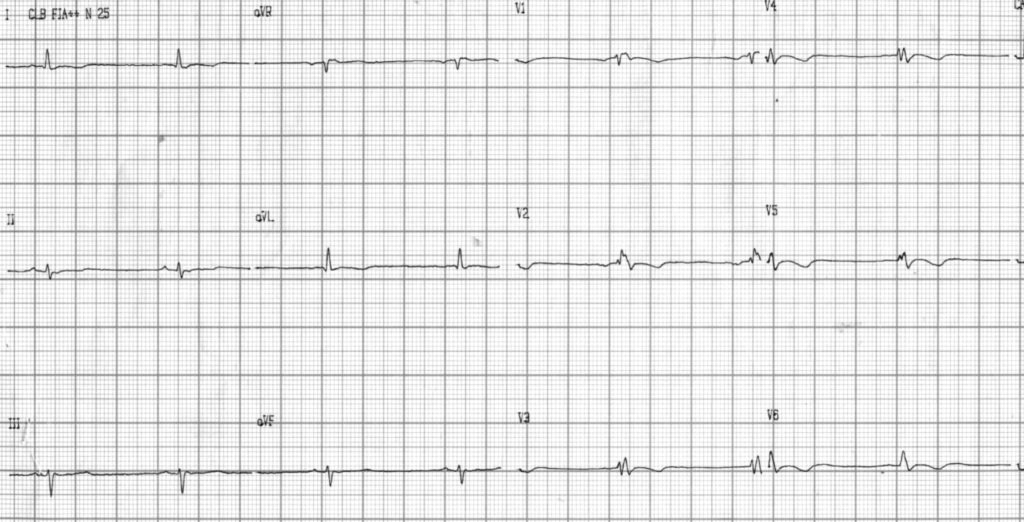
ECG Post cardioversion
Universal low voltage of QRS complexes. Epsilon wave V2 and lead II. T wave inversion in all precordial leads
F-ECG
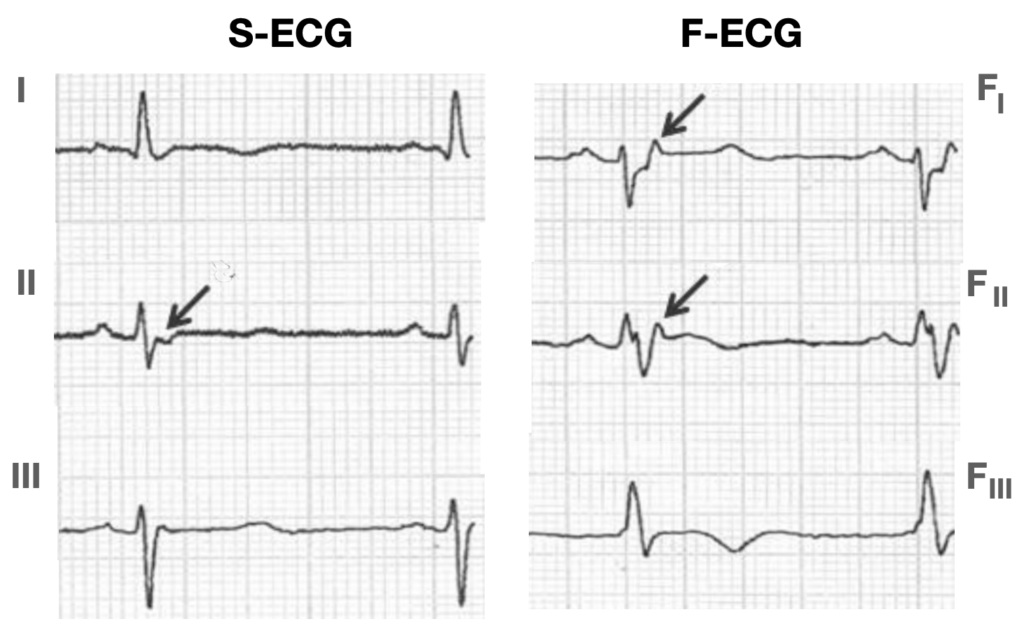
Pérez-Riera AR. 2019
Example 3
Related Topics
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
- Right ventricular outflow tract VT
- ECG Exigency 008 — Sudden Syncope on the Soccer Field
References
- Corrado D, Biffi A, Basso C, Pelliccia A, Thiene G. Twelve-lead ECG in the athlete: physiological versus pathological abnormalities. Br J Sports Med 2009; 43: 669-676. [PMID: 19734501]
- Perez Diez D, Brugada J. Diagnosis and Management of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia: An article from the E-Journal of the ESC Council for Cardiology Practice, European Society of Cardiology 2008.
- Fontaine G et al. Stimulation studies and epicardial mapping in ventricular tachycardia: study of mechanisms and selection for surgery. In: Kulbertus HE, ed. Re-entrant Arrhythmias: Mechanisms and Treatment. 1977: 334 –350.
- B. Gottschalk et al. The use of Fontaine leads in the diagnosis of arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol, 2014; 19(3): 279-284
ECG Library Basics
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
[cite]
ECG LIBRARY
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner


How do tell the difference between a Epsilon wave and a J (Osborne) wave on each?
Let us know what the difference is between Epsilon and J waves. Thank you!