Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
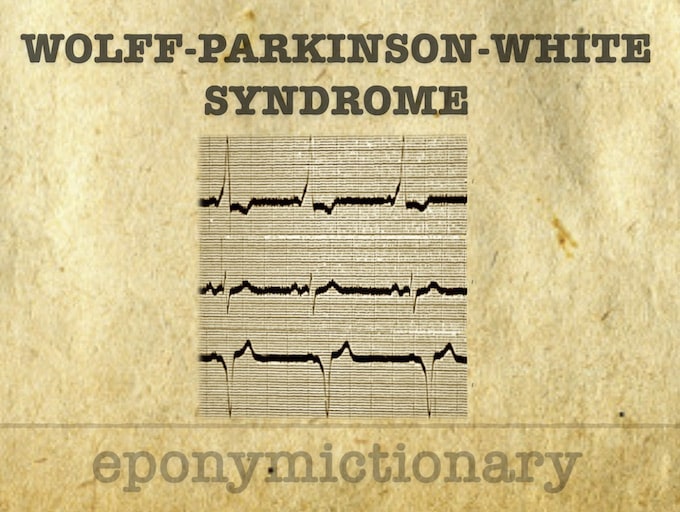
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmia.

Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmia.

A woman in her 60s with a broad complex tachycardia. There are two ECG features that suggest an accessory pathway, can you spot them?

In patients with AF and pre-excitation, the presence of an accessory pathway allows for rapid AV conduction, with a risk of degeneration into VT and VF

Tachyarrhythmia that occurs in patients with accessory pathways, due to formation of a re-entry circuit between the AV node and accessory pathway

Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmias

Funtabulously Frivolous Friday Five 326 - Just when you thought your brain could unwind the medical trivia FFFF

Paul Dudley White (1886-1973) was an American cardiologist. White with Louis Wolff and John Parkinson (WPW syndrome 1930); McGinn-White pattern (1935)

Sir John Parkinson (1885-1976) was an English cardiologist. In 1930, Parkinson along with Louis Wolff and Paul Dudley White, described WPW Syndrome

Louis Wolff (1898-1972) was an American cardiologist. Eponymously affiliated with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) described in 1930

35 yr old male who presented to the Emergency Department complaining of palpitations, dyspnoea, and lightheadedness. Describe and interpret this ECG. LITFL Top 100 ECG

33 year old male presents with shortness of breath and dizziness during an indoor soccer game. Describe and interpret this ECG. LITFL Top 100 ECG