Biatrial Enlargement
To best understand ECG features of biatrial enlargement, it is recommended that you first review ECG changes seen in left atrial enlargement and right atrial enlargement.
Biatrial Enlargement Definition
- Biatrial enlargement is diagnosed when criteria for both right and left atrial enlargement are present on the same ECG.
- The diagnosis of biatrial enlargement requires criteria for LAE and RAE to be met in either lead II, lead V1 or a combination of leads
ECG Criteria for Biatrial Enlargement
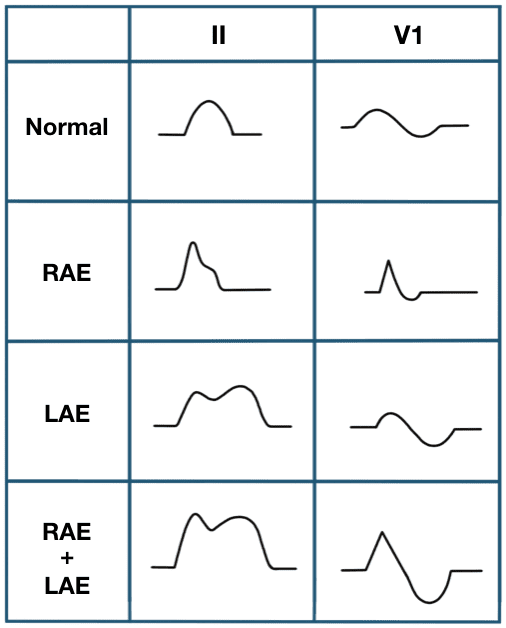
The spectrum of P-wave changes in leads II and V1 with right, left, and biatrial enlargement is summarised below:
In lead II
Bifid P wave with
- Amplitude ≥ 2.5mm AND
- Duration ≥ 120 ms
In V1/V2
Biphasic P waves with
- Initial positive deflection ≥ 1.5mm tall AND
- Terminal negative deflection ≥ 1mm deep AND
- Terminal negative deflection ≥ 40 ms duration
Combination criteria
- P wave positive deflection ≥ 1.5 mm in leads V1 or V2 AND
- Notched P waves with duration >120 ms in limb leads, V5 or V6
P wave changes with Biatrial Enlargement
Causes of Biatrial Enlargement
Combination of both left and right atrial enlargement.
- Pulmonary hypertension due to:
- Chronic lung disease (cor pulmonale)
- Tricuspid stenosis
- Congenital heart disease (pulmonary stenosis, Tetralogy of Fallot)
- Primary pulmonary hypertension
- Mitral valve disease
- Aortic valve disease
- Hypertension
- Aortic stenosis
- Mitral incompetence
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HOCM)
ECG Examples
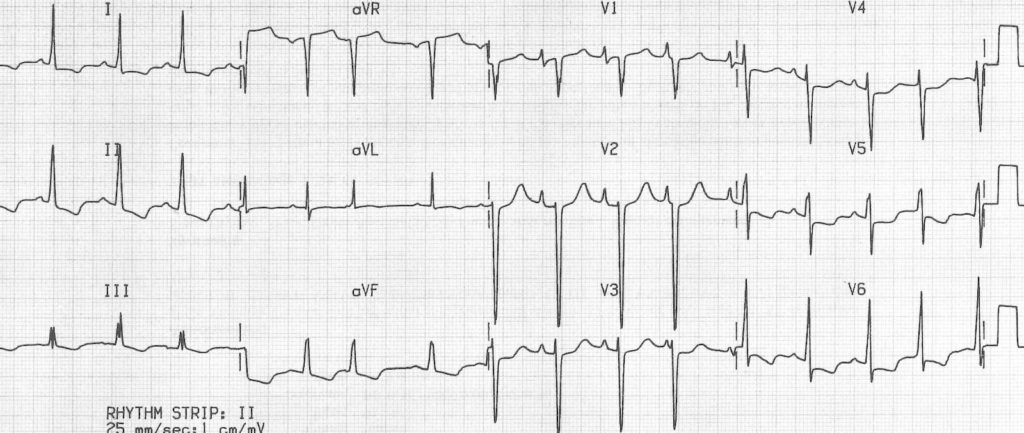
Example 1
Biatrial enlargement:
- Lead II: Bifid P wave with Amplitude ≥ 2.5mm AND Duration ≥ 120 ms
- P wave positive deflection ≥ 1.5 mm in lead V2
- Leads V5 and V6: Notched P waves with duration >120 ms in limb leads
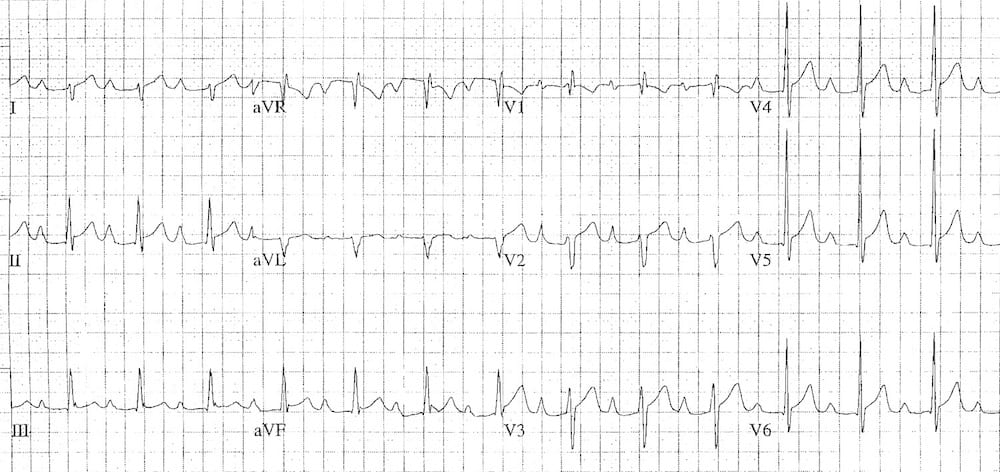
Example 2
Biatrial enlargement due to idiopathic cardiomyopathy:
- Biphasic P waves in V1 with a very tall positive deflection (almost 3 mm in height!) and a negative deflection that is both deep (> 1 mm) and wide (> 40 ms).
Example 3
Biatrial enlargement:
- P waves in lead II are tall (> 2.5mm) and wide (> 120 ms).
- P waves in V2 are tall (> 1.5 mm), while the terminal negative portion of V1 is deep (> 1mm) and wide (> 40 ms).
Related Topics
References
- Edhouse J, Thakur RK, Khalil JM. ABC of clinical electrocardiography. Conditions affecting the left side of the heart. BMJ. 2002 May 25;324(7348):1264-7
- Harrigan RA, Jones K. ABC of clinical electrocardiography. Conditions affecting the right side of the heart. BMJ. 2002 May 18;324(7347):1201-4.
- Chung DC, Nelson HM. ECG – A Pictorial Primer [internet].
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner



I need to thank you for the ECG Library. It’s helping me a lot! I’m from Brazil, still on my way through med school. And at every cardiology class, I feel stupid looking at the ECGs and listening to the teacher. He talks as if we students understand ECG, but we don’t. And now I get it. It’s a huuuge subject, and a difficult one to explain. So… Just wanted to say thanks, because these posts have been really helpful to me, and the links and references… amazing! Now I’m actually learning ECG!