
Ernst Brücke
Ernst von Brücke (1819–1892) described the eye’s red reflex, paving the way for Helmholtz’s ophthalmoscope and modern retinal examination

Ernst von Brücke (1819–1892) described the eye’s red reflex, paving the way for Helmholtz’s ophthalmoscope and modern retinal examination

Franciscus Donders (1818–1889), Dutch ophthalmologist and physiologist, pioneered refraction studies, eye movement laws, and mental chronometry

William Cumming (1822–1855), Moorfields surgeon who first observed the living eye’s luminous reflex, paving the way for Helmholtz’s ophthalmoscope.

Heinrich Küchler (1811–1873): German ophthalmologist who pioneered early eye charts, advanced corneal surgery, and reformed medical and military health services

Eduard Jaeger (1818–1884), Austrian ophthalmologist; introduced Jaeger Test-Types, advanced ophthalmoscopy, and first described diabetic retinopathy

Louise L. Sloan (1898–1982) developed Sloan optotypes (LogMAR), pioneering colour vision screening, perimetry, and low-vision rehabilitation
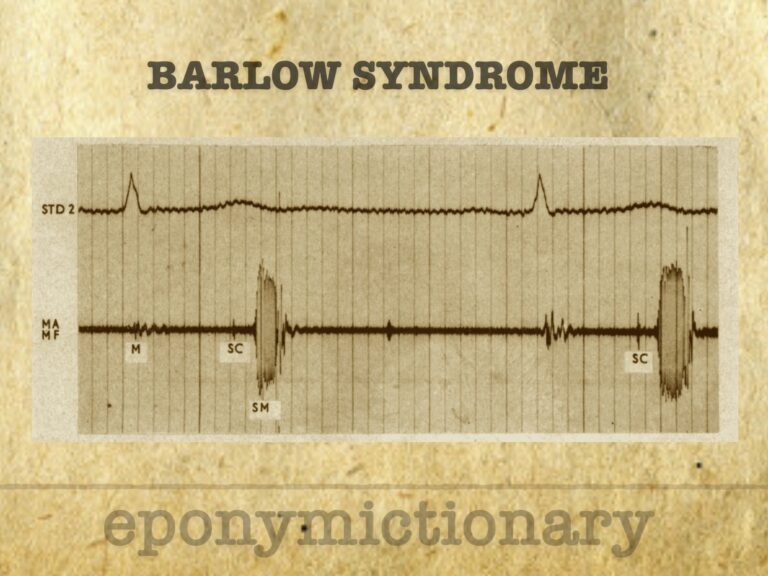
Barlow syndrome (primary billowing mitral leaflet syndrome (BMLS)). Auscultatory findings of late systolic murmur with non-ejection ('mid-late') systolic click

Leo George Rigler (1896-1979) was an American radiologist. Eponymously affiliated with Rigler sign; Rigler triad; Rigler notch sign; Hoffman-Rigler sign

John Brereton Barlow (1924-2008) was a South African cardiologist. Barlow described mitral valve prolapse (eponymously known as Barlow’s syndrome) in 1963

Herman Snellen (1834–1908): Dutch ophthalmologist who created the Snellen chart and standardized visual acuity testing, transforming eye care worldwide

Charles Henry Hudson (1903-1962) was an American dentist, inventor and medical entrepreneur. Inventor of the Hudson Mask

Joseph Jones (1833–1896), Confederate surgeon who defined hospital gangrene, advanced malaria research, and shaped Southern public health