
Morell Mackenzie
Sir Morell Mackenzie (1837–1892), pioneer of laryngology, founder of the Throat Hospital, author of the ‘laryngologist’s Bible’, and royal physician

Sir Morell Mackenzie (1837–1892), pioneer of laryngology, founder of the Throat Hospital, author of the ‘laryngologist’s Bible’, and royal physician
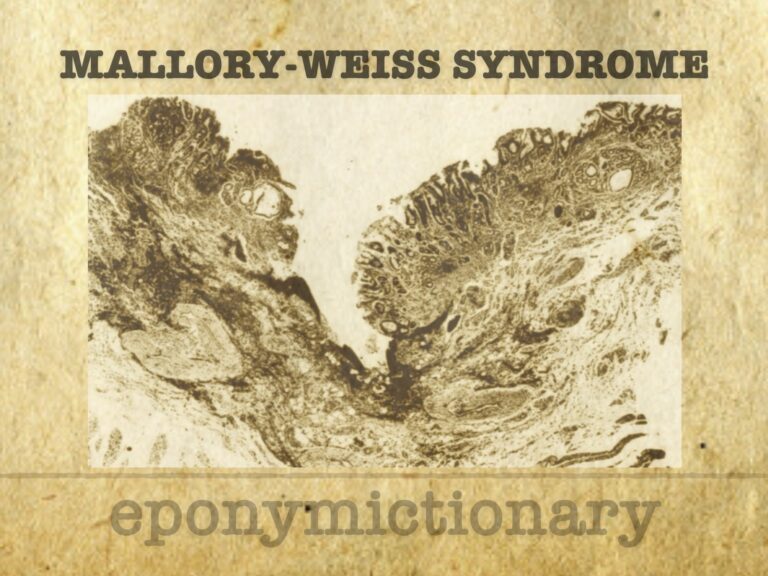
Mallory–Weiss syndrome: upper GI bleeding from gastroesophageal tears. History, key figures, first descriptions, diagnosis, and treatment.

Soma Weiss (1898-1942) was a Hungarian-born American physician. Mallory-Weiss Syndrome/lesion/tear and Charcot-Weiss-Baker Syndrome.

George Kenneth Mallory (1900–1986), American pathologist, co-described Mallory–Weiss syndrome and advanced cardiac, renal, and hepatic pathology

Illusion of Perfection. Medicine’s Most Dangerous Myth. Perfection is a lie. A neurological glitch wrapped in white coats and stitched into our stethoscopes.

Philip R. Allison (1907–1974), pioneering thoracic surgeon, defined reflux oesophagitis, advanced Barrett’s oesophagus, and led Oxford surgery
Norman Barrett (1903–1979), thoracic surgeon, pioneer of oesophageal surgery, first repair of Boerhaave’s syndrome, and namesake of Barrett’s oesophagus.

Emergency Procedure: closing lacerations. Three updated videos covering the Simple Suture, Advanced Skills and Stapling

The Weber and Rinne tuning fork tests differentiate conductive from sensorineural hearing loss using the principles of bone and air conduction.

Pioneer of the Allen test and anticoagulant therapy, Edgar V. Allen (1900–1961) advanced vascular medicine with key insights into dicumarol use and lipedema

Allen Test: a bedside exam assessing hand arterial flow via radial/ulnar patency; used before ABG, cannulation, or radial artery harvest.

Sir James Mackenzie (1853–1925), Scottish GP and pioneer cardiologist, invented the ink polygraph and defined arrhythmias, angina, and atrial fibrillation