
Echo basics: Mitral Stenosis
Echocardiography basics. Grading and quantifying mitral stenosis (MS) with planimetry, pulsed wave Doppler, PHT and Continuity Equation Method

Echocardiography basics. Grading and quantifying mitral stenosis (MS) with planimetry, pulsed wave Doppler, PHT and Continuity Equation Method

Mitral regurgitation (MR) is a common pathology detected during echocardiography. Accurate identification and grading rely heavily on colour and spectral Doppler imaging across multiple standard views.

Pioneer of clinical cardiac electrophysiology, Sir Thomas Lewis (1881–1945) advanced ECG use, defined effort syndrome, and discovered the Lewis Triple Response.
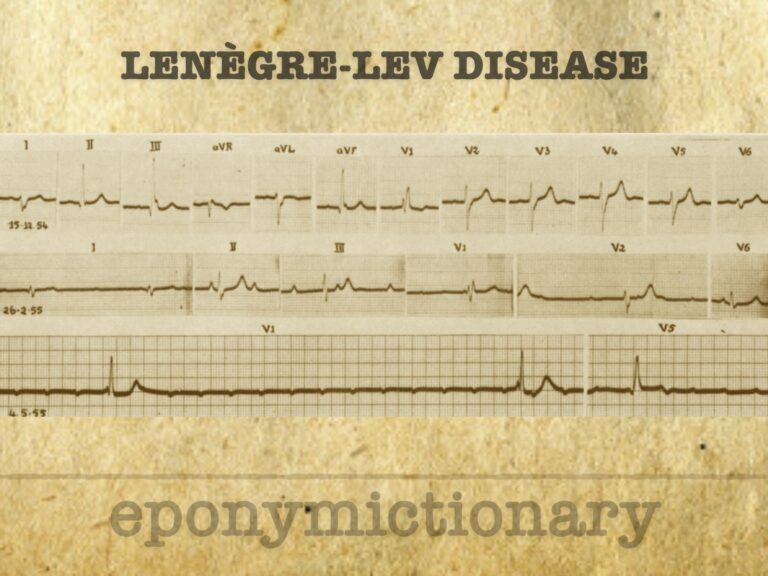
Acquired fibrous degeneration of the left and right bundle branches, eventually manifesting as permanent complete atrioventricular (AV) dissociation with cardiac pauses and Adams-Stokes attacks

The mitral valve is a dominant structure in most standard echocardiographic views. Understanding its anatomy in each window is essential for accurate assessment.

John Hay (1873-1959) English physician first to record second degree atrioventricular (AV) block now better known as Mobitz type II AV block

Jean Lenègre (1904–1972), French cardiologist, defined Lenègre’s disease and pioneered cardiac electrophysiology, catheterization, and bundle branch pathology

Maurice Lev (1908–1994), pathologist and teacher, defined Lev’s disease and advanced cardiac conduction and congenital heart pathology through over 500 publications

Stokes-Adams syndrome is an abrupt, transient loss of consciousness due to a sudden but pronounced decrease in the cardiac output
Robert Adams (1791–1875), Dublin physician, first described Adams–Stokes syndrome and pioneered clinical-pathological correlation in heart disease

Alfred Lewis Galabin (1843-1913) English obstetric physician. Using an apexcardiogram he was documented atrioventricular (AV) block in humans.

Echocardiography and valve measurements. Comprehensive assessment requires measurements to be made from 2D images and the waveforms generated during Doppler investigations