ECG Case 009
55-year old patient presenting with chest pain
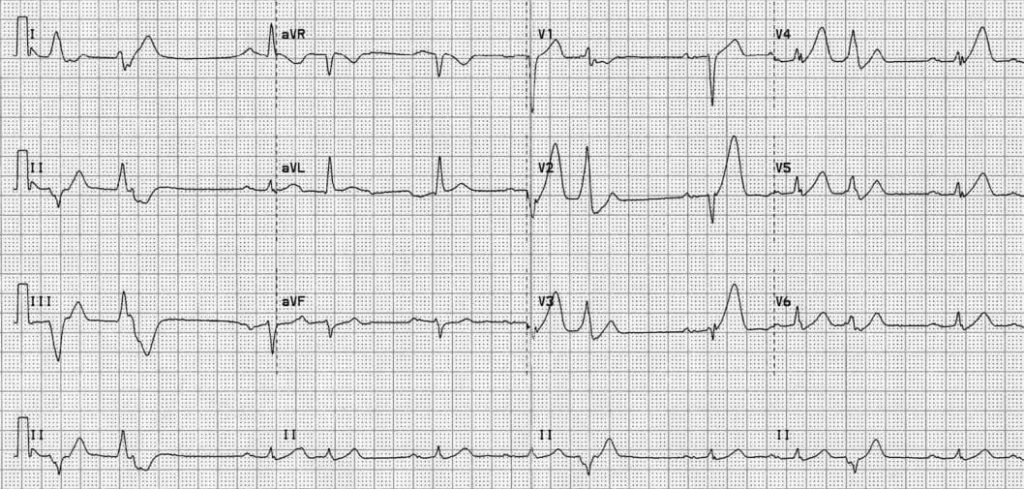
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
This ECG is an example of hyperacute anterolateral STEMI:
- There are markedly peaked, asymmetrical T waves (= hyperacute T waves) in V2-5
- The associated loss of R wave height (analogous to early Q wave formation) causes the enlarging precordial T waves to tower over the diminishing R waves
- There is also some subtle ST elevation in aVL, indicating LAD occlusion proximal to the D1
- There are frequent ventricular ectopic beats, which are concerning in this context as they suggest underlying myocardial irritability and a risk of deterioration to malignant ventricular dysrhythmias such as VF or VT
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |

