ECG Case 060
16-year old male presenting with syncope. Describe and interpret his ECG.
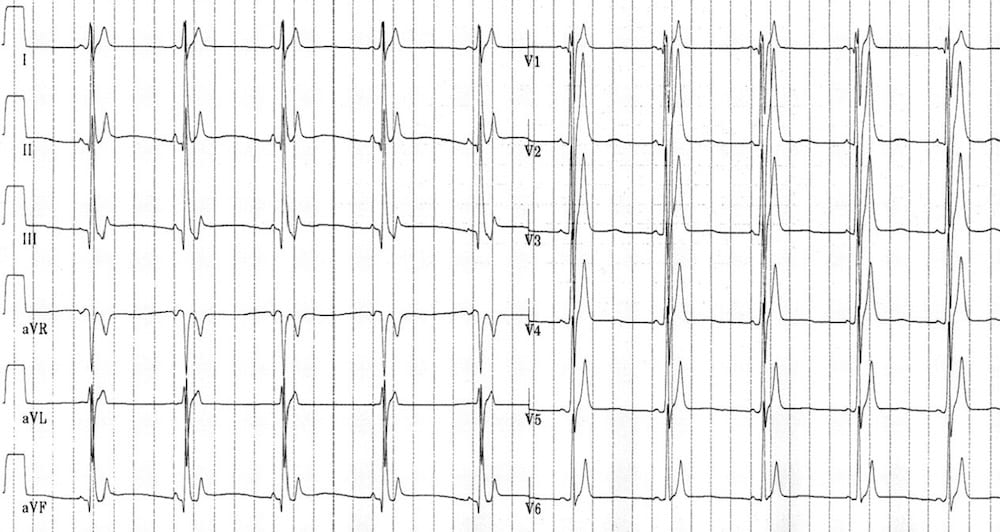
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Main Abnormalities
- Markedly peaked T waves in V2-6.
- Extremely short QT interval (~240 ms).
In a patient presenting with syncope, this ECG pattern is very suspicious for the short QT syndrome.
Short QT Syndrome
- This is a recently-described arrhythmogenic condition associated with paroxysmal atrial and ventricular fibrillation.
- The hallmark is a significantly shortened QT interval (at least < 360 ms, often < 330 ms) with associated T-wave peaking.
- SQTS is a genetically-inherited cardiac channelopathy on the same spectrum as other familial arrhythmogenic diseases such as Long QT Syndrome (LQTS), Brugada Syndrome and Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia (CPVT).
CLINICAL PEARLS
When to Suspect SQTS
- Any patient with a QT interval < 330 ms.
- QT interval < 360 ms and convincing symptoms (syncope, cardiac arrest) or family history.
Differential Diagnosis
- Peaked T waves and short QT interval may be seen with severe hyperkalaemia.
- A shortened QT interval may also be seen with severe hypercalcaemia.
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
