Hypercalcaemia
ECG Changes in Hypercalcaemia
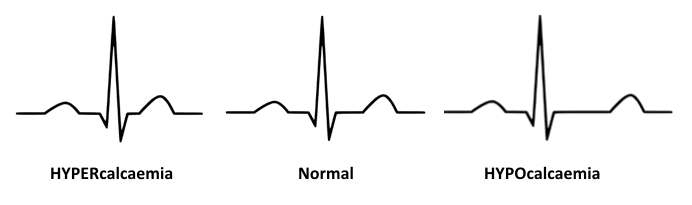
- The main ECG abnormality seen with hypercalcaemia is shortening of the QT interval
- In severe hypercalcaemia, Osborn waves (J waves) may be seen
- Ventricular irritability and VF arrest has been reported with extreme hypercalcaemia
Hypercalcaemia Overview
- Normal serum corrected calcium = 2.1 – 2.6 mmol/L
- Mild hypercalcaemia = 2.7 – 2.9 mmol/L
- Moderate hypercalcaemia = 3.0 – 3.4 mmol/L
- Severe hypercalcaemia = greater than 3.4 mmol/L
Causes of Hypercalcaemia
- Hyperparathyroidism (primary and tertiary)
- Myeloma
- Bony metastases
- Paraneoplastic syndromes
- Milk-alkali syndrome
- Sarcoidosis
- Excess vitamin D (e.g. iatrogenic)
ECG Examples
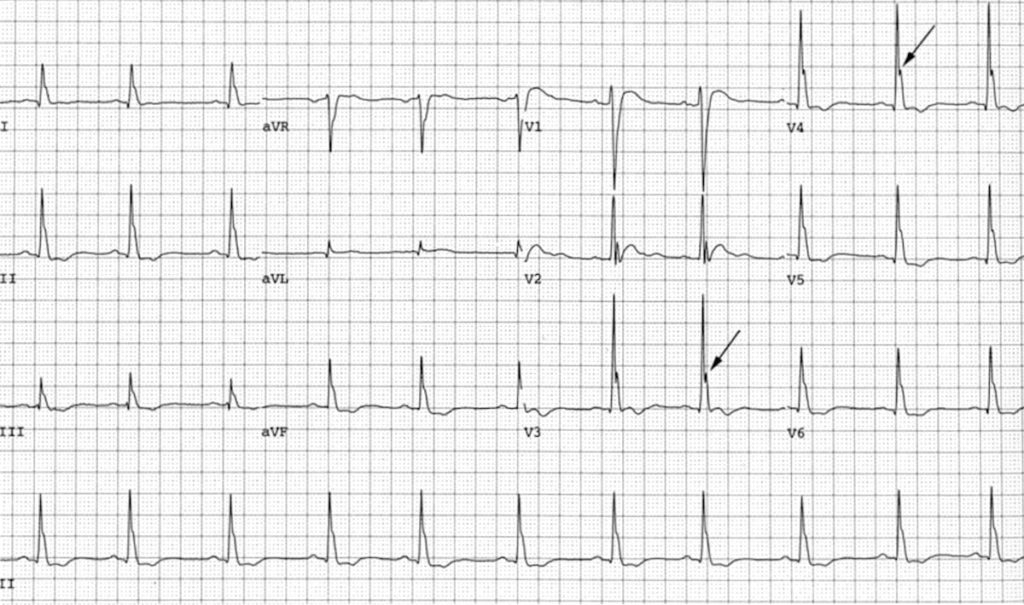
Example 1
Hypercalcaemia
- Osborn waves in severe hypercalcaemia (4.1 mmol/L)
- Image reproduced from Otero & Lenihan [PMC101092]
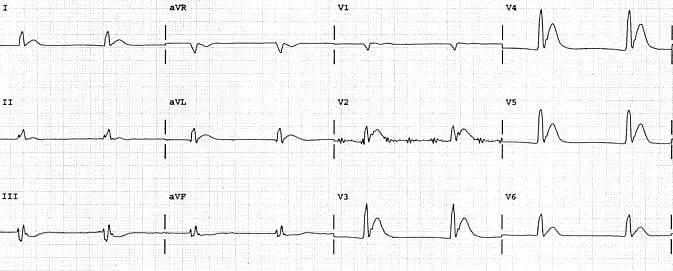
Example 2
- Hypercalcaemia causing marked shortening of the QT interval (260ms).
- Image originally featured in Kyuhyun (K.) Wang’s excellent Atlas of Electrocardiography
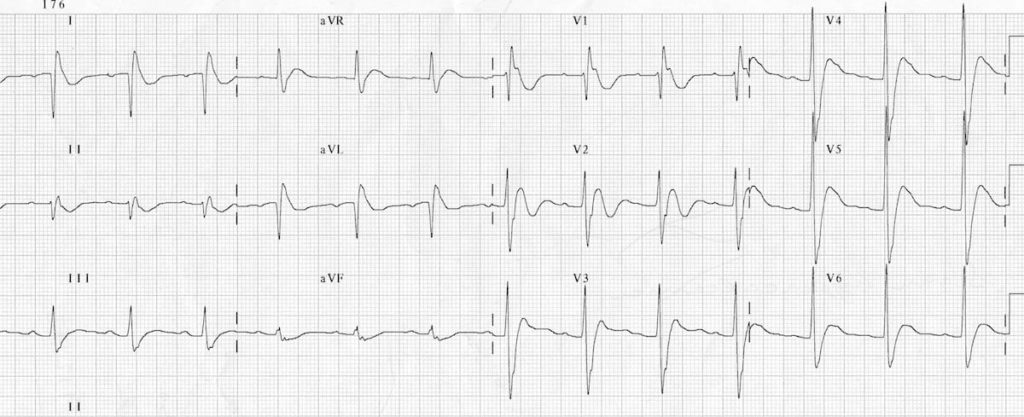
Example 3
This is the ECG of a 41-year old man with a parathyroid adenoma who presented to ED critically unwell with a serum calcium of 6.1 mmol/L. He suffered a VF arrest not long after this ECG was taken. The ECG shows:
- Bizarre-looking QRS complexes
- Very short QT interval
- J waves = notching of the terminal QRS, best seen in lead V1
Many thanks to Dr James Hayes, FACEM, for this fantastic ECG!
Related Topics
- Hypocalcaemia
- Osborn waves
- Measurement of the QT interval
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypokalemia
- Hypercalcemia
- Hypomagnesemia
References
- Slovis C, Jenkins R. ABC of clinical electrocardiography: Conditions not primarily affecting the heart. BMJ. 2002 Jun 1;324(7349):1320-3.
- Otero J, Lenihan DJ. The “normothermic” Osborn wave induced by severe hypercalcemia. Tex Heart Inst J. 2000;27(3):316-7.
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS (UWA) CCPU (RCE, Biliary, DVT, E-FAST, AAA) Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Editor-in-chief of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner


Example 3 shows a limb lead error (left arm – right arm reversal)
To correct this:
Inverted lead I
II and III switch places
aVR and aVL switch
Yes the ECG would still be abnormal but not quite as abnormal as it appears here.