Left Ventricular Aneurysm
Left ventricular aneurysm formation following acute STEMI causes persistent ST elevation on the ECG.
ECG Features of Left Ventricular Aneurysm
- ST elevation seen > 2 weeks following an acute myocardial infarction
- Most commonly seen in the precordial leads
- May exhibit concave or convex morphology
- Usually associated with well-formed Q- or QS waves
- T-waves have a relatively small amplitude in comparison to the QRS complex (unlike the hyperacute T-waves of acute STEMI)

The pattern of persistent anterior ST elevation (> 2 weeks after STEMI) plus pathological Q waves has a sensitivity of 38% and a specificity of 84% for the diagnosis of ventricular aneurysm.
Pathophysiology
- Following an acute STEMI, the ST segments return towards baseline over a period of two weeks, while the Q waves persist and the T waves usually become flattened or inverted
- However, some degree of ST elevation remains in 60% of patients with anterior STEMI and 5% of patients with inferior STEMI
- The mechanism is thought to be related to incomplete reperfusion and transmural scar formation following an acute MI
- This ECG pattern is associated with paradoxical movement of the ventricular wall on echocardiography (ventricular aneurysm)
Clinical Significance
Ventricular aneurysms predispose patients to an increased risk of:
- Ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death (myocardial scar tissue is arrhythmogenic)
- Congestive cardiac failure
- Mural thrombus and subsequent embolisation
Causes
The following conditions may cause an LV aneurysm:
- Acute myocardial infarction (by far the most common)
- Cardiomyopathy
- Cardiac infection
- Congenital abnormalities
Differentiation from acute STEMI
In patients presenting with chest pain and ST elevation on the ECG it is vital to be able to be able to distinguish between LV aneurysm (“old MI”) and acute STEMI.
Factors favouring left ventricular aneurysm
- ECG identical to previous ECGs (if available)
- Absence of dynamic ST segment changes
- Absence of reciprocal ST depression
- Well-formed Q waves
Factors favouring acute STEMI
- New ST changes compared with previous ECGs
- Dynamic / progressive ECG changes — the degree of ST elevation increases on serial ECGs
- Reciprocal ST depression
- High clinical suspicion of STEMI — ongoing ischaemic chest pain, sick-looking patient (e.g. pale, sweaty), haemodynamic instability
Other discriminating features
The ratio of T-wave to QRS complex amplitude has been validated as a means of differentiating between LV aneurysm and acute STEMI:
- T-wave/QRS ratio < 0.36 in all precordial leads favours LV aneurysm
- T-wave/QRS ratio > 0.36 in any precordial lead favours anterior STEMI
ECG Examples
Example 1
60 year old male, chronic smoker, presents with mild chest pain and shortness of breath 2 weeks following an episode of severe chest pain for which he sought no medical attention.
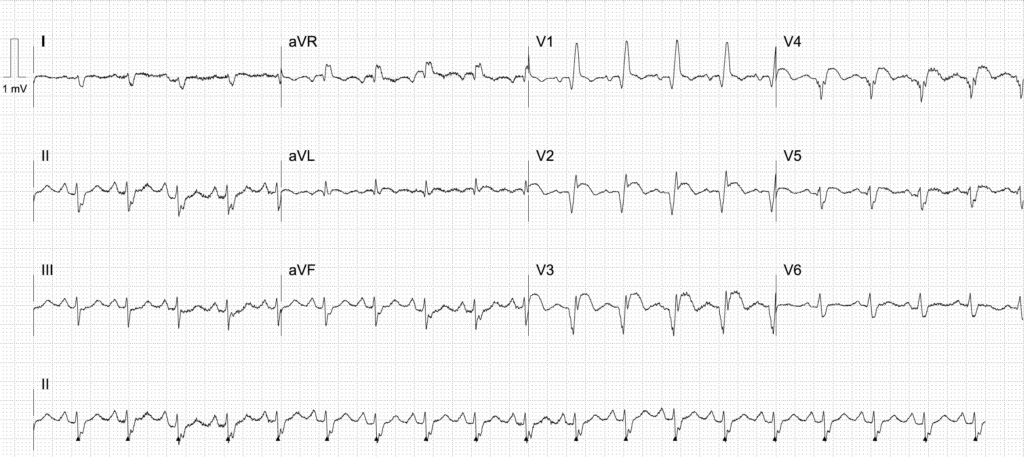
Left Ventricular Aneurysm
Example 2
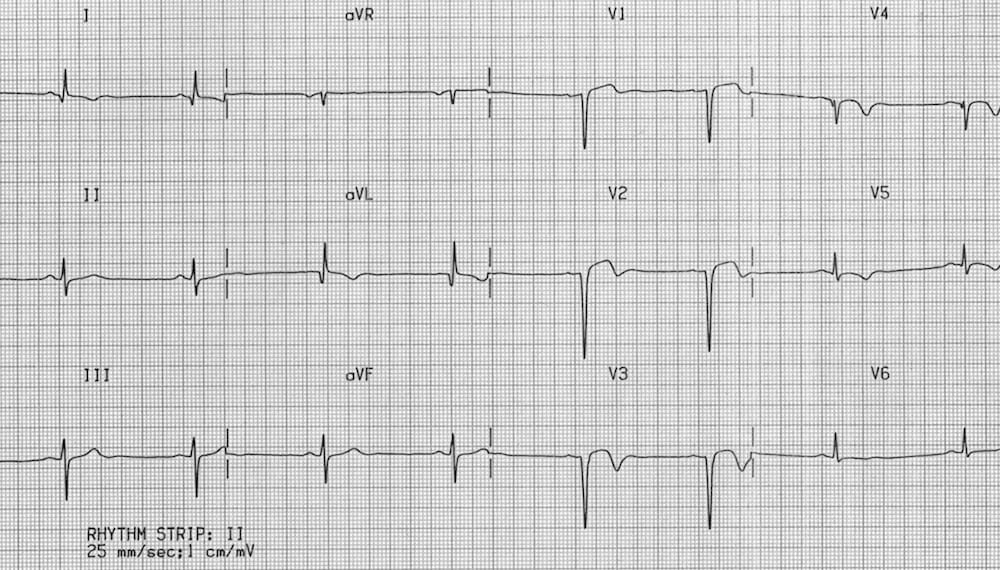
Anterior Left Ventricular Aneurysm:
- Minimal ST elevation in V1-3 associated with deep Q waves and T-wave inversion
- This is a LV aneurysm secondary to a prior anteroseptal STEMI
- Note the T-wave/QRS ratio is < 0.36 in all precordial leads
Example 3
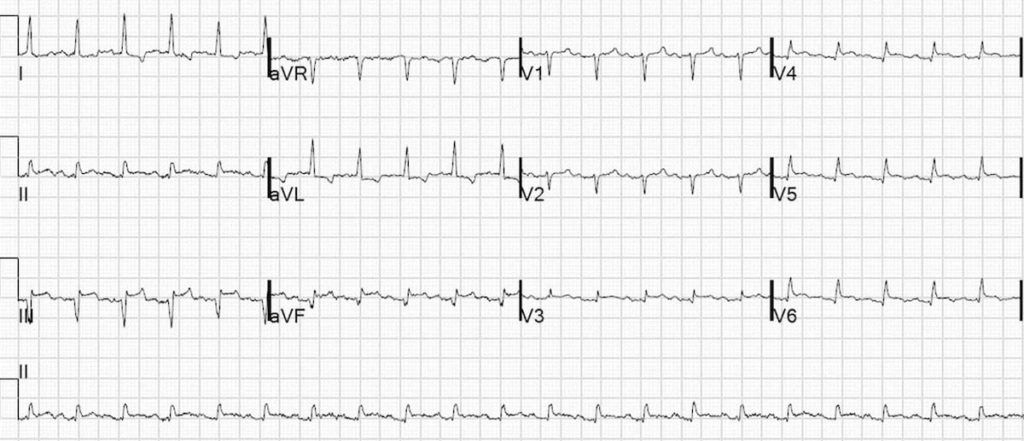
Inferior Left Ventricular Aneurysm:
- Old inferior STEMI with persistent ST elevation (LV aneurysm morphology)
- ECG is reproduced from Dr Smith’s ECG Blog
Related Topics
References
- Edhouse J, Brady WJ, Morris F. ABC of clinical electrocardiography: Acute myocardial infarction-Part II. BMJ. 2002 Apr 20;324(7343):963-6
- Smith SW. T/QRS ratio best distinguishes ventricular aneurysm from anterior myocardial infarction. Am J Emerg Med. 2005 May;23(3):279-87
- Bouthillet T. Left ventricular aneurysm vs. acute anterior STEMI EMS-12 lead
- Smith SW. Cases of left ventricular aneurysm Dr Smith’s ECG Blog
- Klein et al. Electrocardiographic criteria to differentiate acute anterior ST-elevation myocardial infarction from left ventricular aneurysm. The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 2015 June;33(6):786-780
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner

