Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
ECG Features of Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
- Low voltage QRS complexes
- Non-specific ST segment / T wave changes
- Bundle branch blocks
- Atrioventricular block (3rd degree AV block may occur in sarcoidosis)
- Pathological “pseudo-infarction” Q waves
- Atrial and ventricular dysrhythmias
Pathophysiology
Restrictive cardiomyopathy is the least common form of cardiomyopathy. It occurs in the advanced stages of myocardial infiltrative disease — e.g. due to haemochromatosis, amyloidosis or sarcoidosis.
- Diffuse myocardial infiltration leads to low voltage QRS complexes.
- Atrial fibrillation may occur due to atrial enlargement; ventricular arrhythmias are also common
- Infiltration of the cardiac conducting system (e.g. due to septal granuloma formation in sarcoidosis) may lead to conduction disturbance — e.g. bundle branch blocks and AV block.
- Healing granulomas in sarcoidosis may produce “pseudo-infarction” Q waves
Example ECG
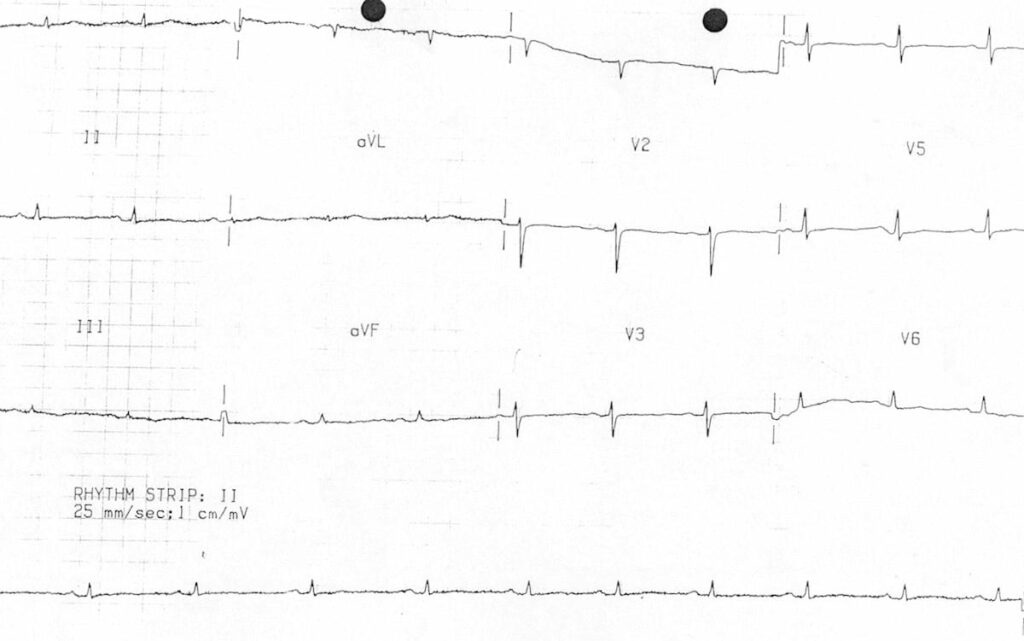
ECG of a patient with restrictive cardiomyopathy, demonstrating:
- Low voltage QRS complexes
- Widespread flattening of T waves
Related Topics
References
- Edhouse J, Thakur RK, Khalil JM. ABC of clinical electrocardiography. Conditions affecting the left side of the heart. BMJ. 2002 May 25;324(7348):1264-7
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner

