
Hypokalaemia
Hypokalaemia causes typical ECG changes of widespread ST depression, T wave inversion, and prominent U waves, predisposing to malignant ventricular arrhythmias

Hypokalaemia causes typical ECG changes of widespread ST depression, T wave inversion, and prominent U waves, predisposing to malignant ventricular arrhythmias

This review will change your approach to localised ST depression on the ECG, which on its own does not accurately localise ischaemia, and may be the first sign of subtle occlusion
EM attendings are generally faster and more accurate at ECG interpretation than residents and medical students. But how are they able to process this information so much quicker while maintaining accuracy?

Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmias

In left anterior fascicular block (LAFB), impulses are conducted to the left ventricle via the posterior fascicle, producing characteristic ECG changes

Left posterior fascicular block LPFB (left posterior hemiblock), impulses are conducted to the left ventricle via the left anterior fascicle

A review of the ECG features of right ventricular outflow tract tachycardia (RVOT), a type of VT, with example ECGs.

Isolated low serum Mg levels are associated with atrial depolarisation and ventricular repolarisation abnormalities, predisposing to ventricular arrhythmias

Trifascicular block (TFB) refers to the presence of conducting disease in all three fascicles: RBBB, LAFB, LPFB. LITFL ECG Library

ECG Axis. Hexaxial QRS Axis analysis for dummies. Quick and easy method of estimating ECG axis with worked examples and differential diagnoses

Left Bundle Branch Block LBBB - normal direction of septal depolarisation is reversed (becomes right to left), as the impulse spreads
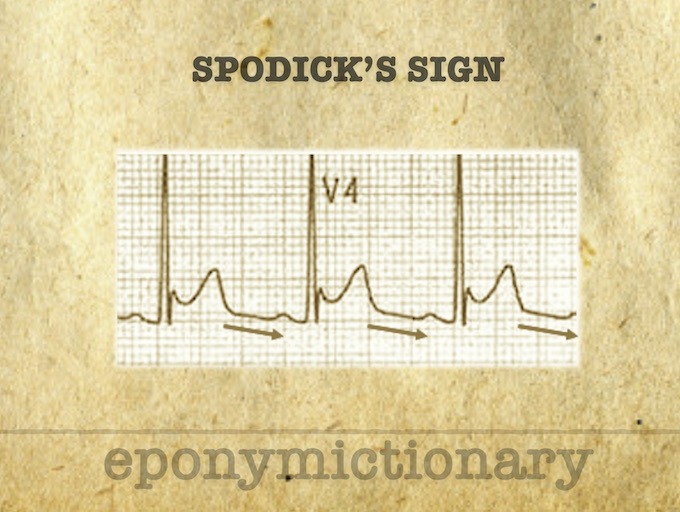
Spodick Sign: Stage I Pericarditis, a downsloping of the TP line. Described 1974 by American Cardiologist, David H Spodick (1927 – 2019)