Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
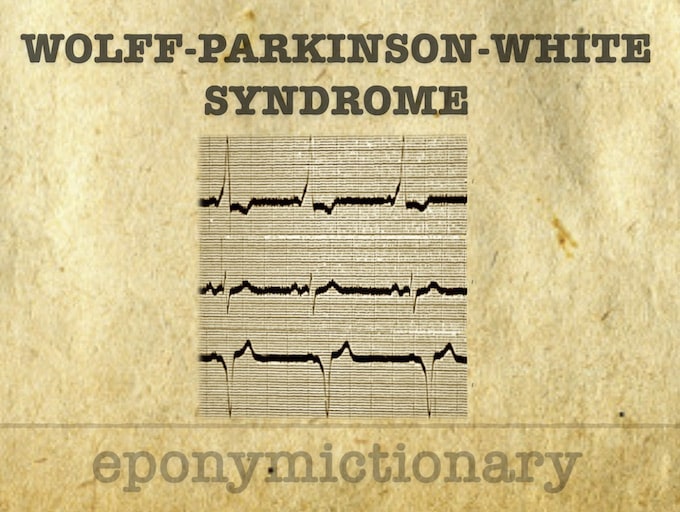
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmia.

Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmia.

A woman in her 60s with a broad complex tachycardia. There are two ECG features that suggest an accessory pathway, can you spot them?

In patients with AF and pre-excitation, the presence of an accessory pathway allows for rapid AV conduction, with a risk of degeneration into VT and VF

Tachyarrhythmia that occurs in patients with accessory pathways, due to formation of a re-entry circuit between the AV node and accessory pathway
Heart HQ - Episode 2: Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome, myocarditis and COVID 19 Vaccines

The average Emergency Clinician is interrupted every 6 minutes. When busy, it can be tempting to quickly “sign off” an ECG. These are the patterns not to miss.

Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmias

ECG of a 14yr old female who presents following an episode of palpitations and associated dizziness. Interpret her ECG using the Arruda algorithm

35 yr old male who presented to the Emergency Department complaining of palpitations, dyspnoea, and lightheadedness. Describe and interpret this ECG. LITFL Top 100 ECG

33 year old male presents with shortness of breath and dizziness during an indoor soccer game. Describe and interpret this ECG. LITFL Top 100 ECG

ECG of a 7 year old boy presenting with intermittent feeling of 'butterflies fluttering' in his chest

Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmia.