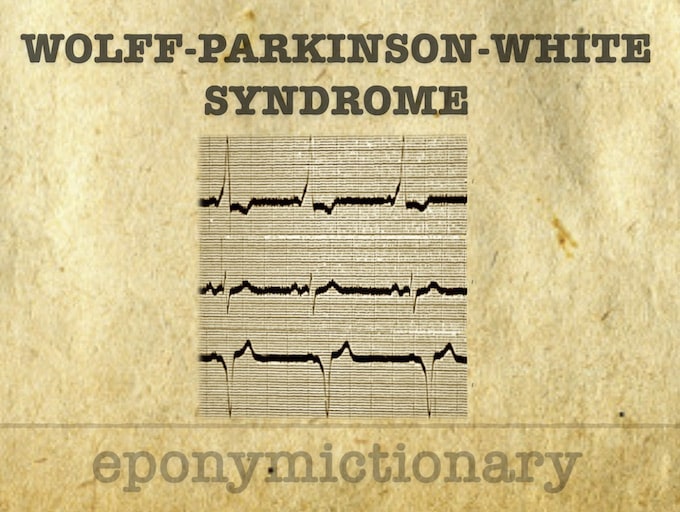
Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmia.

Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmia.

In patients with AF and pre-excitation, the presence of an accessory pathway allows for rapid AV conduction, with a risk of degeneration into VT and VF

Tachyarrhythmia that occurs in patients with accessory pathways, due to formation of a re-entry circuit between the AV node and accessory pathway
Heart HQ - Episode 2: Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome, myocarditis and COVID 19 Vaccines

Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmias

Funtabulously Frivolous Friday Five 326 - Just when you thought your brain could unwind the medical trivia FFFF

The characteristic ECG findings in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome include a slurred upstroke to the QRS complex (the Delta wave)

Part four of a 5 part lecture series on ECG/EKG Interpretation on tachyarrhythmias with Dr Theo Sklavos and cardiologist A/Prof William Wang.

Paul Dudley White (1886-1973) was an American cardiologist. White with Louis Wolff and John Parkinson (WPW syndrome 1930); McGinn-White pattern (1935)

Sir John Parkinson (1885-1976) was an English cardiologist. In 1930, Parkinson along with Louis Wolff and Paul Dudley White, described WPW Syndrome

Louis Wolff (1898-1972) was an American cardiologist. Eponymously affiliated with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) described in 1930

ECG of a 14yr old female who presents following an episode of palpitations and associated dizziness. Interpret her ECG using the Arruda algorithm