Abdominal CT: interstitial pancreatitis
Identifying acute interstitial pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis commonly presents with upper abdominal pain, elevated lipase (an enzyme that is released when the pancreas becomes inflamed) and elevated white blood cell count
The most common causes of acute pancreatitis are related to alcohol use or blockage of the pancreas duct due to gallstones. In some cases, the cause is unknown.
While CT is not necessary to diagnose acute pancreatitis, it can be helpful to evaluate severe cases or when there is concern of complications. Specifically, CT can help differentiate between the two major types of pancreatitis:
- Interstitial pancreatitis (inflammation of the tissue only)
- Necrotizing pancreatitis (pancreas tissue loses its blood flow and starts to die)
Key findings for acute interstitial pancreatitis
There are three common imaging findings to look for when diagnosing acute interstitial pancreatitis
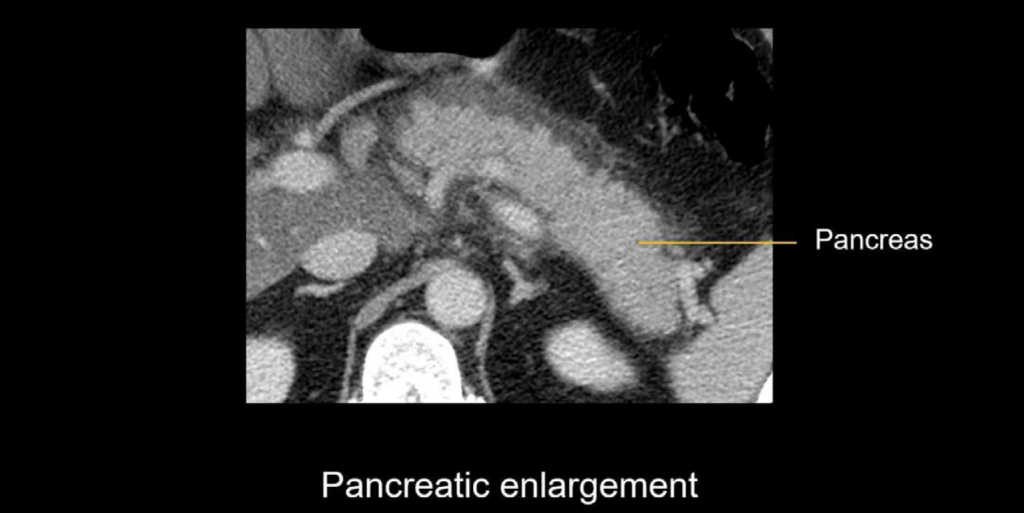
- Pancreatic enlargement
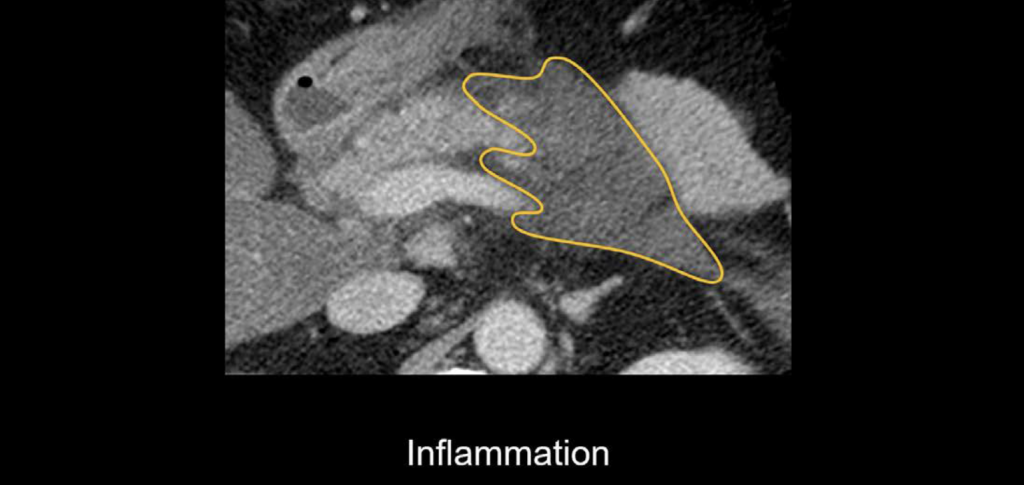
- Inflammation
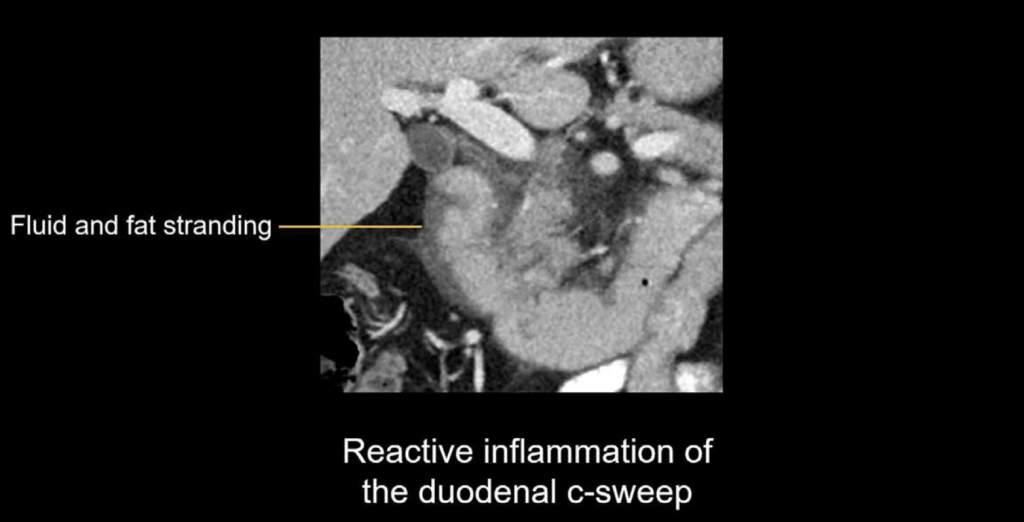
- Reactive inflammation
Pancreatic enlargement due to increased inflammation and fluid (i.e., oedema) in the tissue
Inflammation: This appears as fluid or stranding in the surrounding fat.
Reactive inflammation: In addition to inflammation of the pancreas, you may also see inflammation in nearby structures such as the duodenal c-sweep (shown below with surrounding fluid and fat stranding).
Clinical Case 1
Scroll through these images from a patient presenting with severe abdominal pain.
- Scroll through the pancreas and notice how it appears mildly enlarged and slightly oedematous. This means it has increased fluid content.
- Notice that there is fat stranding and unorganized fluid surrounding the pancreas and extending into the retroperitoneum.
- While the pancreas is edematous, it is uniformly enhancing, and thus no areas of necrosis are present.
- These findings are consistent with acute interstitial pancreatitis and are supported by the patient’s clinical presentation of abdominal pain and elevated lipase.
This is an edited excerpt from the Medmastery course Abdominal CT Pathologies by Michael P. Hartung, MD. Acknowledgement and attribution to Medmastery for providing course transcripts
- Hartung MP. Abdominal CT: Common Pathologies. Medmastery
- Hartung MP. Abdominal CT: Essentials. Medmastery
- Hartung MP. Abdomen CT: Trauma. Medmastery
References
- Top 100 CT scan quiz. LITFL
- Nickson C. Acute pancreatitis. CCC
- Farkas J. Acute Pancreatitis (including hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis). IBCC
Radiology Library: Acute abdomen. Solid organ and Vascular pathology
- Hartung MP. Abdominal CT: acute interstitial pancreatitis
- Hartung MP. Abdominal CT: acute necrotizing pancreatitis
- Hartung MP. Abdominal CT: renal stones and the flank pain CT
- Hartung MP. Abdominal CT: renal infections
- Hartung MP. Abdominal CT: cholecystitis
- Hartung MP. Abdominal CT: intestinal ischaemia
- Hartung MP. Abdominal CT: rupturing abdominal aortic aneurysm
Abdominal CT interpretation
Assistant Professor of Abdominal Imaging and Intervention at the University of Wisconsin Madison School of Medicine and Public Health. Interests include resident and medical student education, incorporating the latest technology for teaching radiology. I am also active as a volunteer teleradiologist for hospitals in Peru and Kenya. | Medmastery | Radiopaedia | Website | Twitter | LinkedIn | Scopus
MBChB (hons), BMedSci - University of Edinburgh. Living the good life in emergency medicine down under. Interested in medical imaging and physiology. Love hiking, cycling and the great outdoors.


