AV block: 2nd degree, “fixed ratio” blocks
Fixed Ratio AV blocks
- Second degree heart block with a fixed ratio of P waves: QRS complexes (e.g. 2:1, 3:1, 4:1).
- Fixed ratio blocks can be the result of either Mobitz I or Mobitz II conduction.
ECG Examples of Fixed Ratio AV blocks
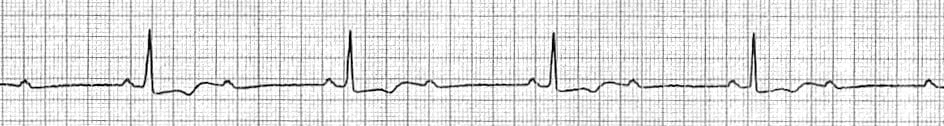
2:1 block
- The atrial rate is approximately 75 bpm.
- The ventricular rate is approximately 38 bpm.
- Non-conducted P waves are superimposed on the end of each T wave.
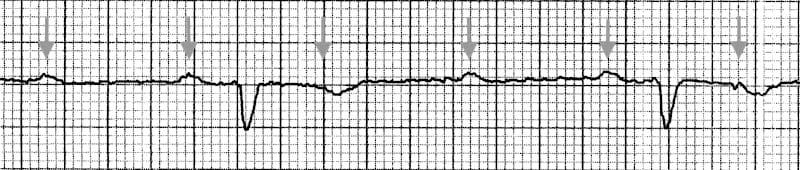
3:1 block
- The atrial rate (purple arrows) is approximately 90 bpm.
- The ventricular rate rate is approximately 30 bpm.
- Note how every third P wave is almost entirely concealed within the T wave.
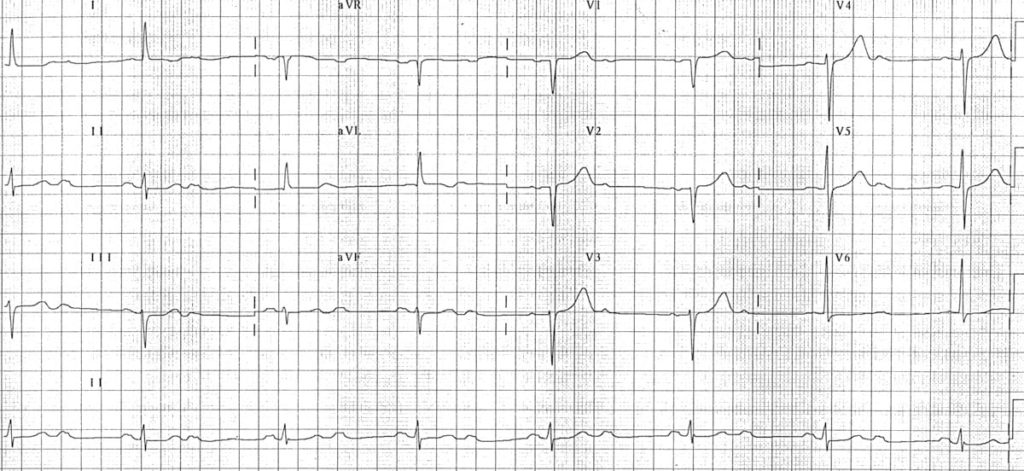
4:1 block
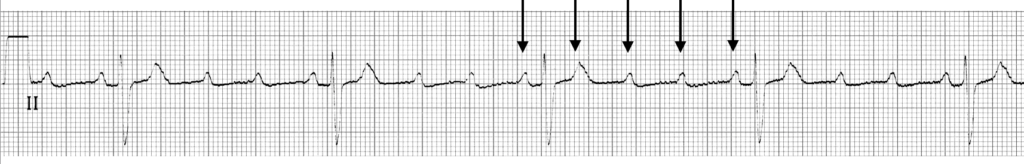
- High-grade AV block (4:1 conduction ratio)
- Atrial rate is approximately 140 bpm.
- Ventricular rate is approximately 35 bpm.
- See High Grade AV Block
Mobitz I or II?
- It is not always possible to determine the type of conduction disturbance producing a fixed ratio block, although clues may be present.
- Mobitz I conduction is more likely to produce narrow QRS complexes, as the block is located at the level of the AV node. This type of fixed ratio block tends to improve with atropine and has an overall more benign prognosis.
- Mobitz II conduction typically produces broad QRS complexes, as it usually occurs in the context of pre-existing LBBB or bifascicular block. This type of fixed ratio block tends to worsen with atropine and is more likely to progress to 3rd degree heart block or asystole.
- However, this distinction is not infallible. In approximately 25% of cases of Mobitz II, the block is located in the Bundle of His, producing a narrow QRS complex. Furthermore, Mobitz I may occur in the presence of a pre-existing bundle branch block or interventricular conduction delay, producing a broad QRS complex.
- The only way to be certain is to observe the patient for a period of time (e.g. watch the cardiac monitor, print a long rhythm strip, take serial ECGs) and observe what happens to the PR intervals. Often, periods of 2:1 or 3:1 block will be interspersed with more characteristic Wenckebach sequences or runs of Mobitz II.
Related Topics
- AV block: 1st degree
- AV block: 2nd degree, Mobitz II
- AV block: 2nd degree, “high grade AV block”
- AV block: 3rd degree (complete heart block)
History
- Eponymythology: History of Second-degree AV block.
- Eponym. Karel Frederik Wenckebach (1864 -1940)
- Eponym. Woldemar Mobitz (1889 – 1951)
- Eponym. John Hay (1873 – 1959).
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |