Carbamazepine Cardiotoxicity
Massive carbamazepine overdose (> 50mg/kg) is associated with cardiotoxicity due to fast sodium channel blockade. ECG changes are not usually as dramatic as those seen in TCA overdose.
ECG features of Carbamazepine Cardiotoxicity
- Subtle QRS widening
- 1st degree AV block
- Dominant secondary R wave in aVR is less common than in TCA overdose
ECG Examples
Example 1a
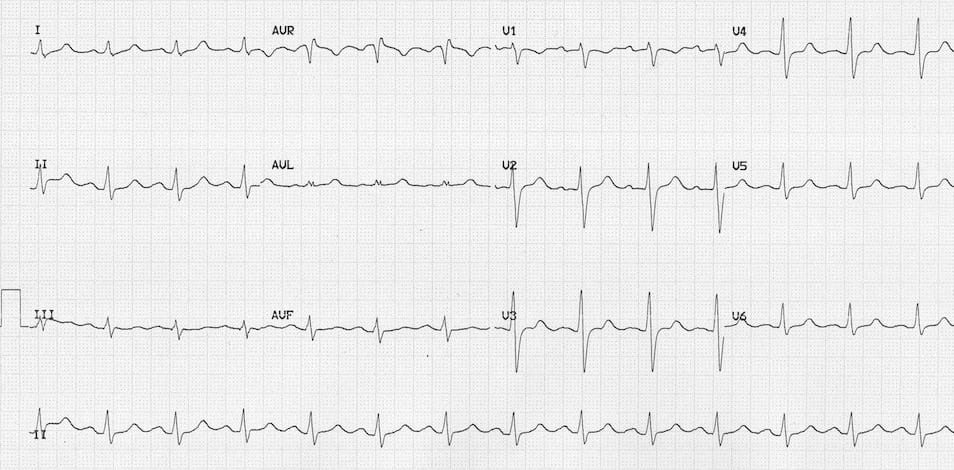
- This first ECG was taken several hours after massive carbamazepine overdose (150-200 mg/kg), by which time the patient was beginning to manifest clinical signs of cardiotoxicity (hypotension requiring noradrenaline).
- Carbamazepine level around that time was 33 mg/L.
- There is subtle ECG evidence of fast sodium channel blockade: Note the QRS widening (135 ms), 1st degree heart block (PR 240ms) and small secondary R wave in aVR.
Example 1b
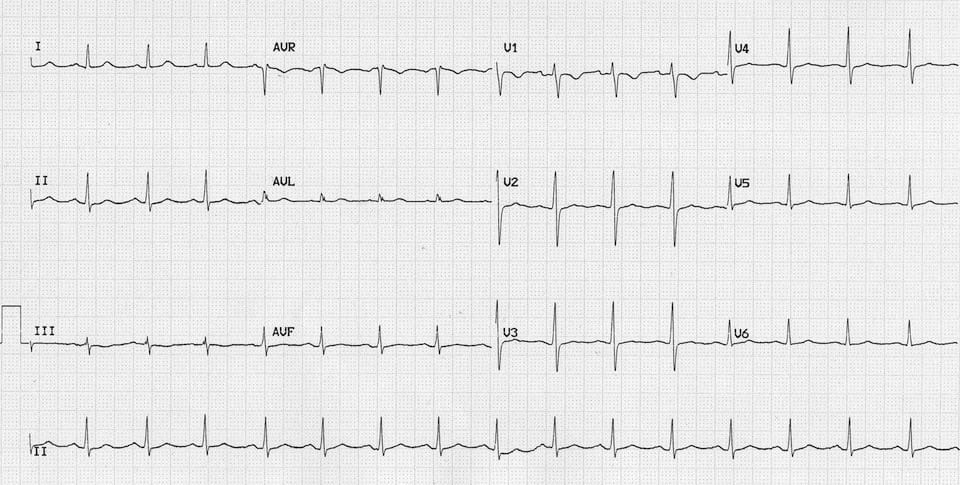
- This second ECG was taken several hours after intubation and treatment with hyperventilation (to pH 7.50) and haemofiltration.
- Carbamazepine level is now down to 17 mg/L and haemodynamic instability has resolved.
- Note the QRS duration and PR interval have now normalised, while the secondary R wave in aVR has reduced in amplitude.
Example 2

- This ECG demonstrates more obvious cardiotoxicity following a massive carbamazepine overdose.
- QRS complexes are broad and there is a large R’ wave in aVR.
Related Topics
- Beta-blocker toxicity
- Calcium-channel blocker toxicity
- Quetiapine toxicity
- Tricyclic overdose (sodium-channel blocker toxicity)
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner

