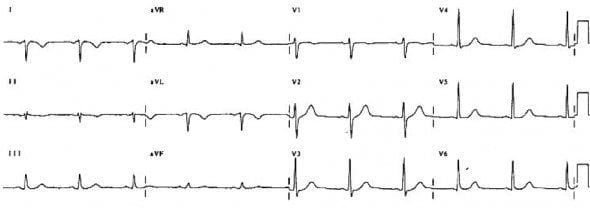
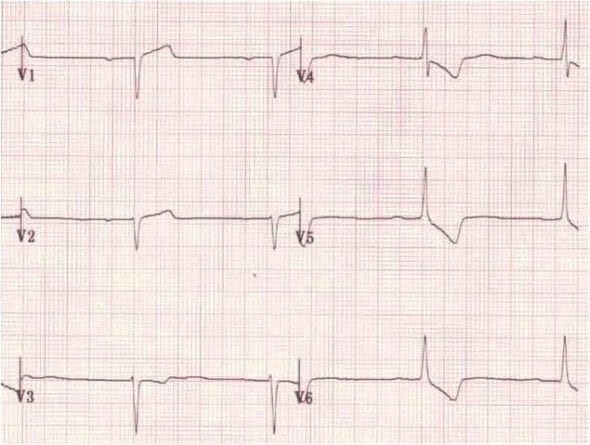
R wave
R wave Overview
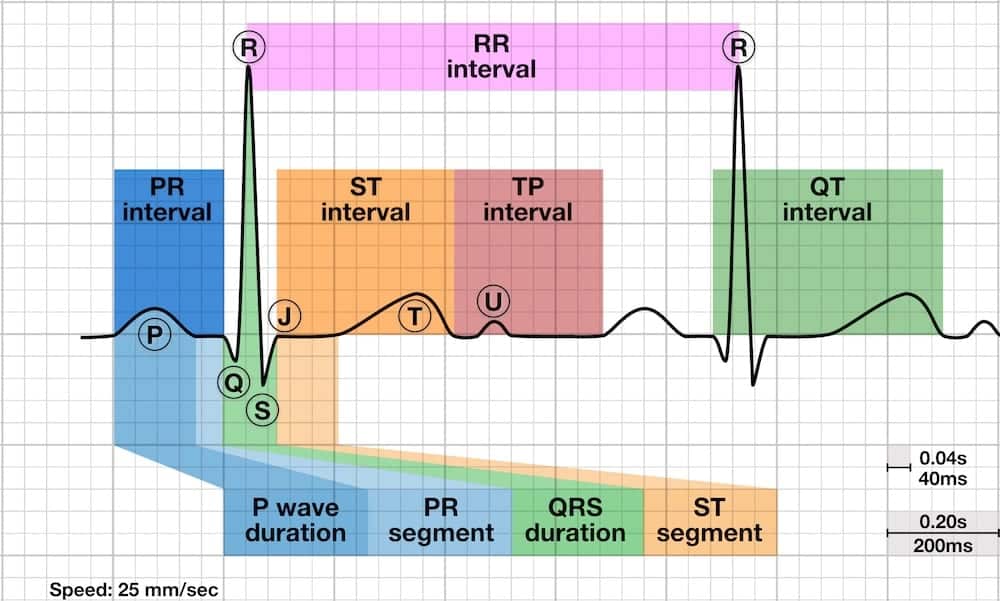
The R wave is the first upward deflection after the P wave. The R wave represents early ventricular depolarisation
Abnormalities of the R wave
There are three key R wave abnormalities:
- Dominant R wave in V1
- Dominant R wave in aVR
- Poor R wave progression
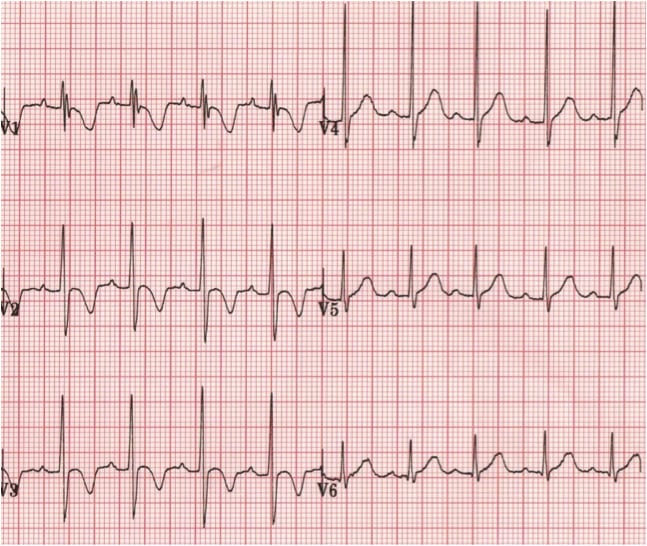
1. Dominant R wave in V1
Causes of Dominant R wave in V1
- Normal in children and young adults
- Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (RVH)
- Pulmonary Embolus
- Persistence of infantile pattern
- Left to right shunt
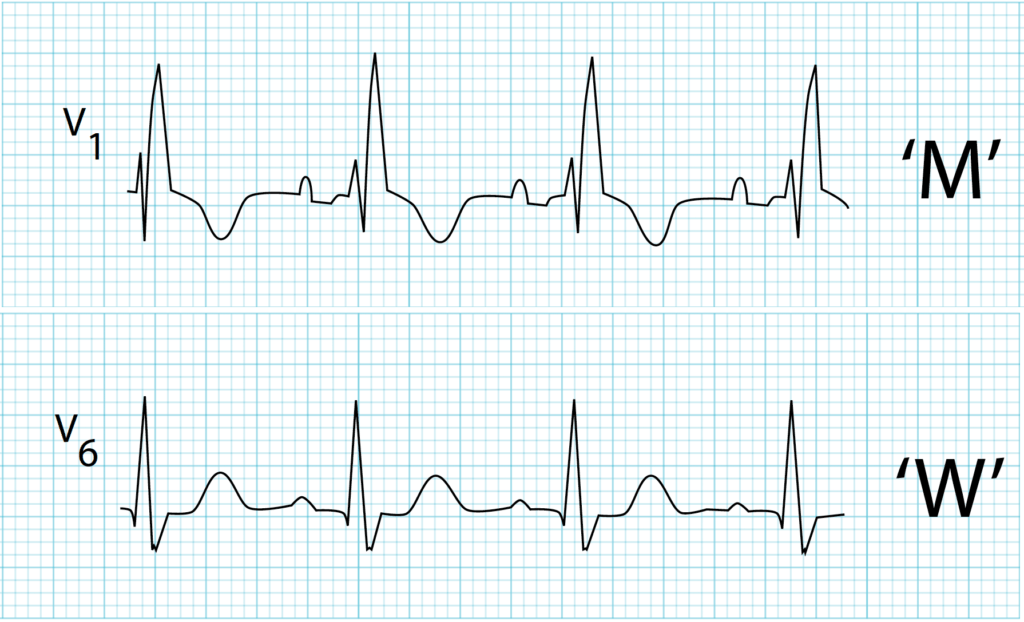
- Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
- Posterior Myocardial Infarction (ST elevation in Leads V7, V8, V9)
- Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Type A
- Incorrect lead placement (e.g. V1 and V3 reversed)
- Dextrocardia
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Dystrophy
- Myotonic dystrophy
- Duchenne Muscular dystrophy
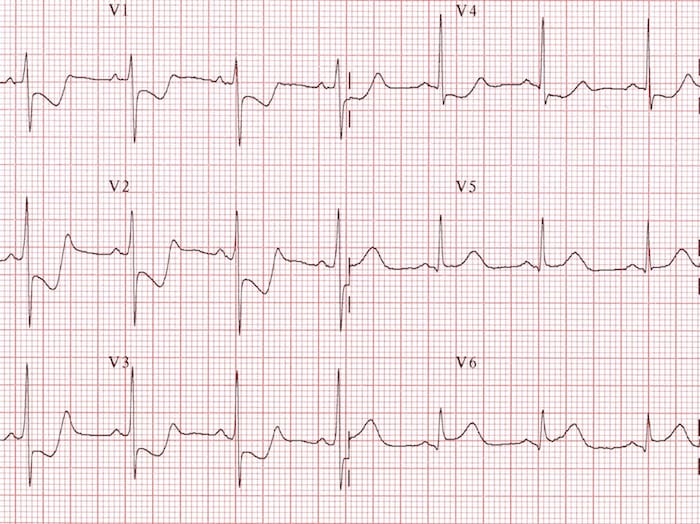
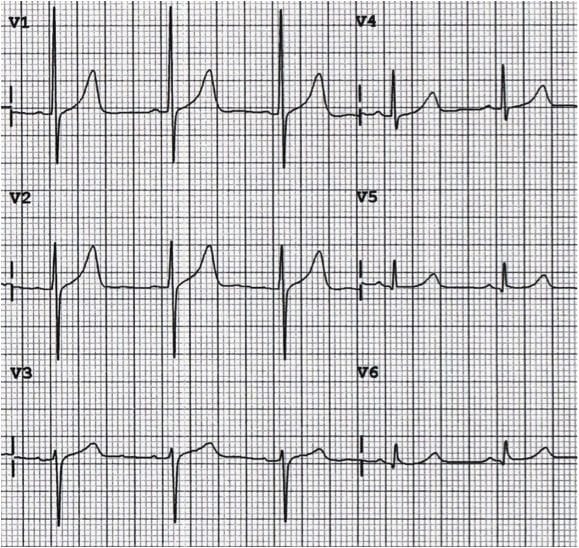
Examples of Dominant R wave in V1
Normal paediatric ECG (2 yr old)
Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (RVH)
Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
Posterior MI
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Type A
Leads V1 and V3 reversed
- Note biphasic P wave (typically seen in only in V1) in lead “V3”
Muscular dystrophy
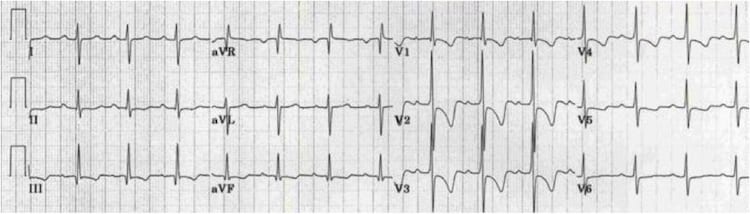
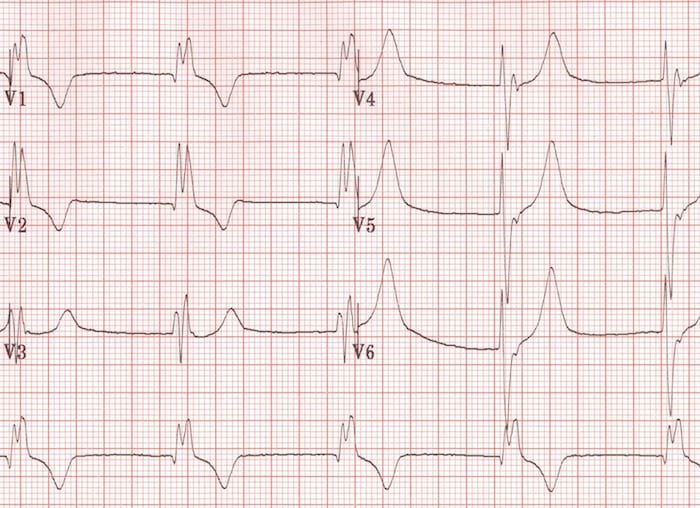
2. Dominant R wave in aVR
- Poisoning with sodium-channel blocking drugs (e.g. TCAs)
- Dextrocardia
- Incorrect lead placement (left/right arm leads reversed)
- Commonly elevated in ventricular tachycardia (VT)
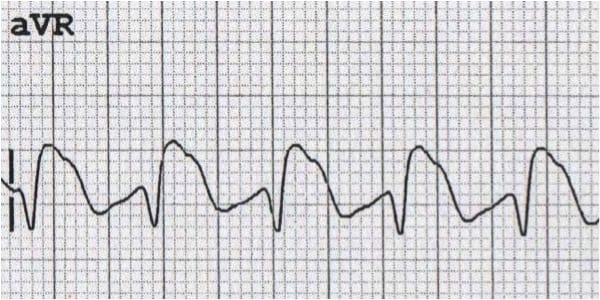
Examples of Dominant R wave in aVR
Poisoning with sodium-channel blocking drugs
- Causes a characteristic dominant terminal R wave in aVR
- Poisoning with sodium-channel blocking agents is suggested if:
- R wave height > 3mm
- R/S ratio > 0.7
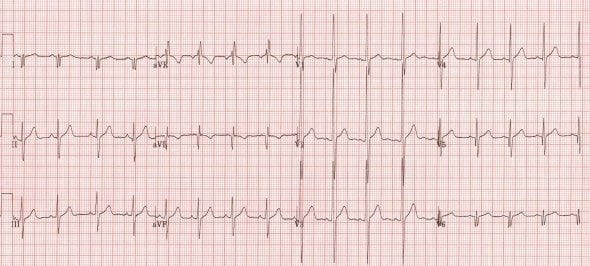
Dextrocardia
This ECG shows all the classic features of dextrocardia:
- Positive QRS complexes (with upright P and T waves) in aVR
- Negative QRS complexes (with inverted P and T waves) in lead I
- Marked right axis deviation
- Absent R-wave progression in the chest leads (dominant S waves throughout)
Left arm/right arm lead reversal
The most common cause of a dominant R wave in aVR is incorrect limb lead placement, with reversal of the left and right arm electrodes. This produces a similar pattern to dextrocardia in the limb leads but with normal R-wave progression in the chest leads. With LA/RA lead reversal:
- Lead I becomes inverted
- Leads aVR and aVL switch places
- Leads II and III switch places
Ventricular Tachycardia
3. Poor R wave progression
Poor R wave progression is described with an R wave ≤ 3 mm inV3 and is caused by:
- Prior anteroseptal MI
- LVH
- Inaccurate lead placement
- May be a normal variant
Note that absent R wave progression is characteristically seen in dextrocardia (see previous ECG).
ECG Library Basics
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY