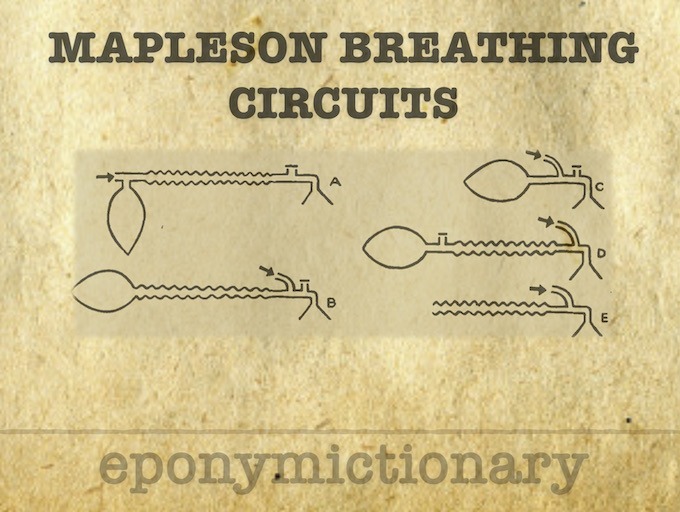
Mapleson Circuit
The Mapleson Circuit Systems are used for the delivery of oxygen and anaesthetic agents and the removal of carbon dioxide during general anaesthesia. There are five Mapleson circuits: A, B, C, D and E (F was added later by Wills et al)