
Allen test
Allen Test: a bedside exam assessing hand arterial flow via radial/ulnar patency; used before ABG, cannulation, or radial artery harvest.

Allen Test: a bedside exam assessing hand arterial flow via radial/ulnar patency; used before ABG, cannulation, or radial artery harvest.

Tietze syndrome: benign swelling of upper costochondral cartilage, causing localized chest pain. Often confused with costochondritis; self-limiting.

Acute, transient viral myositis involving intercostal and abdominal muscles associated with Coxsackievirus B. Eponym: Ejner Sylvest (1930)

Searchable database for medical journal abbreviations, both modern and historical, aiding researchers in accessing articles to facilitate easier navigation of medical literature through improved referencing.

Holmes–Adie syndrome: a benign neurological condition marked by tonic pupils and areflexia, historically mistaken for neurosyphilis.

From ancient “cat’s‑eye” reflections to AI‑assisted retinal imaging: the story of the ophthalmoscope from Helmholtz’s 1851 Augenspiegel to digital, confocal and smartphone‑based system
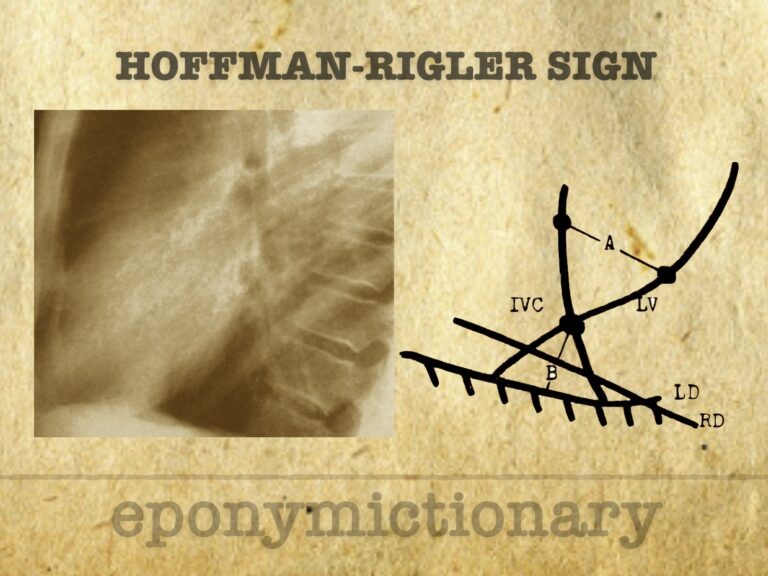
Radiographic sign of left ventricular enlargement on lateral chest X-ray, based on LV extension behind the IVC; described by Hoffman and Rigler in 1965

Rigler notch sign: Indentation in the border of a solid lung mass (thought to represent a feeding vessel) suggestive of a bronchial carcinoma

Rigler triad; Imaging findings in patients with gallstone ileus with an ectopic gallstone causing small bowel obstruction, and pneumobilia
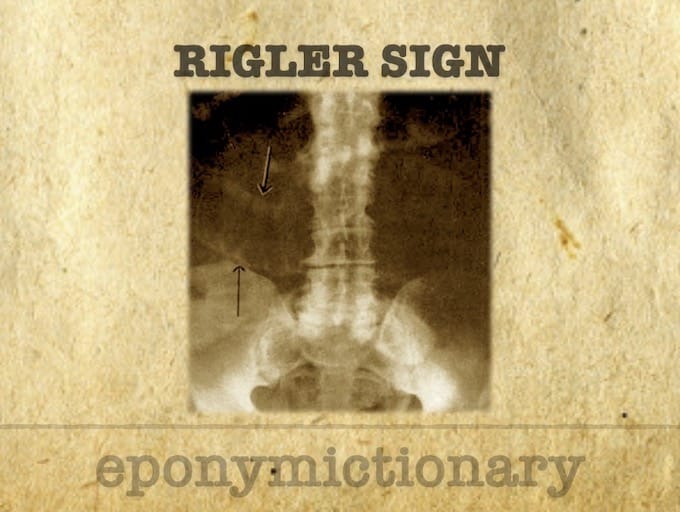
Radiological signs of pneumoperitoneum: history, diagnosis, and key eponyms including Rigler’s sign, Popper’s sign, football sign, and inverted V sign
Necrotizing fasciitis: life-threatening soft tissue infection, historically hospital gangrene, term coined by Ben J. Wilson in 1951

Bamberger–Marie syndrome (hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy): clubbing, bone periostosis, and joint effusions—historically recognised as a paraneoplastic syndrome linked to lung disease.