Battle Sign
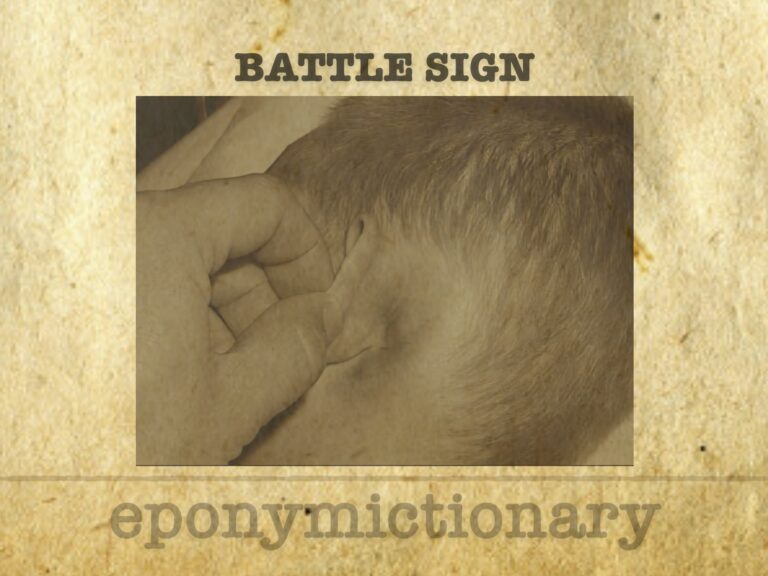
Battle sign: mastoid ecchymosis indicating basilar skull fracture, described by W.H. Battle in 1890; it holds >75% PPV for posterior fossa injury.

Battle sign: mastoid ecchymosis indicating basilar skull fracture, described by W.H. Battle in 1890; it holds >75% PPV for posterior fossa injury.
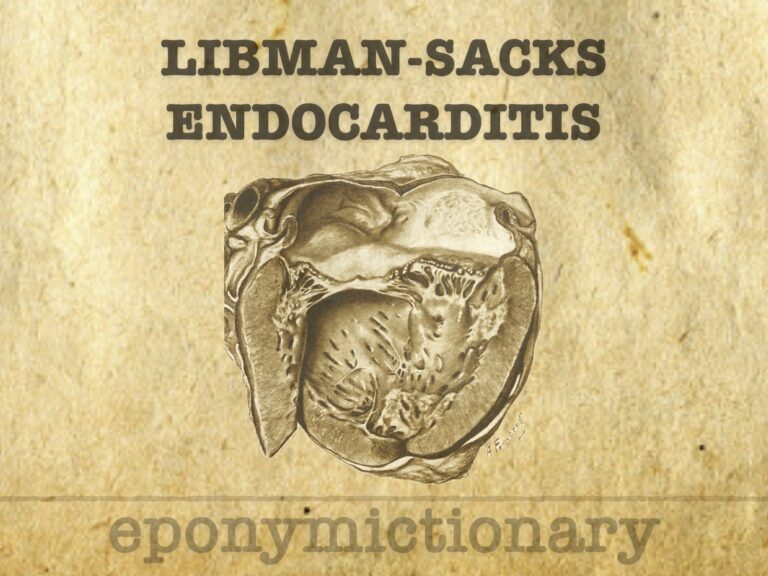
Libman–Sacks endocarditis is a sterile cardiac valve lesion linked to lupus and antiphospholipid syndrome, often detected via echocardiography
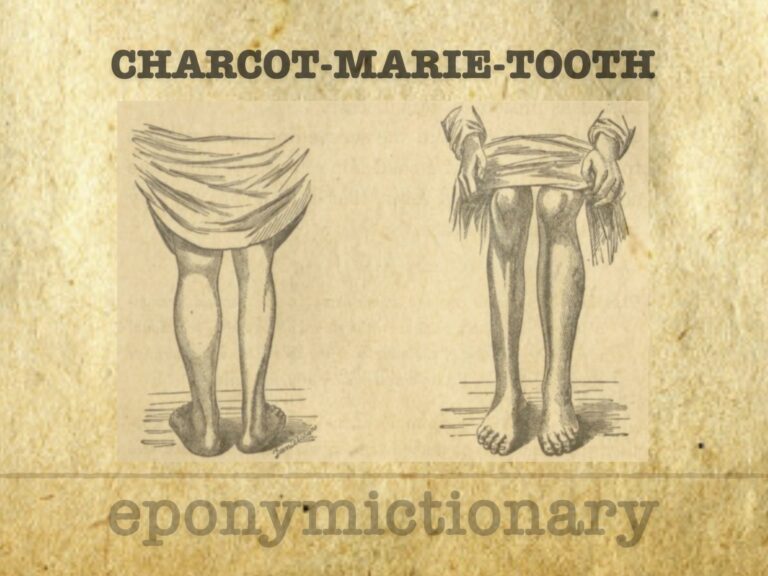
Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT) is the most common inherited neuropathy, encompassing genetically diverse subtypes of peripheral nerve dysfunction.
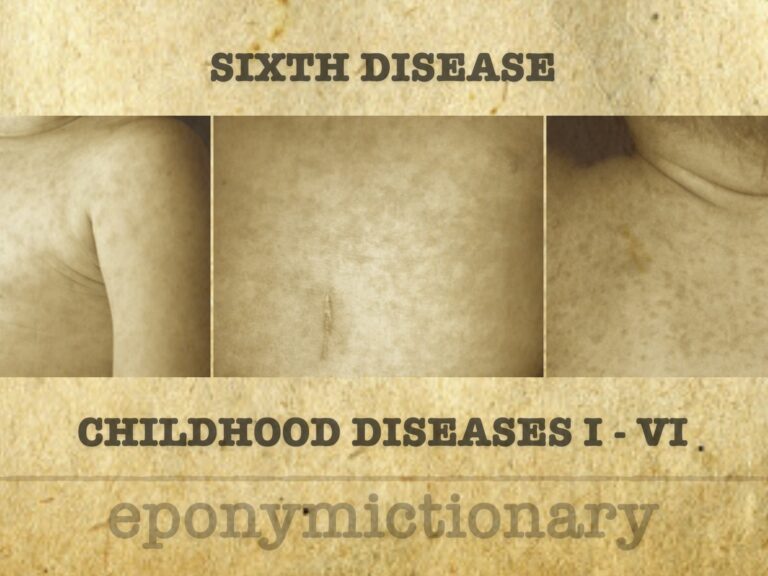
Common viral illness in infants caused by HHV-6. Roseola presents with high fever followed by sudden rash; also known as sixth disease or exanthem subitum.
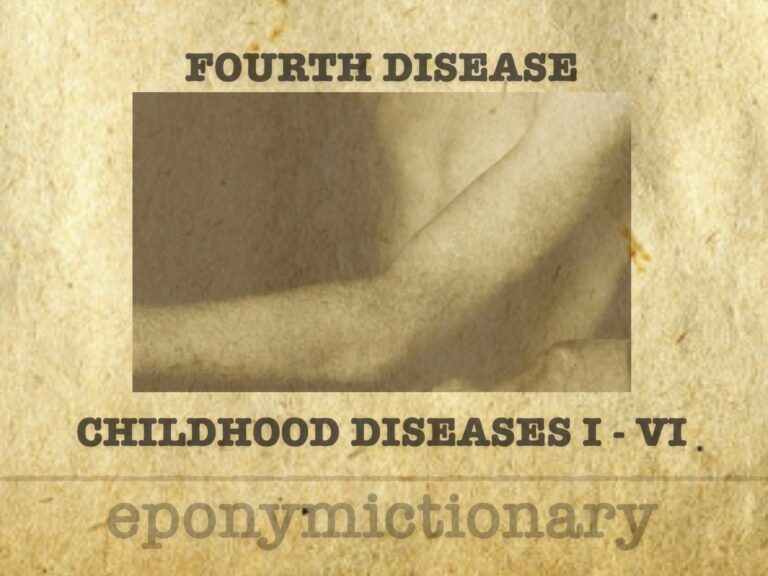
Filatov-Dukes disease, or fourth disease, was a proposed childhood exanthem now largely dismissed as a misclassification of rubella or scarlet fever.
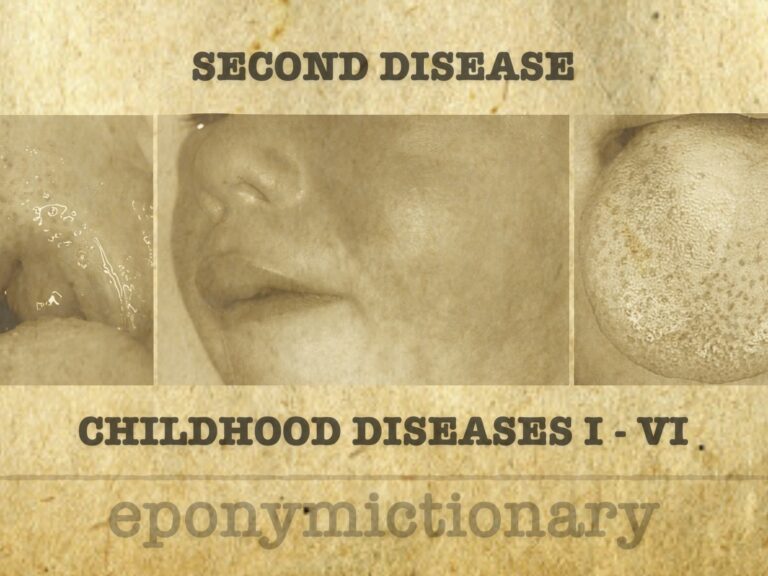
Mild viral exanthem in children; dangerous in pregnancy. Rubella causes rash and lymphadenopathy, with congenital infection leading to CRS.
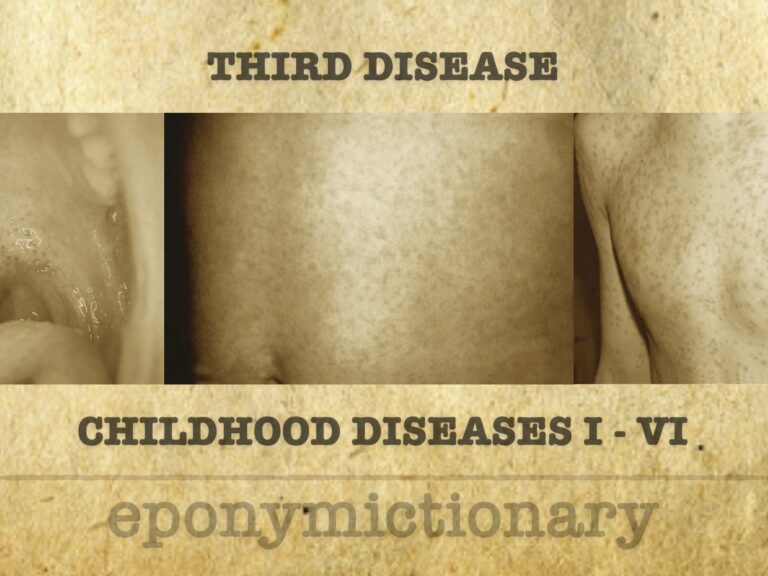
Scarlet fever (second disease). Contagious GABHS infection in kids under 10 with sore throat or rash; caused by S. pyogenes strains producing erythrogenic toxin.
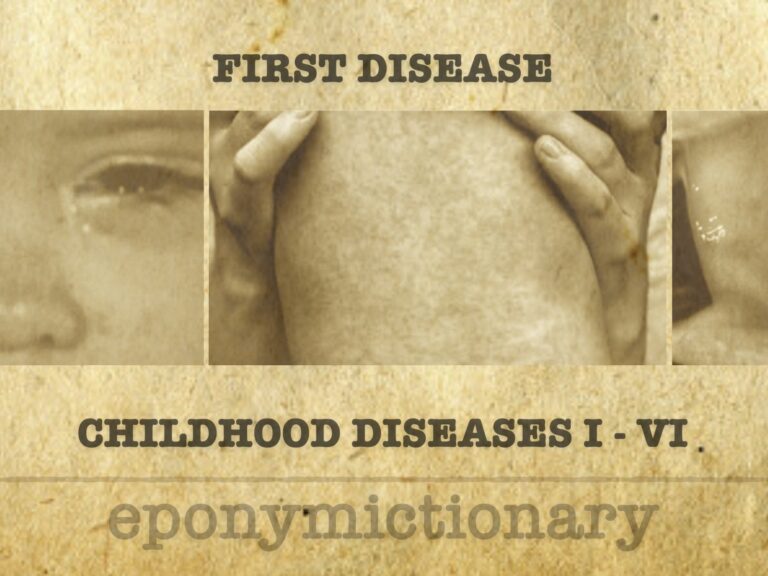
Measles (First Disease): classic childhood exanthem caused by Morbillivirus, with high infectivity, pathognomonic signs, and vaccine-preventable
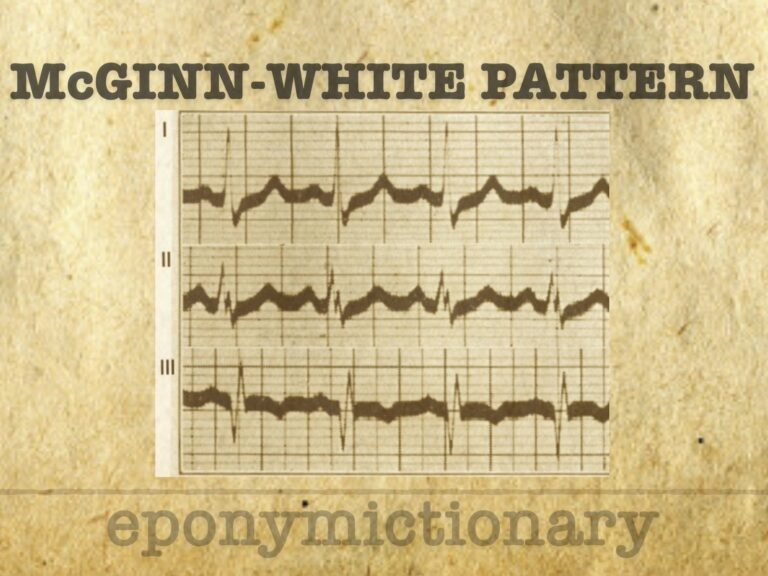
S1Q3T3 McGinn-White pattern indicates right heart strain and predicts severe PE outcomes. ECG sign of pulmonary embolism described in 1935.

Eponymous medical triads, tetrads, and pentads: clusters of signs and symptoms aiding diagnosis and clinical teaching

Dieulafoy’s lesion: minute gastric erosion over a large arteriole, causing massive GI bleeding. First defined as exulceratio simplex in 1898.
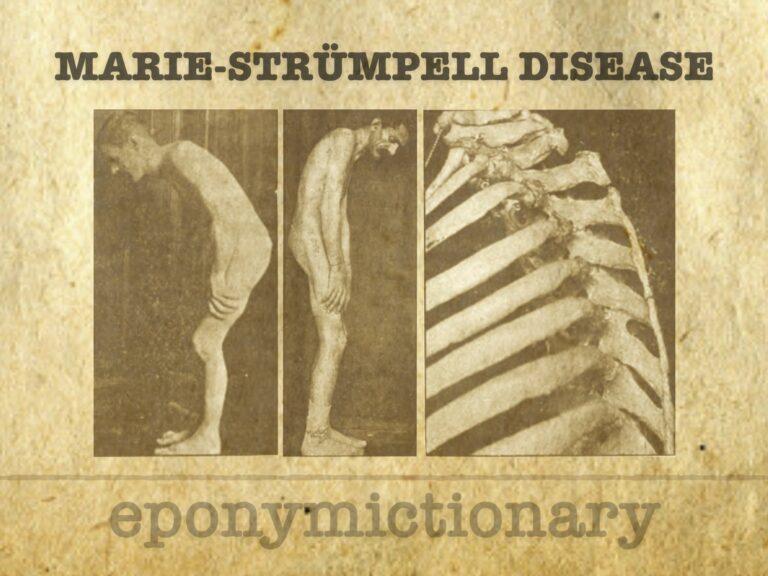
Marie-Strümpell disease (ankylosing spondylitis): a chronic inflammatory spinal arthritis with progressive axial fusion, first described by Pierre Marie and Adolf Strümpell in the late 19th century.