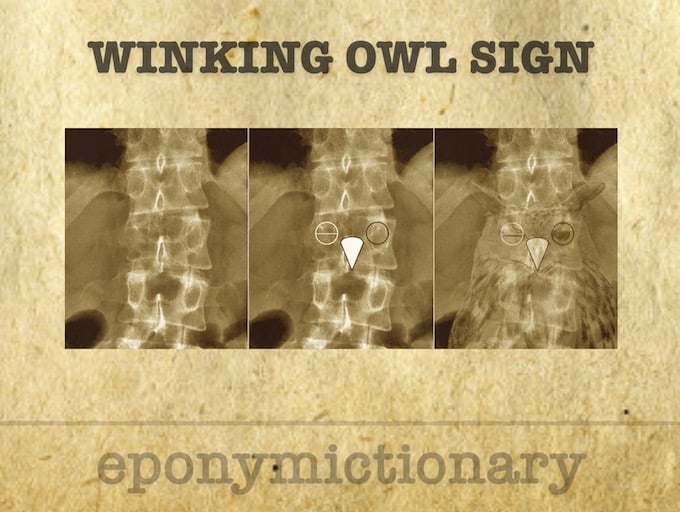
Winking owl sign
One of the first signs of vertebral metastases is disappearance of the pedicle on the AP X-ray. This is known as the 'absent pedicle' or 'winking owl sign'.

One of the first signs of vertebral metastases is disappearance of the pedicle on the AP X-ray. This is known as the 'absent pedicle' or 'winking owl sign'.

Throckmorton sign (John Thomas sign) where Penis Points to Pathology on X-ray. Tom Bentley Throckmorton (1885-1961) was an American neurologist

Segond fracture: Avulsion fracture (small) of the lateral surface of the lateral tibial condyle. Paul Ferdinand Segond (1851-1912) described 1879

Lindsay nails (half-and-half nails) is an apparent leukonychia of the proximal portion of the nail which is white with distal 20-60% reddish-brown

Cotton fracture (trimalleolar fracture) described in 1915 by Frederic Jay Cotton (1869-1939); fracture of the ankle that involving the lateral malleolus, medial malleolus and distal posterior aspect of the tibia (posterior malleolus).

Characteristic R wave notching seen in inferior leads in a large proportion of patients with ostium secundum ASD

Murphy’s sign is elicited in patients with acute cholecystitis by asking the patient to take in and hold a deep breath while palpating the right subcostal area. John Benjamin Murphy (1903)

Williams-Beuren syndrome: Generalized disorder characterized by unusual facies, abnormal behavioral abilities, cardiovascular anomalies, especially supravalvular aortic stenosis (SVAS), renal and other abnormalities
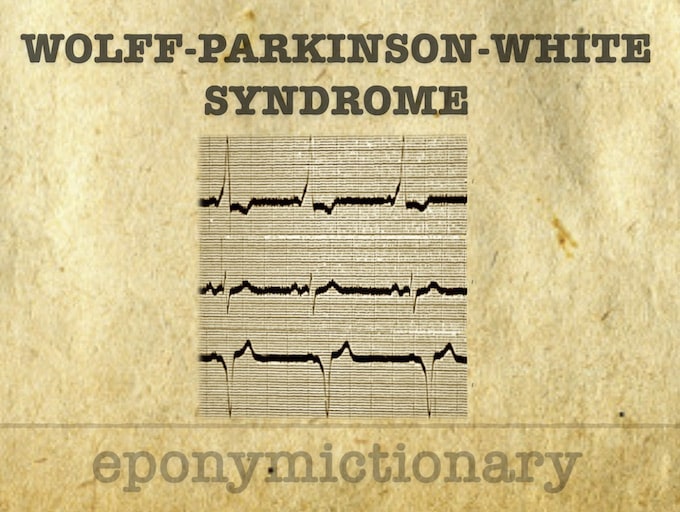
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmia.

Rovsing sign (1907): In acute appendicitis, palpation of the left lower quadrant may elicit pain in the right lower quadrant. Niels Rovsing and Emil S Perman (1904)

Schamroth sign. Simple sign to determine the presence of finger clubbing. One of the earliest signs of clubbing is obliteration of the Schamroth 'window'.
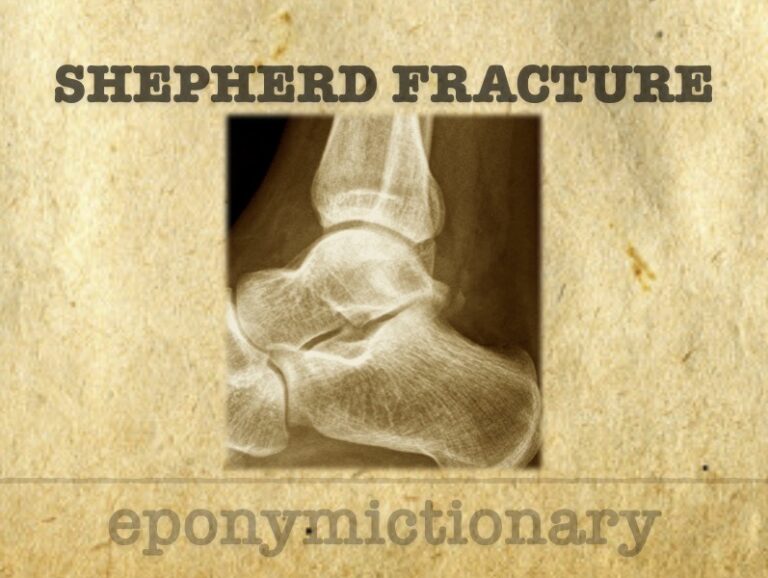
Sherpherd fracture: Posterior talar process fracture with injury to the lateral tubercle caused by inversion or extreme equinus (1882)