
Bernhard Naunyn
German physician Bernhard Naunyn (1839–1925), pioneer of experimental medicine, defined acidosis, advanced diabetes and gallstone research, and co-founded Naunyn–Schmiedeberg’s Archives

German physician Bernhard Naunyn (1839–1925), pioneer of experimental medicine, defined acidosis, advanced diabetes and gallstone research, and co-founded Naunyn–Schmiedeberg’s Archives

Hans Kehr (1862–1916), pioneer of gallbladder surgery, introduced the T-tube for bile duct drainage; eponymously linked to Kehr’s sign of splenic rupture.
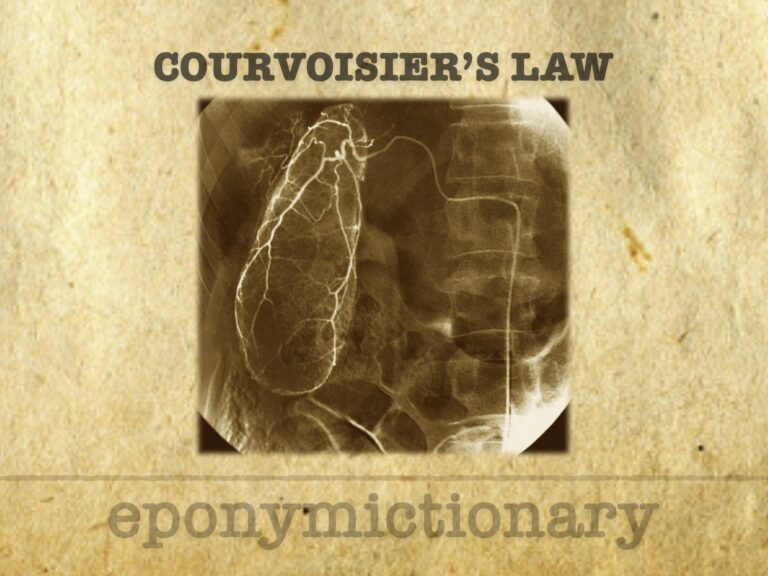
Courvoisier’s sign: palpable gallbladder with painless jaundice suggests malignant obstruction, not gallstones. A key clinical diagnostic clue.

Ludwig Georg Courvoisier (1843-1918) was a Swiss surgeon, academic, and naturalist best remembered for Courvoisier’s sign / law (1890)
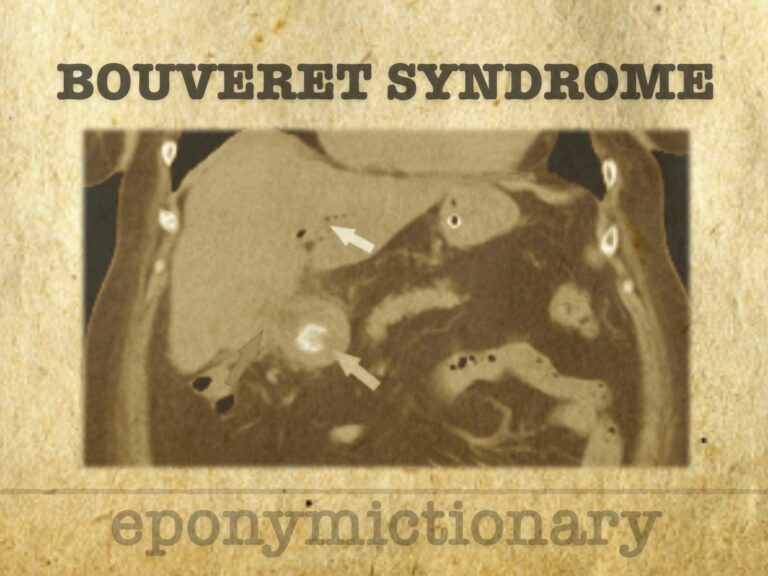
Bouveret syndrome: gastric outlet obstruction following passage of a gallstone from gallbladder to duodenum/pylorus via bilioenteric fistula
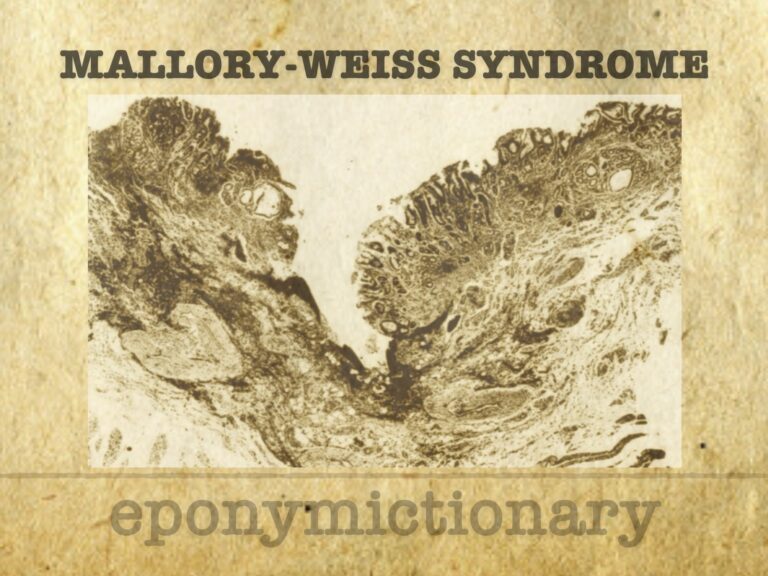
Mallory–Weiss syndrome: upper GI bleeding from gastroesophageal tears. History, key figures, first descriptions, diagnosis, and treatment.

Rigler triad; Imaging findings in patients with gallstone ileus with an ectopic gallstone causing small bowel obstruction, and pneumobilia

Leo George Rigler (1896-1979) was an American radiologist. Eponymously affiliated with Rigler sign; Rigler triad; Rigler notch sign; Hoffman-Rigler sign
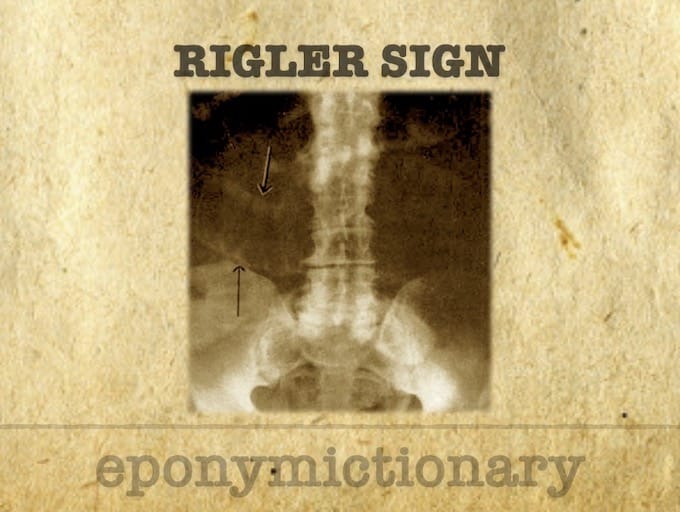
Radiological signs of pneumoperitoneum: history, diagnosis, and key eponyms including Rigler’s sign, Popper’s sign, football sign, and inverted V sign

Alexis Littré (1654–1726), French anatomist; Littré’s hernia, glands, and operation; anatomical insights with lasting surgical impact

Thomas Stephen Cullen (1869 – 1953) was a Canadian gynecologist. Eponymously affiliated with Cullen sign (1918)

Dieulafoy’s lesion: minute gastric erosion over a large arteriole, causing massive GI bleeding. First defined as exulceratio simplex in 1898.