ECG Case 031
Young adult patient presenting with syncope. History of eating disorder. Describe the ECG.
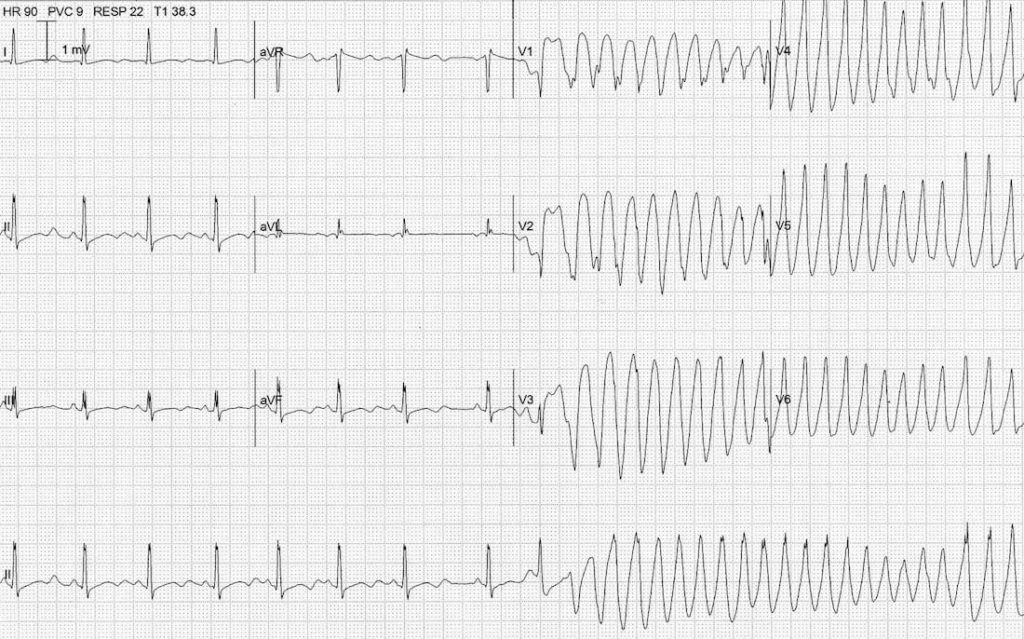
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Main Abnormalities
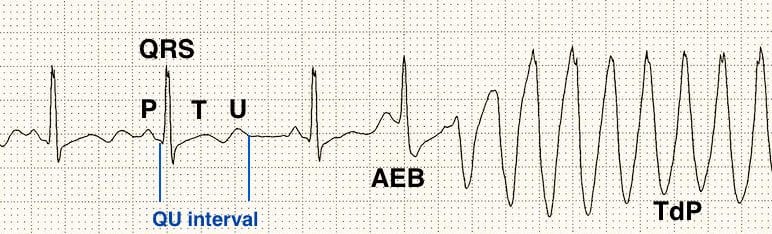
- The first half of the ECG shows sinus rhythm with prominent U waves and a long QU interval (520ms).
- An atrial ectopic beat kicks off a run of Torsades de Pointes by landing on the T/U wave during the vulnerable phase of repolarisation and causing “R on T” (or “R on U”) phenomenon.
Diagnosis
The combination of…
- Atrial ectopy
- Prominent U waves
- Long QU interval
- Torsades de Pointes
… is strongly suggestive of severe hypokalaemia. This patient had a K of 1.9 mmol/L.
Hypokalaemia occurs in eating disorders via multiple mechanisms including:
- H+ is lost in vomiting — renal distal tubular reabsorption of H+ occurs in exchange for K+ (primary mechanism)
- Loss of K+ in bodily secretions — vomiting, purging with laxatives or diuretics
- Reduced oral intake
- Metabolic alkalosis from vomiting causing intracellular shifts of K+
- Hypovolaemia causing secondary aldosteronism with renal loss of K+
CLINICAL PEARLS
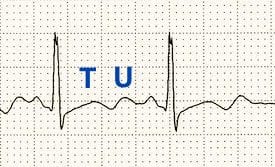
U wave morphology
The appearance of U waves in hypokalemia may vary. This example demonstrates discrete U waves that are clearly distinguishable from the T wave.
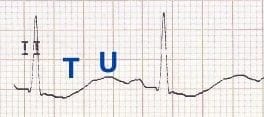
Compare this with Quiz ECG 006, where the whole ST-T-U complex is fused together to produce a “rollercoaster” appearance, with the U wave appearing as a positive deflection that emerges from a negative ST segment and T wave.
Discrete U waves
“Rollercoaster” U waves
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner


i would mention the typical short long short start to a torsade de point